Google groundbreaking research on Project Aristotle showed that high-psychological safety teams are 67% less likely to fail and 47% more likely to perform better. However, most organizations are not able to develop a culture where employees are comfortable to express themselves, present ideas or confess their errors without the fear of being punished.
The answer is not in the form of additional team-building events or inspirations. It is a methodical psychological safety training that changes the way individuals interact, communicate and work together.
This guide exposes time-tested training strategies that transform fearful, isolated teams into high-performing teams where innovation is the order of the day and issues are solved within a short time. You will learn about particular frameworks, tools, and implementation strategies that have been applied by the top organizations to establish psychological safety at the bottom up.
What is Psychological Safety Training?
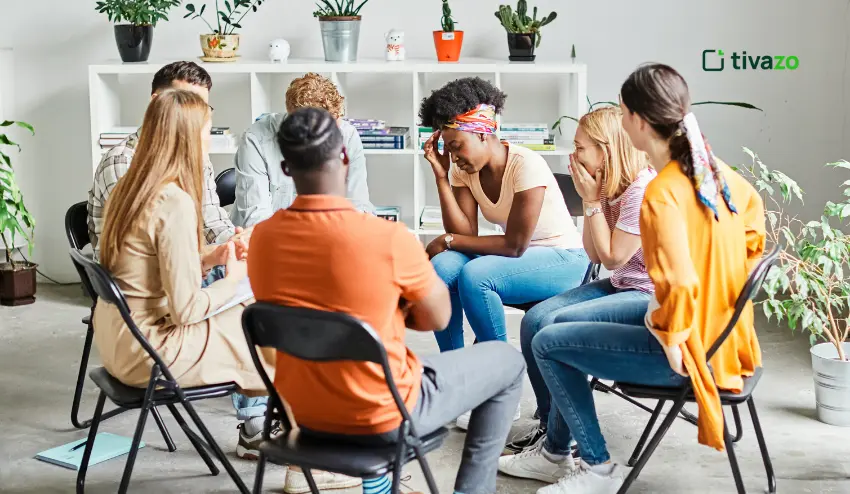

Psychological safety training educates individuals on how to establish a workplace where all individuals feel free to speak up. It is an organized learning process that establishes trust and free communication within the teams.
This training is not just like the normal team building activities. It pays attention to certain skills such as active listening, feedbacking, and constructive management of mistakes. The participants are taught by way of interactive activities and real-life work situations.
Behavior change is the primary objective. When colleagues confess their mistakes or inquire, people get to understand how to react. They are used to developing supportive responses rather than judgment or blame.
The most successful programs are the ones that incorporate theory and practice. The participants know the importance of psychological safety. They recognize the existing issues in their workplace. Then they come up with particular action plans on how to improve.
This form of training focuses on making other people successful. It educates the managers and team members on how to establish environments that people flourish in. It is about developing trust and not just individual performance.
The training usually includes such fundamental areas as constructive feedback techniques and conflict resolution strategies. These abilities aid in the transition of teams that operate in fear of each other to those that learn together.
Why Psychological Safety Training Matters for Modern Teams
The current workplaces are challenging in ways never experienced before making psychological safety more important than ever. Working remotely, different cultures, and quick change have established new obstacles to open communication.
Studies indicate that 89 % of the employees feel that psychological safety at work is a necessity. However, these conditions are not naturally created in most organizations.
The main advantages of the Psychological Safety Training are:
- Improvements in performance: Within six months, teams will experience 27 percent turnover reduction and 12 percent productivity growth.
- Innovation enhancement: When individuals feel secure enough to present innovative concepts, innovation metrics go up.
- Financial effect: 76% increased employee engagement results in increased customer satisfaction and profit margins.
- Change management: Necessary when companies are undergoing a merger, restructuring, and implementation of technology in which people need to express their concerns.
- Diversity support: Assists in closing the differences between the various backgrounds, generations and work styles using universal communication principles. This creates an inclusive workplace.
Current Workplace Issues Resolved:
- Virtual meetings have remote work obstacles that inhibit the natural interaction cues.
- Online communication distances that diminish trust and relationship.
- Quick changes in an organization that demand fast adjustment.
- Various team dynamics that require deliberate inclusion work.
- Market forces that require accelerated innovation processes.
The payback period is usually higher than 300 % in the initial year. Top talent, high performers, and faster adjustments to the market changes provide organizations with competitive advantages.
4 Core Types of Psychological Safety Training Programs
There are various training methods that organizations can adopt depending on their needs and culture. All types address various parts of psychological safety development.

1. Leadership-focused training
This strategy focuses on creating leaders who demonstrate psychological safety behaviors. Team leads and senior managers are taught certain methods of promoting open communication and reacting positively to feedback.
The training includes vulnerability leadership, during which the leaders provide their own mistakes and doubts. The participants learn to ask improved questions rather than give direct answers. They are taught to make room to allow divergent views without being personal.
Leadership programs are generally 2-3 day programs accompanied by post-program coaching. It focuses on behavioral change that trickles down the organization.
2. Team-based workshops
These immersive sessions unite whole teams to create psychological safety as a team. An exercise is done by everyone to demonstrate the existing patterns of communication and learn new strategies.
The training takes place in the form of teams working through actual scenarios in the workplace. They find certain stimuli that close open communication. Then they come up with team agreements regarding the way of dealing with disagreements and errors.
Workshop models tend to be 1-2 day intensive training sessions with monthly follow-ups. The collective experience establishes responsibility and support towards behavioral changes.
3. Organization-wide culture programs
Massive programs that incorporate the concept of psychological safety into the organizational systems and operations. Such holistic programs involve policy revisions, recruitment, and performance appraisal revisions.
The training aspect entails the use of more than one level of employees at a time. HR departments get to know how to use psychological safety questions during interviews. There is an update of performance management to compensate on speaking up and learning through failures.
The culture programs normally cover 6-12 months with continuous reinforcement efforts. They need a large amount of leadership dedication yet produce the most sustainable outcomes.
4. Skills-based micro-learning
Brief, intensive training units to impart certain psychological safety skills. Every session is dedicated to one of the primary behaviors such as active listening, feedback, or graceful admissions of mistakes.
The participants take weekly 15-20 minute modules over a number of months. The bite-sized methodology fits the hectic schedule but gives time to master each skill and then move on to another.
Micro-learning is suitable in remote teams and continuous development. Online applications monitor the advancement and offer customized suggestions regarding personal requirements.
7 Evidence-Based Psychological Safety Training Strategies
The best psychological safety training programs employ research-supported measures that result in sustainable behavior change. These seven techniques have had proven outcomes in various industries and size of a team.
1. Conversation Skills Training
The strategy of psychological safety training aims at educating individuals on how to engage in hard conversations without developing defensiveness. Participants get to know certain question formats which promote open conversations.
The training includes active listening skills and the reaction to a person who tells something alarming. Individuals learn to ask questions rather than make defensive statements. They get taught to first stop and clarify questions before responding.
Role-playing activities are the simulation of a workplace situation. The teams train on how to talk about deadlines that are missed, quality problems and differing views. The aim is to develop trust in tackling issues at an early stage before they get out of control.
2. Vulnerability and Trust Exercises
Vulnerability exercises are usually psychological safety training programs that develop team trust over time. Leaders demonstrate the right way of self-disclosure regarding their problems and errors.
The exercises begin small with low risk sharing exercises. Individuals may exchange learning experiences or little work frustrations. The more comfortable people become, the more serious are the issues discussed and doubts raised.
Psychological safety is achieved by trust-building activities that generate mutual understanding. The team members find out that they share experiences and have common concerns. This helps to eliminate the fear of being criticized in case one expresses unpopular views.
3. Conflict Resolution Frameworks
Proper psychological safety training provides particular models of dealing with disputes positively. The training focuses on the distinction between ideas and identity to minimize personal attacks in conflict situations.
The participants are taught how to be inquisitive and advocacy. They do not jump to their defence but pose questions to learn other points of view. This leaves room to joint problem-solving.
The model contains de-escalation strategies and word patterns that preserve the respect in heated conversations. Individuals learn to react to criticism without being defensive and ending the discussion.
4. Feedback Culture Development
This psychological safety training plan changes the way teams receive and provide feedback. Rather than doing annual reviews, individuals are taught continuous feedback strategies that are not intimidating.
The training includes the so-called feedforward methods aimed at improving in the future instead of learning the lessons of the past. The participants learn to make certain, practical recommendations rather than vague criticisms or general compliments.
Teams come up with feedback norms that all members are supposed to adhere to. This involves timing, language preferences and follow-ups. The mutual agreements establish predictability that minimizes fear of getting input.
5. Inclusive Leadership Practices
Leader psychological safety training focuses on establishing inclusion among members of a team. This is not just about diversity but about making sure that everyone has a voice that is heard and appreciated during the process of making decisions.
Leaders are taught to identify when some individuals take up too much of the discussions and leave the other individuals quiet. Their intervention methods are such that they are able to extract silent voices without making anyone feel forced.
The training is comprised of unconscious bias awareness and methods of ensuring fair participation. Leaders learn how to organize meetings in which all people make significant contributions to the results.
6. Mistake-Learning Protocols
The approach educates teams to react to mistakes in a manner that promotes learning as opposed to blame. The psychological safety training programs focus on the importance of mistakes as sources of information.
Participants are taught systematic debriefing techniques which are aimed at making improvements in the system and not blaming an individual. The strategy poses the question, what can we learn? In place of who made the mistake?
The teams rehearse the failure stories as learning moments. This aspect of psychological safety training assists organizations in being more adaptive and innovative in the long run.
7. Continuous Assessment Methods
Good psychological safety training involves the use of continuous measurement tools that monitor the progress. Teams are taught how to evaluate their psychological safety levels at present with the help of validated survey tools.
The training will help individuals know how to identify early warning signs in psychological safety when it is declining. This involves tracking the patterns of participation, frequency of questions, and readiness to dispute the ideas.
Frequent evaluation brings about accountability and enables teams to modify their methods according to what is working. The measurement aspect guarantees the sustainability of the psychological safety training.
Real-World Case Study: Google’s Project Aristotle Training Success
Google’s Project Aristotle provides one of the best recorded instances of how psychological safety training has changed the performance of a team. The technological giant analyzed 180 teams to learn why certain groups proved to be much more efficient than others.
The study found out that the most significant factor in high-performing team was the psychological safety. This result shocked the culture of data-driven at Google, where technical competence or personal talent was supposed to be most important.
The Challenge
The engineering departments at Google presented tremendous differences in their performance even though they had equal talent. There were also teams that were always able to provide innovative products on time. Some had a problem with simple project completion and failure to meet deadlines.
Conventional theories, such as the composition of the team, the IQ score of individuals, or management styles, had no relationship with success. Google required another method to comprehend and copy high performance in all the teams.
The Training Implementation
Google created a program of psychological safety training that is founded on their discoveries. The program had three main elements that the teams practiced in a period of six months.
First, the managers were given intensive training on how to facilitate psychological safety. They were taught certain conversation skills and they rehearsed on how to respond positively when the team members raised concerns or when they confessed mistakes.
Second, complete teams were involved in the workshops that defined new communication standards. Teams made clear arrangements regarding the management of conflicts, exchange of dissenting views, and talk about failures positively.
Third, Google introduced periodic psychological safety evaluations on the basis of validated questionnaires. The teams monitored their progress every month and changed their strategies according to the data.
Measurable Results
The psychological safety training program delivered considerable changes in important performance indicators. Project delays were reduced by 27% and revenue generation increased by 19% in the first year in teams that had gone through the training.
The score of employee satisfaction improved by 12% in trained teams and control groups. The voluntary turnover reduced by 15 percent among the participants, which saved Google millions in recruitment and onboarding expenses.
Measures of innovation also increased significantly. More improvements suggestions were made and more ideas were accepted to be implemented in teams that were more psychologically safe.
Key Success Factors
The psychological safety training offered by Google was a success because of several important factors. The leadership dedication was crucial, and the executives were not left out in the training with the front-line employees.
At the company, measurement and continuous improvement were emphasized as well. The teams were not simply taken through training and moved on. They also assessed the degree of their psychological safety on a periodic basis and changed it constantly.
Most importantly, Google associated psychological safety training with important business outcomes. Teams came to an understanding that open communication directly impacted their success in the project and career development.
As it can be seen in this case study, psychological safety training does not lack tangible results when implemented in an organized manner and with a strong organizational support.
Essential Tools and Resources for Psychological Safety Training
The combination of assessment tools, learning platforms, and implementation resources is the right formula to successful psychological safety training. These are the tools that are necessary to assist organizations in measuring the existing states, providing efficient training, and tracing progress throughout the time.
1. Assessment tools and surveys
Edmondson Psychological Safety Scale is still the gold standard in the measurement of the level of psychological safety within a team. This survey of seven questions gives credible baseline measurements prior to the commencement of psychological safety training.
Another validated assessment option is the Team Diagnostic Survey of Google. The instrument quantifies the psychological safety and other variables of team effectiveness. Organizations are able to compare their scores with the vast database of Google.
The Q12 engagement survey by Gallup incorporates the indicators of psychological safety into the larger employee engagement metrics. This strategy is effective in the case of organizations that already have Gallup measurement systems in place.
Specific assessment tools enable organizations to deal with particular issues in the industry. Healthcare teams may work on the levels of comfort with error reporting. Technology companies usually focus on innovation and safety of risk taking.
Psychological safety training is followed up with regular pulse surveys that monitor training progress between major assessments. Ongoing feedback can be given by the use of short monthly surveys consisting of 2-3 questions that do not lead to survey fatigue.
2. Training platforms and software
Psychological safety training modules are provided on a large scale by learning management systems such as Cornerstone OnDemand and Workday Learning. Such platforms monitor the completion rates and offer individual learning paths.
There are specialized platforms that are dedicated to the development of psychological safety. Gartner Evanta has specific modules to senior executives. Culture Amp offers training on a team basis that has inbuilt measurement tools.
The virtual reality training environments produce the illusion of psychological safety. Other businesses such as Strivr create a scenario where participants rehearse tough conversations in virtual safe settings.
Microlearning programs such as Axonify provide small sized pieces of psychological safety training. The employees go through 5-minute modules every day, and they develop skills slowly without stressful schedules.
Training platforms using video offer interactive material with real life situations in the workplace. Such websites as LinkedIn Learning and Udemy provide the courses in psychological safety with the recognized experts.
3. Templates and frameworks
The Psychological Safety Action Planning Template assists the teams in developing specific improvement goals post-training. The framework consists of the present state evaluation, target behaviors, and accountability.
Facilitation guides are step-by-step directions on how to hold psychological safety discussions. The templates assist the leaders in maneuvering delicate discussions concerning the dynamics of the team and communication patterns.
Feedback conversation models provide individuals with systematic methods of providing and receiving tough feedback. The templates contain certain language proposals and de-escalation methods.
Teams can learn through mistakes without any blame assigned to any individual after the Action Review templates. These psychological safety training instruments put the discussion on how the system can be improved instead of blaming the individual.
Psychological safety agreements are included in the formal team documents in team charter templates. Teams set clear standards regarding communication, conflict management, and errors.
The behavioral psychological safety is combined with the conventional metrics as performance review templates. Managers are able to identify and acknowledge individuals who add to the psychological safety of the teams by their behaviors.
The combination of various tools is strategic, and this is the way in which psychological safety training can be more effective. The superior programs rely on assessment tools to define needs, platforms to convey content, and models to maintain behavior change.
5 Critical Mistakes to Avoid in Psychological Safety Training
These are the pitfalls that may ruin even the most effective psychological safety training courses and squander resources.

1. Surface-level training approaches
- Short-term workshops with no continuous skills training.
- Team building events that are generic and do not solve actual problems in the workplace.
- Remedy: Create multi-month programs that have frequent practice sessions.
2. Lack of leadership commitment
- Leaders either miss training or fail to model new behaviors.
- Training messages do not make executives punish people who speak up.
- Solution: Leaders are engaged in the same training and are vulnerable.
3. No measurement or follow-up
- None of the baseline measurements or progress measurements.
- Issues are not realized until they impact performance.
- Remedy: Pre-training tests and frequent check-ins.
4. One-size-fits-all programs
- Generic programs do not consider team and industry variations.
- Same strategy to all departments despite special challenges.
- Solution: Train to be personalized and not to violate the fundamental principles of psychological safety.
5. Ignoring organizational culture
- Reward systems do not go hand in hand with training because they penalize errors.
- Performance reviews are not about learning, but blame.
- Solution: Match company policies with the objectives of the psychological safety training.
Effective implementation of psychological safety training is only possible when it is viewed as a cultural change and not merely a learning experience.
Conclusion
The psychological safety training helps to convert the fear based teams to high performing cultures where innovation is flourishing. Companies that invest in a systematic process of psychological safety development report significant increases in engagement, retention, and business performance in the first year.
The success is in the fact that the psychological safety training is a long-term cultural program, but not a one-time event. Begin with leadership commitment, assess your status and select methods of training that best suit your situation. It is important to remember that sustainable change is a long process that needs regular reinforcement.
Are you now ready to start your psychological safety training? Begin by making a baseline evaluation with your team and pinpoint one area to be improved. Minor actions today result in transformational outcomes tomorrow.