In the modern dynamic business environment, the greatest barrier to expansion is not necessarily technology or finance, but the growing skills gap. Organizations tend to fail due to lack of skills among the employees to adapt to the changing roles, new tools, and emerging trends in the industry.
The representatives of the industry always underline that it is not an option to close skill gaps. Teams might be doing well, but there can be underlying weaknesses that slow projects, limit innovations, and even affect compliance. Companies that actively address this problem experience higher productivity, employee engagement, and long-term development.
In this blog, we will deconstruct what a skill gap is, some common examples of gaps, reasons why gaps open, and practical ways to address them. At the end of it, you will understand how to make your workforce stronger and how you can match the skill set of your team with business objectives.
What is a Skill Gap?
A skill gap is a situation where employees or teams lack the skills to perform their job well. Such gaps can be:
- Technical: Not skilled in software, analytics tools or dedicated platforms.
- Soft skills: Inadequacy in communication, teamwork or problem-solving.
- Leadership: Inability to handle teams, mentor or make strategic decisions.
An example of this is that a marketing analyst can be strong in executing campaigns but weak in data visualization. Similarly, a software developer can be a great coder but fail to know about modern cybersecurity activities.
The skill issues should be identified because they have a direct effect on productivity, innovation, and the performance of the business as a whole.
Understanding Skill Gaps
It takes more than recognizing poor performance to understand skill gaps; it is an evaluation of the gap between the current capabilities and the capabilities required to be successful.
According to industry experts, skill gaps tend to occur when:
- Employees cannot keep up with the change in job roles.
- Employee learning is behind technology adoption.
- Organizations grow fast without revising learning and development programs.
The gap between perceived and actual skill gaps is essential. In some cases, employees can be seen to be competent but there are underlying weaknesses in thinking or teamwork that can delay projects or cause mistakes. The L&D leaders and managers need to detect these gaps as early as possible in order to initiate effective interventions.
Early identification is beneficial to both the organization and to the employees. Employees are empowered and motivated and businesses can strategize on specific training to address the changing business needs.
5 Examples of Skill Gaps
The identification of the gaps in the real-world skills helps to create particular training, mentoring, and development programs. The five general types are:
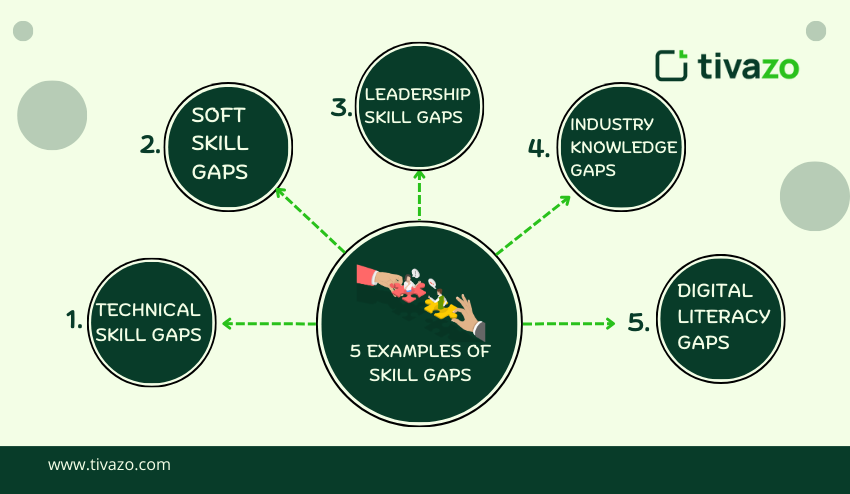
1. Technical Skill Gaps
- Employees lack skills in the use of tools, software, or technologies.
- Examples: Marketing teams that are experiencing issues with analytics tools, IT teams in need of new cybersecurity expertise.
- Impact: The project will be delayed, less innovation, and potential risks in operations.
- Solution: On-the-job training and learning and developmental programs.
2. Soft Skill Gaps
- Not having the skills in communication, collaboration, flexibility, or critical thinking.
- Examples: data analysts who produce great reports yet do not communicate their findings to non-technical stakeholders.
- Implication: Low cooperation, failures in communication and diminished team output.
- Solution: Proper Coaching and mentoring to the staff, soft skills workshops.
3. Leadership Skill Gaps
- Team leaders or managers may lack mentoring skills, delegation skills or strategic decision-making.
- The consequences: Unmotivated teams, stalled projects, and hapless implementation of projects.
- Solution: Leadership training, mentorship and advice of L&D leaders.
4. Industry Knowledge Gaps
- Employees can be ignorant of the industry trends, regulations, or competitor strategies.
- Examples: finance departments that are not up-to-date with fintech innovations, marketing departments that are not aware of new digital channels.
- Effect: Less effective strategic decisions and innovation.
- Solution: Seek advice of consulting industry experts and Association for Talent Development resources.
5. Digital Literacy Gaps
- Employees may struggle with various cloud tools, and collaboration is not using cybersecurity best practices.
- Outcome: inefficiencies, spinning wheels, errors, or security exposures.
- Operations to support the organization’s using continuous learning and digital skills-focused training.
Reasons for a Widening Skills Gap
There are several reasons for the widening skills gap:
1. Rapidly Changing Technology
As new technologies tools and platforms are released, employees sometimes struggle to keep up with all of the change and their skillsets become outdated.
2. Changing Job Descriptions
Sometimes the skills needed were acceptable at one point, and then things changed. The job functions shift constantly, requiring continuing education.
3. Lacking Learning and Development
If you don’t have strong learning and development available to employees, those employees will become complacent, and productivity and growth may suffer.
4. Limited Methods for Industry Knowledge
In some environments, employees have more exposure to the industry best practices with an industry specialist or some type of association like the Association for Talent Development. Some companies may not have that support and can struggle to see trends as they unfold.
It is through understanding the causes of where you are having a skill gap at within companies can be effective in deploying initiatives that can target specific skill gaps and build a path to developing your employee.
Impact of Skill Gaps on Organizations
The consequences of neglecting skill gaps may be severe and far-reaching to any organization:

1. Reduced Productivity
Employees with inadequate skillbase are less efficient in their duties and err more frequently. Even small errors in everyday productivity accumulate over a long period and may cause project delays and overall decreased productivity. They can also fail to meet deadlines and when people fail to meet deadlines it leads to disruption in the workflow which may affect overall business performance.
2. Increased Employee Turnover
Failing to offer appropriate training or learning and development opportunities at organizations can leave employees feeling unsupported and frustrated. This usually results in increased employee turnover, where skilled employees move to organizations where they can develop and grow through mentorship and skill development programs.
3. Lost Business Opportunities
An unaddressed skills gap in a workforce will not be able to react to new market trends, emerging technologies or client demands. Innovation becomes stagnant and competitors have an upper hand and this may lead to loss of revenue or market share.
4. Competitive and Strategic Risks
Furthermore, experts in the industry have warned that businesses who do not take note of rapidly closing skills gaps might struggle to keep pace in a quickly-changing marketplace because they might not have the ability to be agile, maintain the quality of service or track record of being a leader in their respective industry.
5. Impact on Morale and Reputation
Skills gaps not only impact the business, they also impact the overall organizational culture or employee experience. Employees who do not feel equipped for their role or feel unsupported can easily disengage and not conform to norms, thus lowering morale and collaboration. Furthermore, this can easily negatively impact client satisfaction and tarnish the organization’s brand equity.
Overcoming skill gaps through a variety of purposeful and systematic learning and development, coaching and mentoring, and collaboration with industry experts will ensure that teams can remain focused productive and engaged. Hence, competitive and strategic risks can be mitigated.
How to Identify Skill Gaps
The first step to closing the gap of skills is to identify them. This is how organizations can do it:
- Audits and skills tests
Conduct a comparison of the current employee skills with those needed in the roles to identify the gaps in technical and soft skills. - Employee review
Measure areas in which targets are never achieved to create awareness of areas of possible shortfalls. - Team and managerial feedback
Managers and L&D leaders will be able to give feedback on the areas that need improvement in skills such as critical thinking and leadership skills.
Frequent assessment makes the interventions timely, pertinent, and business-oriented.
5 Steps to bridge the skill gap
There are several different ways to bridge a skill gap:
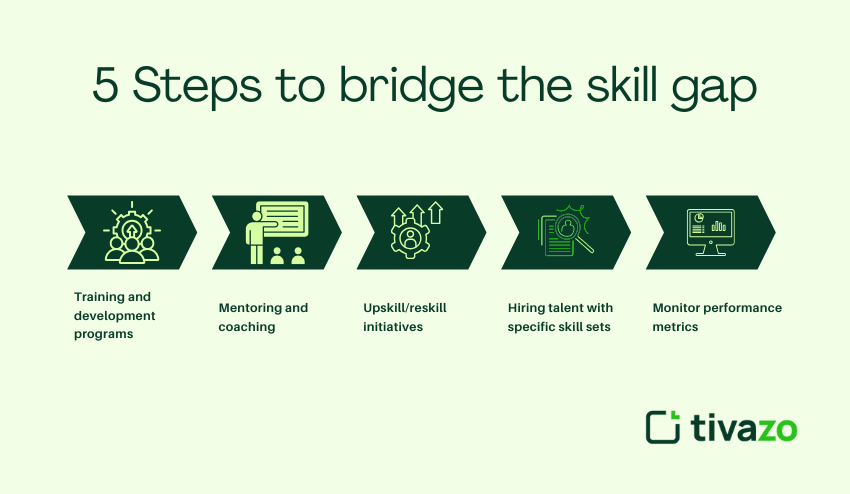
- Training and development programs
Offer workshops, online courses, and certifications that reflect the employee’s role within the organization. Partnering with organizations (for example, the Association for Talent Development) will help create training programs that meet industry standards. - Mentoring and coaching
Pair employees with seasoned mentors or organizational experts. It shortens the learning curve and builds confidence in trying out new skills. - Upskill/reskill initiatives
Regularly refresh employees’ knowledge and skill sets to advance those skills reflecting their evolving roles – particularly in fast-paced technology industries. - Hiring talent with specific skill sets
When internal gaps cannot be filled in rapid time, hire professionals, with the necessary expertise. This complements training and improves the existing team’s skill set. - Monitor performance metrics
Track Employee metrics with a productivity tracking app and assess the productivity, efficiency, and overall performance of the employee.
Implementing these processes will help to close the skills gap widening and help teams remain competitive.
Conclusion
The skill gap is a significant issue that organizations must try to address in a proactive manner. Organizations that identify gaps quickly and early, roll out targeted training, incorporate technology, and talk with subject matter experts will create stronger teams, better performance, and sustainable growth.
Again, bear in mind that a skill gap is not merely a weakness it is a chance. Closing gaps in this way enables employees to develop adaptability to changing roles, develop critical thinking skills, and strategically overcome future organizational challenges.