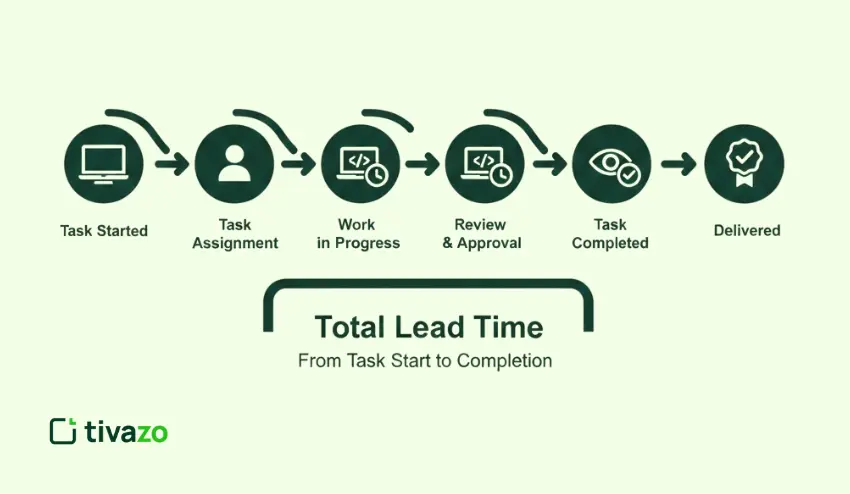
Learning how to calculate lead time is essential to ensure that tasks are properly planned and executed in a business. It is essential to learn how to calculate the exact lead time to measure the wastage of time and optimize it. Every business should be aware of this crucial term.
Learning how to calculate lead time as a software project manager, development team leader, or workflow manager can give you complete control over your projects. It can help you to set realistic deadlines and make your customers happy with deliveries.
What Is Lead Time?
Lead time is the total time taken from the start of a process until its completion. It calculates the time taken for tasks from start to finish. This includes all waiting times, processing times, and delays.
Lead time for business encompasses the entire life cycle of an order or project. It begins when the work starts and ends when the final output is provided. This concept can help you identify inefficiencies.
Lead time and cycle time are two different concepts, and the difference between them is significant. Cycle time calculates only the active work times without waiting times. Lead time calculates everything: work time plus all waiting times between activities.
Why Calculating Lead Time is Important
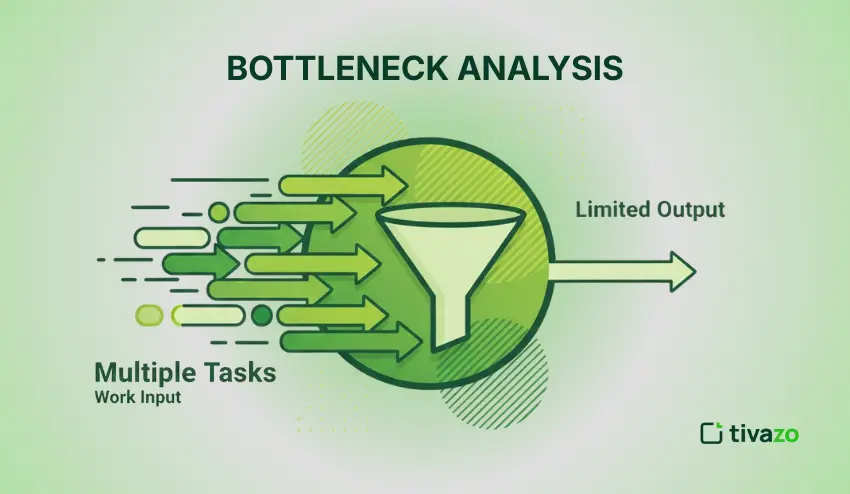
By calculating the lead time, one is able to have factual information to work with, rather than speculations about the time it will take for products to arrive. This will help one understand the time it takes to accomplish a given task, hence improving one’s workflow.
By constantly keeping track of the lead time, one is able to easily identify and fix any bottlenecks that may occur in the workflow, hence improving the speed of the process and eliminating any unnecessary delays that may occur.
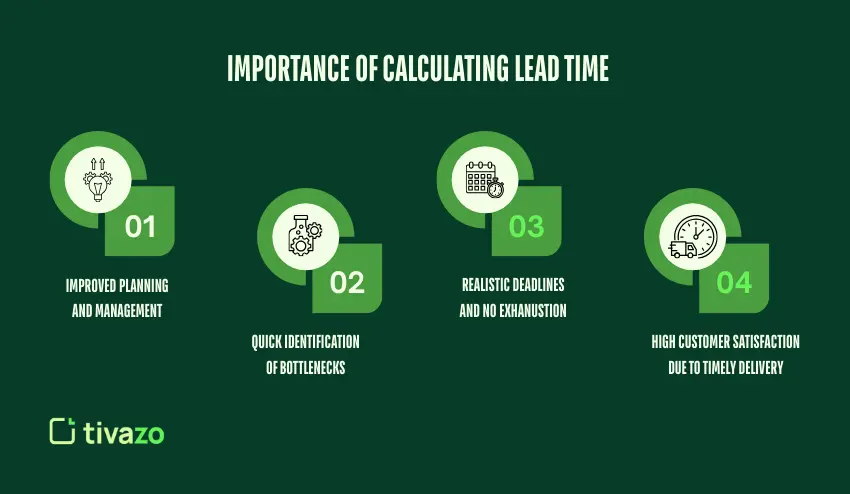
The most important benefits that one stands to gain from calculating the lead time include:
- Improved planning and management
- Quick identification of bottlenecks in the workflow
- Realistic deadlines and no exhaustion of team members
- High customer satisfaction due to timely delivery
In project management, it is very important to measure the lead time to set realistic deadlines and gain the trust of the customer by not over-promising.
How to Calculate Lead Time
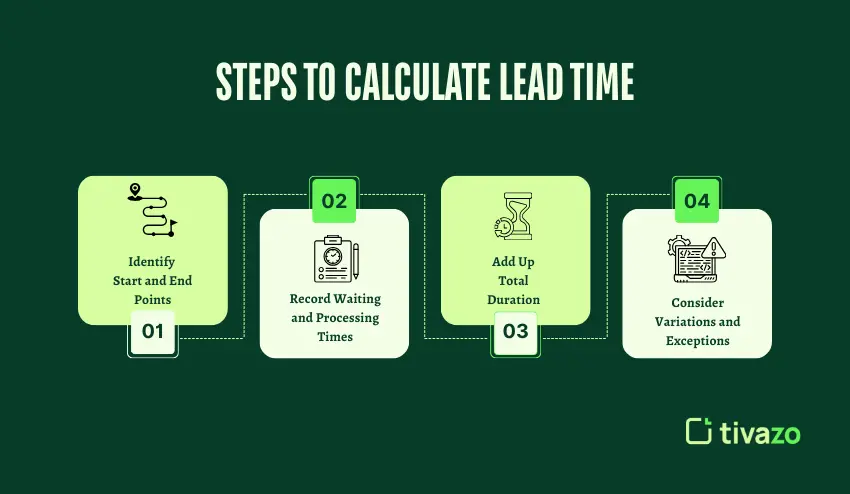
To calculate lead time, you have to follow a simple four-step process. Each step depends on the previous one to help you achieve accurate results. For you to achieve the best results, you have to follow the steps carefully.
Step 1: Identify the Start and End Points of the Process
To calculate lead time, you have to define the exact time when your process begins and ends. In most cases, the starting point occurs when a ticket is created or a feature request happens. On the other hand, the endpoint occurs when the code reaches production or when the client approves the work.
To calculate lead time, you have to be very specific about the starting and ending points. You have to avoid including activities that occur before and after the actual process. This will help you achieve accurate results.
In a situation where you want to fix a particular bug, the starting point could be when the problem occurs.
Step 2: Record All Waiting and Processing Times
Record all the steps involved from the beginning to the end. The processing time is when the developers are coding or even testing. The waiting time is between the steps when nothing is happening.
Record the following steps involved in the lead time:
- Ticket review/prioritization
- Waiting/backlog
- Development/coding
- Code review/waiting
- Testing/quality assurance
- Deployment/waiting
- Release to production
Do not forget to include the waiting times. The waiting times may occupy most of your lead time when it comes to software development.
Step 3: Add Up the Total Duration
At this stage, you have to add up the total processing times. This will give you the final results for your lead time formula.
To get the final results, you need to add up the processing times.
Let us assume you have a feature with the following processing times: ticket review/prioritization takes 1 day, development/coding takes 3 days, code review/waiting takes 1 day, testing/quality assurance takes 2 days, and deployment/waiting takes 1 day.
The total lead time will then be equal to 8 days.
Step 4: Consider Variations and Exceptions
In the real world, the lead time will be different because of various factors, such as the fact that certain features may be simple and thus have a shorter lead time, but others may have problems because of unclear requirements and technical debt.
To determine the lead time, you may consider the following:
- Best-case scenario: simple features and no issues
- Average-case scenario: normal scenario
- Worst-case scenario: features with issues and complexities
This will give you a range, and ranges are very helpful in creating expectations with your clients.
Lead Time Calculation Formulas
Understanding the formula for the lead time helps in easier and consistent computation. There are different formulas for different uses. The right one can be chosen based on the requirements.
Simple Lead Time Formula
The basic formula for computing the lead time is simple and easy to understand:
Lead Time = End Date – Start Date
The formula can be applied when the developer takes up the task on Monday and deploys it on Friday. The lead time in this case will be 4 days.
The formula can also be written in this way:
Lead Time = Task Creation Date to Deployment Date
Advanced Lead Time Formula
However, the formula for Lead Time in project management and complex development projects needs to be more elaborated as follows:
Lead Time = Preprocessing Time + Processing Time + Postprocessing Time + Waiting Time
To elaborate, the formula can be broken down as follows:
- Preprocessing Time: Requirement analysis, ticket refinement, and sprint planning
- Processing Time: Actual coding, development, and implementation
- Postprocessing Time: Code review, testing, and documentation
- Waiting Time: Time waiting between each step
Here is another useful formula that can be applied in software development projects as follows:
Development Lead Time = Requirements Time + Coding Time + Review Time + Testing Time + Deployment Time
This formula helps the development team to understand where the time is being used. Each step can be individually measured and improved.
Lead Time Components Table
| Component | Description | Example Duration |
| Ticket Review | Analyze and prioritize requests | 1 day |
| Backlog Wait | Time in queue before assignment | 3 days |
| Development | Actual coding and implementation | 5 days |
| Code Review | Peer review and feedback | 1 day |
| Testing | QA and bug fixes | 2 days |
| Deployment Prep | Staging and production setup | 1 day |
| Release | Push to production | 0.5 days |
| Total Lead Time | Sum of all components | 13.5 days |
Examples of Lead Time Calculation
It’s much easier to understand the way to calculate lead time by using examples. Let’s consider three different examples related to software development.
Software Feature Development Example
The product development team has been given a new feature request to develop a new user authentication feature. The following is an example of how to calculate lead time in production.
Process Breakdown:
- Feature request review and approval: 2 days
- Gather requirements: 3 days
- Design: 2 days
- Waiting in the backlog: 4 days
- Develop backend API: 5 days
- Develop frontend UI: 4 days
- Code review and changes: 2 days
- QA testing: 3 days
- Bug fix: 2 days
- Deploy to staging environment: 1 day
- User acceptance testing: 2 days
- Deploy to production environment: 1 day
Total Lead Time = 2 + 3 + 2 + 4 + 5 + 4 + 2 + 3 + 2 + 1 + 2 + 1 = 31 days
The team can now inform stakeholders that a new feature will take approximately 4-5 weeks to develop. This will include some buffer time.
Bug Fix Example: Critical Production Issue
The customer has reported a critical bug in the checkout functionality of the application. This is an example of how to calculate lead time for a project:
Bug Resolution Process:
- Bug Reporting and Triage: 2 hours
- Reproducing the Bug: 3 hours
- Root Cause Analysis: 4 hours
- Development of Fix: 6 hours
- Unit Testing: 2 hours
- Code Review: 3 hours
- QA Verification: 4 hours
- Preparation of Hotfix Deployment: 2 hours
- Deployment to Production: 1 hour
- Post Deployment Monitoring: 2 hours
Total Lead Time = 2 + 3 + 4 + 6 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 2 + 1 + 2 = 29 hours
For critical bugs, the bug resolution process is completed in 2-3 business days or 29 working hours.
Comparison Between Lead Time and Cycle Time
Lead time is a calculation of the total time taken from the beginning of the task until it is completely finished, including all the waiting times. On the other hand, cycle time is a calculation of the actual time taken on the task.
To know more about the difference between these two concepts, check our detailed article on Lead Time vs Cycle Time.
Tips to Reduce Lead Time
Once you know how to calculate lead time, the next step is to reduce it to make the process faster.
When lead time is reduced, the outcome is faster releases, faster workflow, and higher customer satisfaction.
The following are some effective tips to minimize lead time:
- Optimize and correct workflow bottlenecks
- Eliminate unnecessary steps
- Automate repetitive work
- Enhance team communication
- Control work in progress
- Perform tasks in parallel
- Minimize external dependencies
- Focus on high code quality
- Provide training to team members
By implementing these tips, it is possible to make the development process faster and more efficient.
Conclusion
The importance of understanding how to calculate lead time is to have better control of your processes or projects. You need to identify both the start and end points of your process or project, track all the time in between, and then choose the best formula for your work.
The importance of calculating lead time is to better understand how to identify bottlenecks in your workflow or to avoid delays in your work or projects. By monitoring your lead time regularly, you will be able to make better decisions.
This will result in faster work or project delivery, consistency in work or project outcomes, and greater productivity for your team in the long run.