In today’s changing workplace, competencies are the basis of performance, growth, and competitive advantage. Whether you’re coming to terms with what they are or intending to work with them in your team, understanding the broad notion of competencies is important. Competencies describe the skills and behaviours needed to perform well, but also to measure performance and to inform professional development. Competency, in the workplace, is critical because organizations can optimize productivity, innovation, and competitive advantage when competencies are clearly articulated and developed. For individuals, developing career prospects, increasing flexibility and adaptability to fluctuating workplace environments, and supporting employees in their efforts to contribute to their team and organization’s success.
Key Highlights:
- What are Competencies?
- Types of Competencies
- Competency Examples in Action
- What Are the Seven Competencies?
- What are the 8 Core Competencies?
- What Are the Five Core Competencies?
- What are the Competencies of Leadership with examples?
- Competency Implementation:
What are Competencies?
Competencies comprise observable and measurable knowledge, skills, behaviors, attitudes, and experiences necessary for success in their roles. The HR profession stands for the combination of skills, knowledge, attributes, and behaviours required to perform the job effectively. Competencies demonstrate the best in performance for each specific position, allowing for parallel hiring, training, and organizational evaluations. By identifying the talents and contributions, and weaknesses of employees can be effectively measured to provide employees with appropriate tools for current and future developmental opportunities. For individuals, gaining an understanding of areas of development related to specific occupations and career paths can enhance performance, confidence, and define a path for career utilisation and advancement in organizations.
Types of Competencies
| Type | Description |
| Core/Behavioural | Soft skills, such as communication, teamwork, and leadership |
| Functional/Technical | Job-specific knowledge, such as financial analysis, project management |
| Organizational | Strategic strengths signal consistent alignment with an organization’s mission, such as innovation, agility |
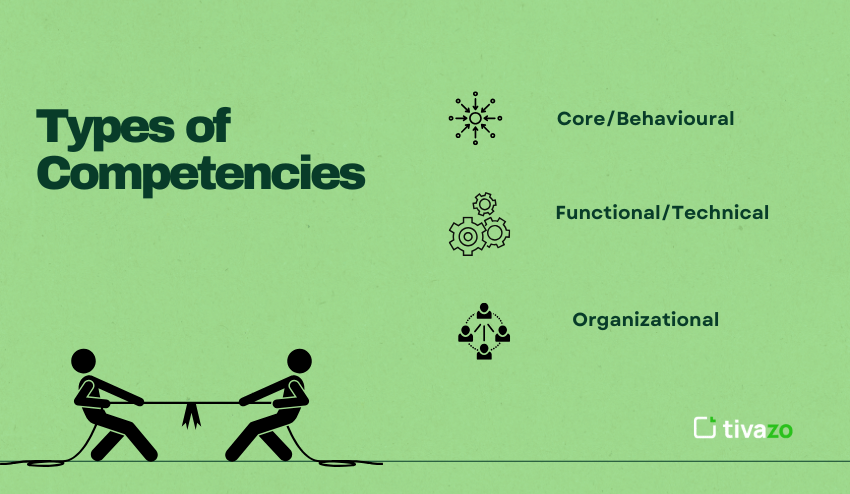
The provided categories of competencies provide a framework for organizing competencies into implementable frameworks for hiring, training, and evaluating performance. By organizing in this way, organizations can identify the expected level of behaviour by role and level. Core gauge on how well an individual aligns with the organization’s culture and whether they can collaborate with others. Functional competencies ensure an individual has the proficiency level needed to carry out their job functions effectively.
Organizational assesses if an employee is acting in alignment with the long-term business goals of the organization. From an organization’s point of view, organized drive measures, proven, measurable development, and tracking the effectiveness of progress within the most strategically important areas for success at both the organizational and personal levels.
Competency Examples in Action
Below are key competencies common across many industries:
Communication
An important competency that enables individuals to communicate ideas clearly through verbal, written, and digital formats – it is required for collaboration across teams, resolving conflicts, and building trust.
Teamwork / Cooperation
It is a base competency that illustrates an individual’s ability to work with a number of different teams, value multiple perspectives in decision making, and accomplish shared objectives.
Problem-Solving / Critical Thinking
This competency reflects the ability to assess a situation and then analyze the options and identify an effective and viable solution.
Adapting & Resilience
An important competency that allows individuals to manage change, stay flexible, and deal well with the discomfort of ambiguity, chaos, and decision-making when time is an issue.
Time Management / Results Orientation
This competency demonstrates the proactive management of workload with appropriate priority, requirements, and deadlines to accomplish measurable outcomes.
Leadership
A high-visibility competency that encourages individuals to harness leadership potential that guides, motivates, and inspires others to demonstrate leadership, vision, and strategic effectiveness in decision making.
Digital Literacy / Technical Proficiency
This competency is becoming more important as digital tools, platforms, and technologies are inevitably integrated into work-life to demonstrate how to efficiently leverage technologies to accomplish goals.
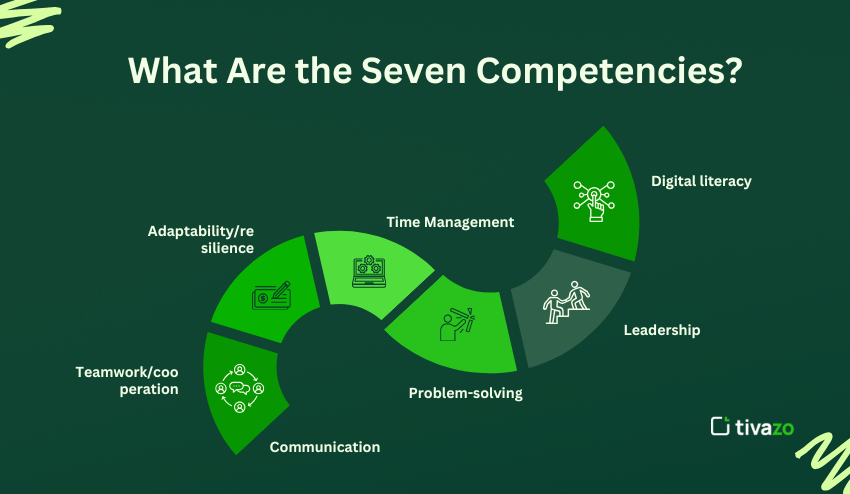
What Are the Seven Competencies?
- 1- Communication
- 2 Teamwork/cooperation
- 3. Problem-solving
- 4. Adaptability/resilience
- 5. Time management/result-oriented
- 6. Leadership
- 7. Digital literacy
What are the 8 Core Competencies?
In addition to the 7 core competencies, some models introduce an additional one, with integrity/ethical behaviour being the broadest. This highlights the value of values-based performance in the context of any role. The core competencies include:
- Communication – Organizing ideas for effective delivery and actively listening to what others are saying.
- Teamwork / Cooperation – Working together and contributing to the success of a group.
- Problem-Solving – Understanding an issue and creating a solution.
- Adaptability / Resilience – Dealing with change and bouncing back when things go wrong.
- Time Management / Result Orientation – Knowing what to do first and doing what is necessary to enable success.
- Leadership – Supporting and moving teams of people towards common goals.
- Digital Literacy – Effectively using and applying technology and technology-based tools.
- Integrity / Ethical Behaviour – Behaving honestly and ethically while recognizing and being accountable to organizational values.
What Are the Five Core Competencies?
Many professional and educational contexts include five core competencies (the critical skills and behaviors that underpin effective performance to support long-term career success) that are important for many industries, roles, and levels of responsibility:
Communication
The ability to effectively convey information, listen to and connect with others, and adjust communication to meet the needs of diverse audiences. Communication competencies promote collaboration, improve understanding, and create smoother workflows when working within teams and organizations.
Leadership
Inspiring and motivating others, developing a clear vision, and guiding teammates and coworkers in the achievement of shared goals. Leadership competencies include making ethical choices and empowering individuals with past leadership decisions.
Teamwork.
Sharing responsibility with others, respecting other points of view, and contributing to a healthy and prosperous team climate. Teamwork competencies provide teams with harmony and efficiency in working toward shared goals.
Problem-solving.
Identifying issues, evaluating information, and creating reasonable solutions. Problem-solving competencies are crucial for improvising, making decisions, and having the capacity to address a variety of challenges in a fast-paced and unpredictable work environment.
Adaptability.
Effectively adjusting to new circumstances, challenges, or changing priorities. Adaptability competencies allow individuals to navigate rapidly changing environments with confidence, productivity, and resourcefulness.
All five core competencies combined serve as a strong foundation to accentuate your ability to succeed in work settings and allow you to be involved in personal and professional development, no matter the context.
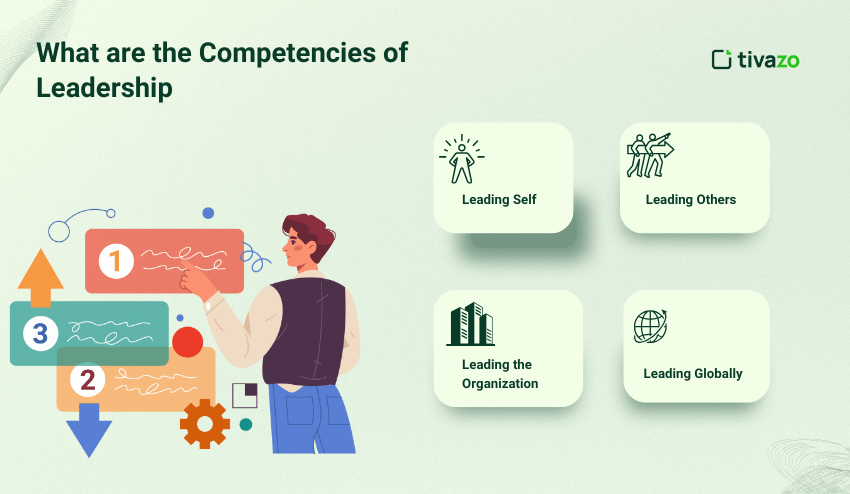
What are the Competencies of Leadership with examples?
Competencies of leadership bring together vision, influence, and execution:
Leading Self
Self-awareness, adaptability. This competency incorporates knowing strengths and weaknesses, managing one’s emotions, and being open to feedback and continued learning. Leaders who possess this can embrace uncertainty as well as model this for their team, as they model resilience.
Leading Others
Motivating, mentoring, and managing conflict. Leaders help team members by motivating and mentoring them, fostering trust, providing support, and effectively resolving conflicts. This competency ensures the team remains engaged, aligned, and productive.
Leading the Organization
Thinking strategically and driving change. Leaders who develop and use this competency operate at the highest level, identifying and leveraging trends (internal and external), informing future vision and transformation across any organization. Leaders use this competency to connect people, resources, and goals while managing opportunity and risk.
Leading Globally
Cultural awareness, global mindset. Today, leaders must develop cultural awareness and respect, making connections across geographies and modifying strategies to various markets and teams globally.
When looking for examples in practice, think of the following:
- Decision making: Activities that include making choices that are timely and informed by using data, options being provided, and thinking about the impact.
- Delegation: Evaluating individuals’ strengths and development needs to assign work, facilitate team accountability, and provide team members with the authority to be empowered.
- Organizational Agility: The ability to work within complex structures, respond instantly to change, and effectively manage competing priorities and ensure the organization is retaining a competitive advantage and response.
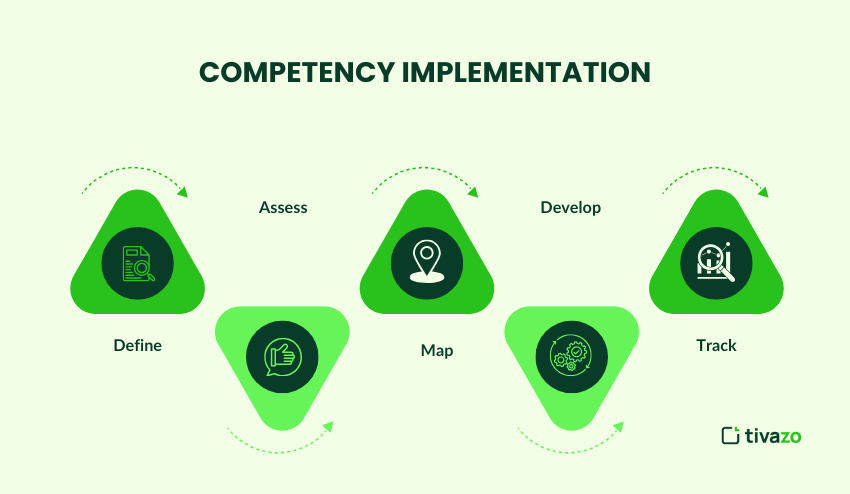
Competency Implementation:
Competence implementation is a procedure that offers everyone a detailed path to understanding what is expected of them to be part of a team. The process can easily look like the following:
Define
Defining competencies is as simple as identifying the competencies needed for every role on your team. You’d want to review job descriptions, conduct interviews with stakeholders, and consider the company’s goals and strategies as you identify the competencies and competency requirements. If you do a good job of building competence into everyone’s understanding in the beginning process, people will have a clear expectation of what is expected of them and the level of competence needed to achieve success.
Assess
Assessing competency is done at the beginning, middle, and end of the line using things like 360-degree feedback, self-assessments, peer assessments, and manager assessments. Looking for strengths and gaps helps everyone understand where they are positioned against their peers and where they can choose to improve and develop new skills. To make the development process even more structured and accessible, incorporating a step-by-step guide creator can help employees follow clear growth paths and complete skill-building tasks with confidence and consistency.
Map
Create a competency map that shows the competencies required for each role as clearly as possible. The map should also show proficiency levels against those competencies (e.g., a competency can be described as: beginner, intermediate, or expert, so you’ll want to map Proficiency Level 0-3). By using a map, it is easier for managers and employees to communicate about where they are on a particular competency, while also knowing the progression path if desired.
Develop
Now that the assessment and mapping have been conducted, triple down with tailored development plans for each employee and groups that incorporate Training, Coaching, Mentoring, or developing based on hands-on project work. Foster lifelong learning by promoting ongoing training and showing employees where to procure resources that incorporate targeted competencies within their skill set.
Track
Regularly track progress using performance appraisals, feedback sessions, and other Key Performance Indicators (KPIs). Use this information to update development plans, celebrate successes, and address challenges. Tracking progress keeps the development process active, engaged, and transformative, resulting in individual and organizational impact.
Quick Reference Table
| Competency | Type Examples |
| Core / Behavioural | Communication, Teamwork, Integrity |
| Functional / Technical | Digital literacy, Project management |
| Organizational | Innovation, Agility, Customer focus |
This table summarizes the primary types of competencies that organizations will focus on to achieve well-rounded employee performance.
Core or behavioural competencies are the primary “soft skills” that define how individuals engage and contribute to a team and an organization. Communication skills, effective teamwork, and integrity are required for building an effective workplace culture to foster collaboration.
Functional or technical competencies are associated with specific job roles and consist of the knowledge and skills required to get the job done. Digital literacy is a functional competency we recognize as being extremely important in a technology-based workplace, and project management skills are required to deliver projects effectively and efficiently.
Organizational competencies consist of broad strategic capabilities that allow employees to sync their work to company objectives. Innovation is a continuous improvement driver that provides competitiveness, and agility allows teams to move quickly with change, using internal and external customer interactions to ensure products and services meet requirements and expectations.
All together, these three competencies encompass a framework for recruitment, development, and performance management.
Conclusion
Taking the time to understand and utilize competencies is critical for both individual and organizational success in today’s fast-paced working environment. Organizations can develop better teams, uplift performance, and remain competitive by identifying, measuring, and developing core, functional, and organizational competencies. For individuals, it is essential to start exploring and improving competencies, whether you are a professional wanting to further develop your skills or a top leader implementing a competency framework for your team.
Developing competencies centered around communication, leadership, adaptability, and more will help enable your growth and achieve your goals. Supporting and investing in the right competencies will do more than just help with our careers, but will develop a culture of lifelong learning and resilience, to help the organization thrive in today’s evolving business climate.