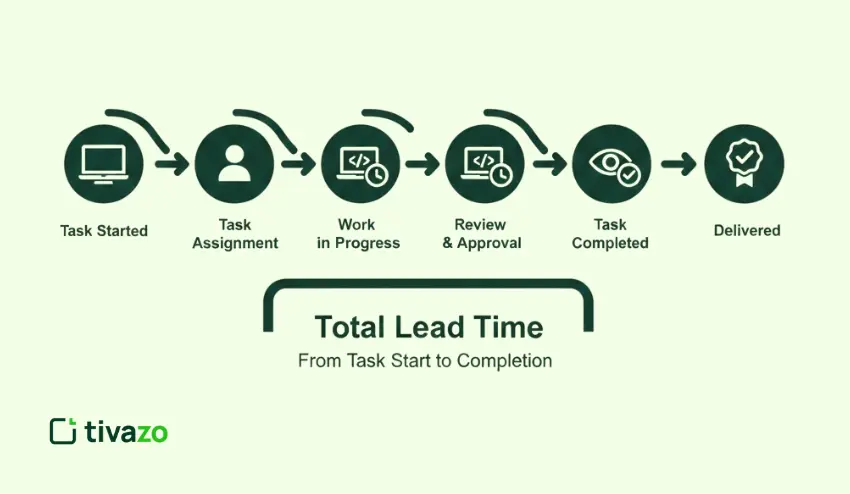
Every business is faced with the challenge of delivering its products or services on time. Time taken to start and finish a process is a major challenge to every business, and it impacts customer satisfaction and the profitability of the business. Knowing what the lead time is will help you manage it better and serve the customers well.
In the modern world, the way you manage your lead time is what will determine the success or failure of your business, and the businesses that manage it well are the ones that attract more customers and earn more profit.
What Is Lead Time?
Lead time is the total time taken from the moment an order is placed until it is received. For instance, if you order a pizza at 7 PM and receive it at 7:30 PM, the lead time is 30 minutes.
Lead time in business: Lead time begins when a customer submits an order and ends when the customer receives the order. Lead time is increased by any delay in the process. Lead time management is important for faster delivery, better use of resources, and cost savings.
Lead time vs. cycle time: Lead time takes into account the total process, including waiting time, whereas cycle time takes into account only the actual working time to complete a task.
Main Types of Lead Time
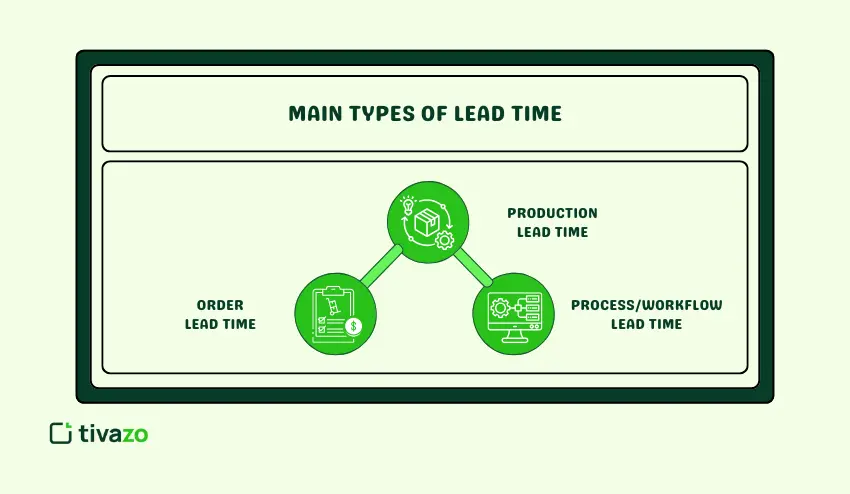
Lead time is not a single entity; it has different types depending on the process. Each type deals with a different facet of the business process. By knowing the types, you can easily pinpoint where the delays are.
Production Lead Time
Production lead time refers to the time taken to produce a product from raw materials. This includes the setup time, production time, and inspection time. This type of lead time is most applicable to manufacturing companies.
For example, a furniture maker needs 10 days to produce a custom-made table. This includes the time to cut the wood, assemble the pieces, and make the necessary finishes. Any delay in the materials or equipment affects the production lead time.
Manufacturing companies take this seriously to meet their delivery commitments. By reducing production lead time, companies can deliver more orders.
Order Lead Time
Order Lead Time is the time period between the customer placing the order and the delivery of the order. In other words, it is the sum of processing time, production time, and shipping time.
If you are purchasing shoes online, then the Order Lead Time includes:
- Confirmation of the order and processing the payment.
- Picking and packing the item.
- Shipping the item.
Customers are mostly concerned about this type of order because it impacts customer satisfaction. Companies market Order Lead Time as Delivery Time or Shipping Time.
Process/Workflow Lead Time
Lead time for workflow measures the time it takes to complete certain tasks or processes. This measure can apply to any business process, not limited to manufacturing companies alone.
For instance, a hospital may want to measure the lead time of getting lab results, while another company may want to measure the time it takes to fix bugs in software development, or the time it takes to approve marketing campaigns.
This type of measurement helps identify bottlenecks in the company’s workflow, thereby improving how work is done.
Simple Real-World Lead Time Examples
Lead time examples can be found in all sectors and in everyday life. By examining actual examples, it is easier to understand the meaning of lead time.
Retail Example: You place an order for a book from an online retailer. The retailer requires 1 day to process your order. It also requires 3 days for shipping. Your lead time is 4 days.
Restaurant Example: A customer places an order for a custom birthday cake. The bakery requires 2 days for preparing ingredients, 1 day for baking and decorating, and same-day pickup. The lead time is 3 days.
Manufacturing Example: An auto parts manufacturer receives an order for 1,000 brake pads. The procurement of materials requires 5 days. Production requires 3 days. Testing and packaging require 2 days. The lead time is 10 days.
Service Example: A graphic designer receives an order for logo design. Client consultation requires 1 day. Design creation requires 3 days. Revisions require 2 days. The lead time for the project is 6 days.
Here’s a comparison of lead times across different industries:
| Industry | Average Lead Time | Main Factors |
| E-commerce | 2-7 days | Processing, shipping, and distance |
| Custom Manufacturing | 2-8 weeks | Material availability, production complexity |
| Fast Food | 5-15 minutes | Order complexity, kitchen capacity |
| Home Construction | 3-6 months | Permits, materials, weather, labor |
| Software Development | 1-4 weeks | Feature complexity, testing, and approvals |
How Lead Time Impacts Productivity and Workflow
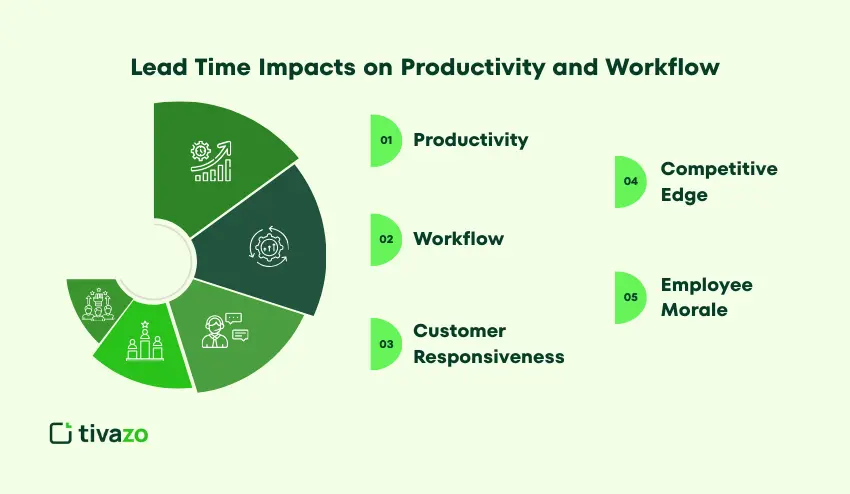
Lead time affects productivity and workflow. This means that a shorter lead time will increase productivity, keep employees busy, and ensure customer satisfaction, but a longer lead time will lead to a slower workflow, causing frustration.
- Productivity: Longer lead times will lead to a decline in productivity due to increased waiting. Conversely, a shorter lead time will increase productivity as more will get done in a shorter time.
- Workflow: Delays in one process will cause a delay in another process, such as marketing waiting for designs or sales waiting for products.
- Customer Responsiveness: Companies with a shorter lead time will respond better to customer needs, thereby increasing customer satisfaction and generating more revenue.
- Competitive Edge: Companies with a shorter lead time will have a competitive advantage over other companies, leading to an increased customer base.
- Employee Morale: Longer lead times will cause frustration, while shorter lead times will create a smoother workflow and satisfy employees.
Common Reasons Lead Time Becomes Too Long
There are many factors that contribute to the lead time blowing out to unreasonable proportions. The first step to fixing these issues is to identify them.
Poor Planning and Forecasting: Organizations that lack effective forecasting often experience delays. They either run out of materials or have excess materials that are left idle for extended periods.
Supply Chain Delays: Delays received from suppliers directly contribute to your organization’s lead time. For example, if a key component is received late, your entire organization comes to a grinding halt.
Inefficient Processes: Organizations with outdated processes and too many steps experience inefficiencies that cause delays. Too many steps and too many approvals cause delays.
Inadequate Resources: Organizations that don’t have enough resources experience delays. For example, insufficient staff and insufficient equipment cause delays.
Communication Issues: Organizations where communication between staff and between staff and management is inadequate experience delays. This causes many different issues, which ultimately contribute to delays.
Quality Issues: Organizations that have products rejected during quality control must remake them, which doubles their lead time.
How to Reduce Lead Time Effectively
Businesses can also take steps to reduce lead time without compromising quality. Small changes in each area result in huge time gains.
Improve Communication: Ensure that all parties are aware of what needs to be done and when. Use project management software to monitor progress. Conduct daily meetings to identify issues early on.
Automate Repetitive Tasks: Employ software to perform mundane tasks such as data entry and order fulfillment. Automation runs 24/7 without any interruptions or mistakes. This allows employees to focus on more important tasks.
Develop Better Relationships with Suppliers: Work with reliable suppliers who deliver goods on time. Find reliable alternatives for key materials that are difficult to obtain.
Reduce Unnecessary Steps: Review your processes and remove steps that are not necessary. This will help you save time.
Develop Your Employees: Employees who are trained are more efficient and less prone to making mistakes. They are also able to handle their problems without waiting for others to assist them.
Maintain the Equipment: Regular maintenance helps to prevent equipment failure, which may cause a stoppage in production. Maintenance is best done during off-peak hours. Old equipment should also be replaced to avoid failure.
Use Just-in-Time for Inventory: Goods should arrive just when they are needed. This will save a lot of time, but it requires good coordination.
Track and Measure Everything: The lead time for every process should be monitored. The process with the longest lead time is the one that is working slowly.
Key Benefits of Shorter Lead Time
Reducing lead time offers numerous benefits that enhance business performance. These benefits include:
- Higher Customer Satisfaction: Serving customers in a shorter time will ensure their satisfaction.
- Increased Revenue: Serving more customers in less time will generate more revenue.
- Reduced Costs: Reducing production or storage time will minimize costs.
- Improved Cash Flow: Serving customers faster will improve cash flow.
- Gaining a Competitive Advantage: Serving customers faster will help gain a competitive advantage in the market.
- Improved Flexibility: Serving customers faster will increase flexibility.
- Reducing Waste: Serving customers more quickly will minimize waste.
Conclusion
What is lead time? It’s the total time it takes to finish a process from beginning to end. Understanding lead time enables businesses to work faster and more efficiently.
Lead time management helps to enhance productivity, satisfaction, and profits, while long lead times result in waste. Having short lead times gives a business a competitive advantage.
The first step to implementing lead time management involves measuring the existing processes and improving them step by step. Improving lead time is a continuous process that yields long-term results.