Do you want to become an excellent Workforce Management Analyst? The world of data is quickly being relied on by companies to make decisions, and it is increasingly clear how important a Workforce Management Analyst role is to improve efficiency, productivity, and employee satisfaction. So, what is the secret to becoming a successful Workforce Management Analyst?
In this article, you will learn about 7 key strategies that every Workforce Management Analyst should strive to learn. If this is your first time in the field or you are trying to take your skills to the next level, these key takeaways will help you distinguish yourself in your career and make a clear impact in your organization.
Key Highlights:
- What is a Workforce Management Analyst
- Key Strategies for Success as a Workforce Management Analyst
- Career Path for a Workforce Management Analyst
- Common Challenges Faced by Workforce Management Analysts
- Tools and Resources for Workforce Management Analysts
- Level Up as a Workforce Analyst
- Staying Ahead of Workforce Management Trends
What is a Workforce Management Analyst?
A Workforce Management Analyst is one who optimizes a company’s labor force to drive efficiency and productivity. They collect and analyze information, forecasting labor requirements, developing schedules, and optimizing work processes, while also lowering expenses and increasing employee satisfaction.
The key responsibilities of a Workforce Management Analyst include:
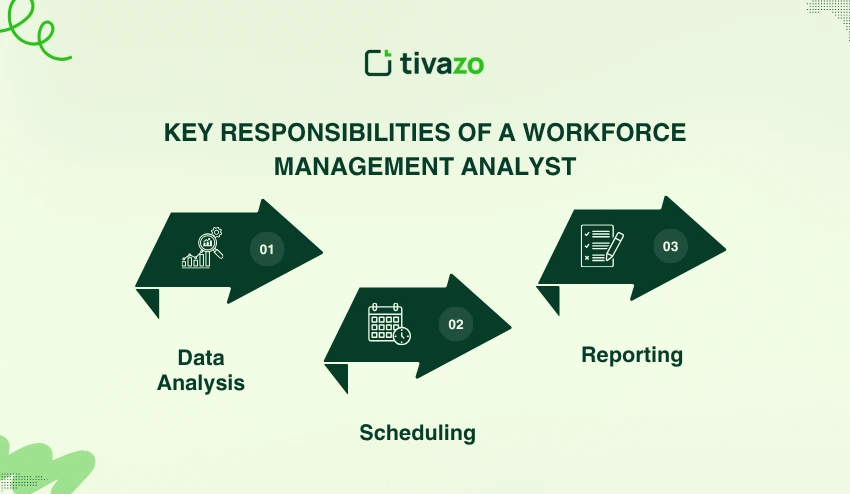
- Data Analysis: One of the key responsibilities of a Workforce Management Analyst is to gather and analyze data to inform labor forecasts and staff improvements, systematic in their staffing.
- Scheduling: Creating schedules and managing employee schedules to ensure the needs of the business are met without overstaffing or understaffing.
- Reporting: Providing frequent reports and insightful recommendations to management for strategic decision-making.
The position necessitates strong analytical skills, proficiency with workforce management software, and the ability to communicate effectively across teams.
Why is the Role of a Workforce Management Analyst Crucial?
Organizations are often looking to streamline operations and make data-informed decisions, resulting in an increasing demand for Workforce Management Analysts. They make sure that companies have scheduled the right number of employees, at the right time, thereby preventing unnecessary overtime costs or understaffing.
Additionally, Workforce Management Analysts work to smartly schedule employees so that they are satisfied with their work schedule. More recently, as remote and hybrid work becomes more common, Workforce Management Analysts will also examine how to shift workforce management to meet new demands when they arise.
7 Key Strategies for Success as a Workforce Management Analyst

1. Master Workforce Management Software
As a Workforce Management Analyst, you will need to be competent in using many software tools (Kronos, ADP, and Workforce Management Suite, to name a few). These software tools help you to manage employee schedules, track attendance, and forecast labor needs. Mastering these software tools will greatly enhance your effectiveness.
- Get familiar with the current leading workforce management software, such as Tillerstack, Kronos, and ADP Workforce Now.
- Use these related software for scheduling, labor forecasting, and reporting real-time statistics.
- Always remain evaluating new software features to stay ahead of the game.
2. Develop Strong Analytical Skills
As a Workforce Management Analyst, you will be required to take complex data and apply it to workforce forecasting. Being experienced in analyzing quantifiable trends, labor costs, and employee performance will give you a competitive edge.
- Use complex data for labor needs, trends, and productivity patterns.
- Analyze employee performance to improve the labor output of the workforce.
- Become an advanced user of Excel or business intelligence tools like Tableau or Power BI.
3. Build Cross-Functional Relationships
As a Workforce Management Analyst, you need to communicate and collaborate with HR, operations, and finance. Working at the level of cross-function will guarantee staffing needs that meet the priorities of the organization.
- Regularly liaise with HR to gain perspective and information for staffing and recruitment.
- Engage closely with finance to better align workforce budgets and labor costs.
- Develop strong ties with operations to make adjustments to staffing in order to meet the business’s needs.
4. Stay Updated with Workforce Trends
Workforce management is a fluid, evolving environment. Trends such as remote work management, advancing AI-enabled scheduling tools, and evolving labor laws, among others, are critical in keeping your workforce management strategies relevant and effective.
- Stay on alert for emerging trends in remote workforce management and hybrid scheduling options.
- Consider AI tools that use predictive analytics to aid in planning workforces.
- Maintain awareness of laws, regulations, and standards that impact scheduling for the workforce both internally and externally.
5. Enhance Reporting and Communication Skills
You need to have the ability to translate complicated data sets into simple information. Reporting effectively is a critical step in explaining workforce needs to leadership for future planning and enhancements. The sooner you master this skill, the sooner you want to be viewed as an advisor to the business.
- Share workforce data with senior management in a clear, concise way.
- Use visual-sharing tools, such as graphs and charts that show labor data and pictorial representations, when reporting the data.
- Consider breaking down data into meaningful and cognitive-enhanced information for users, non-users, and other stakeholders.
6. Focus on Time and Attendance Management
Verify that your company is properly recording employee time and attendance. Timely and accurate timekeeping will reduce errors, improve productivity, and will allow for better management of labor costs.
- Implement automated timekeeping methods to reduce the chance of human error.
- Frequently audit timekeeping records to ensure compliance with labor laws.
- Maximize your scheduling based on your employees’ assignments and labor demand.
7. Plan for Continuous Learning
The workforce management arena is ever-changing. You can stay abreast of new tools and strategies by seeking out a course, certification, or attending an industry conference.
- Consider certification programs like Certified Workforce Planning Professional (CWPP).
- Be sure to attend workforce management conferences to learn about new industry methods.
Career Path for a Workforce Management Analyst
The career progression for a Workforce Management Analyst has room for growth and advancement. Through experience, you can advance to more senior roles like a Senior Workforce Management Analyst, to Workforce Planning Manager, to potentially even a leadership role like an Operations Manager or Chief Operations Officer.
As you advance in your career, you may also want to consider earning certifications like the Certified Workforce Planning Professional (CWPP) or Certified Workforce Management Professional (CWMP). These certifications will demonstrate that you might be an expert in the field and that you intend to keep learning throughout your career.
1. Education
You can start your journey by achieving at least a bachelor’s degree in Human Resources, Business Administration, or Statistics. If you plan to pursue higher leadership roles, consider pursuing a Master’s in Human Resources Management or Business Analytics. Close to 55% of Workforce Analysts hold some sort of bachelor’s degree or higher.
2. Entry-Level Position
Start with a role as a Data Analyst or Human Resources Assistant to acquire entry-level experience in data analysis and HR functions. Obtain this entry-level position for 6 months to 1 year, while learning the role’s practical applications.
3. Junior Workforce Management Analyst
After acquiring experience, seeking a Junior Workforce Analyst position. You will be responsible for data collection, workforce reporting, and trends, which typically requires 1-3 years of experience.
4. Workforce Management Analyst
During this time, you will be responsible for workforce forecasting, scheduling, and production analysis. In this position, it typically takes 2-4 years of experience.
5. Senior Workforce Analyst / Lead Analyst
As a Senior Analyst, you are responsible for leading projects, coaching junior analysts, and developing new workforce strategies for the company. Normally, it takes 4 -6 years of experience to get this position.
6. Workforce Planning Manager
At this point, you have oversight of the employment planning process, aligning personnel to meet the company’s strategic plan. You typically need 6-8 years of experience to become a manager.
Common Challenges Faced by Workforce Management Analysts

1. Handling Complex Data
Dealing with lots of data can feel cumbersome, but take the time to establish and manage how the data is organized and understood this will ultimately help the decision-making process. Dealing with lots of data can feel cumbersome, but taking the time to establish and manage how the data is organized and understood, this will ultimately help the decision‑making process. When considering tools for data integration, compare Fivetran vs. Airbyte to determine which aligns best with your needs for scalability, cost‑control and flexibilityUsing an ETL tool can streamline this process by automating data integration and ensuring consistency across all sources
2. Balancing Labor Costs and Productivity
Finding the sweet spot between simply doing a job with adequate staffing and labor cost is one of the most difficult challenges. However, sound forecasting and data-driven decisions can help to alleviate this challenge.
3. Managing Remote Teams
The rise of remote work applies different dynamics to managing a remote team. As a Workforce Management Analyst, you will need to adapt scheduling and communication to optimize the productivity of remote teams while they are working from home.
Tools and Resources for Workforce Management Analysts
To be successful in being a workforce management analyst, it is crucial you master appropriate tools. Some of the most common software tools include:
1. Workforce Management Software
- Kronos Workforce Ready: This product is used to manage time and attendance and scheduling. It is often used to optimize staffing and help ensure compliance.
- ADP Workforce Now: A comprehensive tool that manages payroll, scheduling, and HR.
- Workforce Analytics Platforms: Tools like Visier provide insight into staffing, labor costs, and productivity.
2. Blogs, Webinars, and Online Resources
- Workforce Institute: It conducts research and regularly scheduled webinars on all things workforce optimization.
- Human Resources Today: A set of curated expert blogs that keep the reader current with trends in managing HR and workforce issues.
- HR Tech News: Developing technologies in workforce management can be discovered here.
3. Learning Platforms
- LinkedIn Learning: Many courses are available in some of the workforce management and analytical software applications.
- Coursera & Udemy: Offer plenty of certifications in workforce analytics and HR management.
The tools listed can provide you with insight into workforce staffing patterns, labor costs, productivity, etc.
In addition, don’t forget to follow some blogs, attend webinars, and participate in online forums devoted to workforce management. The Workforce Institute and Human Resource Today are two valuable resources.
Key Skills Every Workforce Management Analyst Should Develop
While you may not typically think of character traits as something to ‘harden’, it is imperative to develop some characteristics into strengths as a Workforce Management Analyst so that you can take your reporting and workforce data to a level that benefits all parties, which will ultimately be managing the employee processes at your organization.

1. Analytical Thinking
The ability to analyze complex data and formulate insights pertaining to that data is very important for successful workforce management. Strong analytical skills will help you formulate productive workforce management solutions.
2. Communication Skills
Effective communication with management and cross-functional teams is necessary to ensure that your insights are not only actionable but are understood by others at your organization.
3. Technical Expertise
Competency with workforce management software, understanding labor laws, audit principles, policies, and regulations are key technical skills.
4. Time Management
Ability to be able to manage workload and designate importance to which a task is to be done to maintain one step ahead of ever-changing demands.
How Do You Level Up as a Workforce Analyst?
In order to level up as a Workforce Management Analyst, you must continue to grow and develop new skills, and our top piece of advice is to stay informed on current trends and technologies of workforce analysts. Additionally, even if you are a relatively seasoned professional, continuing to pursue advanced certifications can enhance your validation and qualification for future opportunities.
- Certifications such as the SHRM Certified Professional (SHRM-CP), the Professional in Human Resources (PHR), or the Certified Analytics Professional (CAP) will strengthen your knowledge, paving the way for advanced career opportunities.
- Not only will these certifications strengthen your knowledge, but they will also enhance your professional credibility in a competitive market
Another aspect to level up as a workforce management analyst is to be proficient in workforce management technology. Keeping up to date with workforce management software, such as AI-based scheduling or workforce analytics tools, will provide you with the opportunity to work within an appropriate data-driven methodology to improve workforce operations more productively.
Staying Ahead of Workforce Management Trends
The landscape of workforce management continues to change rapidly with emerging technology and a changing work environment. It is important to stay a step ahead of trends so you can keep your organization competitive and ready for the future of work.

1. Remote Workforce Management
With the growing number of remote workers, leaders need to understand how to manage virtual teams and what tools are available to help with remote workforce management.
2. Automation in Workforce Management
Automation can reduce errors and improve efficiency by automating scheduling and timekeeping.
3. AI and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning are changing the landscape of workforce management by predicting labor demand and enabling organizations to schedule staff based on actual labor needs.
Conclusion
To be a successful Workforce Management Analyst, you will need a combination of technical skills, analytical ability, and the ability to adapt and keep current with the latest trends. When you implement the 7 strategies discussed in this article, you will be prepared to improve processes for managing a workforce, build productivity, and manage your career.
You can start to apply these strategies now, to not just add value to the organization you work for, but to also position yourself as someone who is knowledgeable about the current trends in workforce management. Do you feel ready to advance your career?