In the modern business landscape, data is a cornerstone of informed decision-making. Business data collection involves gathering information about markets, customers, operations, and competitors to guide strategic initiatives. By leveraging accurate data, companies can improve operational efficiency, identify opportunities, and mitigate risks.
Data comes in two primary forms: structured and unstructured. Structured data refers to information organized in defined formats, such as spreadsheets or relational databases, making it easy to analyze. Unstructured data, on the other hand, includes emails, social media posts, customer reviews, and multimedia content, which require more sophisticated tools and techniques to interpret. Understanding the distinction between these types is essential for designing effective collection strategies.
Primary Data Collection Methods in Business Data Collection
Primary data is collected firsthand to address specific business questions. Standard methods include surveys, interviews, focus groups, and direct observations.
Surveys are among the most widely used tools, enabling organizations to reach large audiences efficiently. Designing concise, unbiased questions ensures respondents provide accurate insights. Email questionnaires and in-person surveys each offer distinct advantages, depending on the target audience and budget.
Interviews provide a deeper understanding of individual perspectives, offering qualitative insights that surveys might miss. Structured interviews follow a set of predefined questions, while unstructured interviews allow for more conversational exploration.
Focus groups gather a small group of participants to discuss products, services, or concepts. By observing interactions and collecting feedback, businesses can identify patterns and sentiments that inform marketing strategies or product improvements.
Observation is a practical method for understanding behavior in real-world settings. For example, retail businesses may monitor customer movements in-store to optimize layouts. Similarly, online platforms track user engagement patterns to improve user experience. Integrating insights from these primary methods often requires collaboration with a data capture services provider to ensure that collected information is both accurate and actionable.
Best practices for primary data collection include clearly defining objectives, selecting representative samples, and maintaining consistency in data collection. This ensures that results are reliable, meaningful, and aligned with business goals.
Secondary Data Sources
Secondary data comes from information that has already been collected, compiled, or published. Typical sources include industry reports, government databases, market research publications, and internal company records. Leveraging secondary data saves time and resources while providing valuable context for primary research findings.
However, not all secondary data is equally reliable. Evaluating credibility requires considering the source, publication date, methodology, and potential biases. Cross-referencing multiple sources can help confirm accuracy and reduce the risk of relying on outdated or flawed information.
Businesses often collaborate with a data science development company to integrate secondary datasets with internal analytics systems. This allows for deeper insights, such as comparing market trends with in-house sales data or benchmarking performance against competitors. When used correctly, secondary data complements primary data, providing a comprehensive view of the business environment.
Digital Data Capture Techniques
Advancements in technology have transformed how businesses collect data. Digital methods include web scraping, customer relationship management (CRM) systems, and Internet of Things (IoT) sensors.
Web scraping automates the extraction of data from websites, enabling companies to monitor competitor pricing, consumer reviews, or social media trends. CRM systems centralize customer interactions, tracking sales history, preferences, and engagement metrics to improve personalization and marketing strategies. In industries such as banking or wealth management, a CRM for financial services like Creatio supports compliance, portfolio tracking, and client communication in one secure platform. IoT sensors capture real-time data from connected devices, such as manufacturing machinery and wearable health devices, enabling predictive maintenance and enhanced service delivery.
Digital data collection offers speed, scalability, and the ability to handle vast amounts of information. However, potential limitations include data quality issues, technical challenges, and compliance with privacy regulations. Combining digital techniques with traditional methods often yields the most comprehensive insights.
Leveraging Productivity and Time-Tracking Data
In addition to traditional and digital data collection, businesses can benefit greatly from employee productivity and time-tracking insights. Platforms like Tivazo capture real-time work hours, project progress, and task completion patterns. This information allows managers to identify workflow bottlenecks, optimize team schedules, and allocate resources more efficiently.

By analyzing time-tracking data alongside customer or market insights, companies can make smarter operational decisions. For example, if certain tasks consistently take longer than expected, managers can provide targeted support or automate repetitive work, improving overall efficiency.
Integrating Analytics for Smarter Decisions
Combining data from multiple sources—such as surveys, CRM systems, and time-tracking platforms—provides a holistic view of business performance. Using dashboards and analytics tools, managers can spot trends in employee productivity, customer engagement, and project outcomes. This integrated approach ensures that decisions are based on actionable insights, not just assumptions.
Real-Time Insights for Agile Businesses
In fast-moving markets, real-time data is essential. Digital tracking tools can monitor employee activities, project deadlines, and team collaboration patterns instantly. Businesses can respond quickly to operational challenges, adjust workloads, and improve team performance, all while maintaining compliance and respecting privacy.
Integrating these practices with data from customer feedback, market research, and competitor analysis gives companies a competitive advantage. It also aligns closely with Tivazo’s focus on enhancing productivity through data-driven insights.
Ensuring Data Privacy and Compliance
Data collection is not just about gathering information—it also requires careful attention to legal and ethical standards. Businesses must comply with data protection regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe, which governs how personal data is processed, stored, and shared.
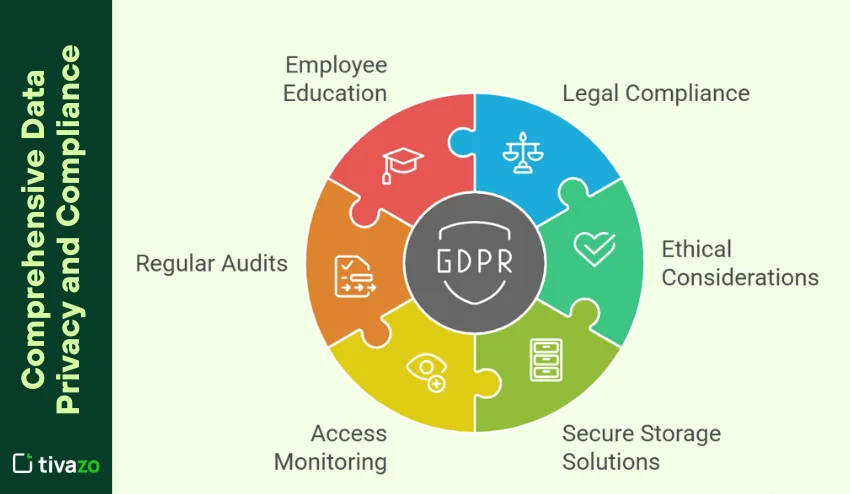
Ethical considerations include obtaining consent, anonymizing sensitive information, and ensuring transparency in how data is used. Organizations that prioritize privacy and compliance build trust with customers, strengthen brand reputation, and avoid costly fines or legal issues.
Implementing secure storage solutions, monitoring access to sensitive data, and regularly auditing data practices are essential steps for maintaining compliance. Additionally, educating employees about data protection policies ensures that ethical standards are consistently upheld across the organization.
Practical Tips and Case Studies
Successful businesses often combine multiple data collection methods to gain a holistic understanding of their markets and customers. For example, an e-commerce company may use web scraping to track competitor pricing, surveys to gauge customer satisfaction, and CRM analytics to identify purchasing patterns.
Lessons learned from such initiatives highlight common pitfalls. Over-reliance on a single data source can lead to biased insights, while poor survey design may produce inaccurate responses. Similarly, neglecting data privacy can result in reputational damage and regulatory penalties.
To maximize the value of collected data, companies should focus on integration and analysis. Leveraging data analytics platforms enables organizations to uncover trends, make predictions, and drive strategic decisions. Companies that treat data as a strategic asset—not just a byproduct of operations—gain a competitive edge in their industries.
Conclusion
In conclusion, effective Business Data Collection in modern organizations requires a strategic combination of primary research, secondary sources, digital capture techniques, and strict adherence to privacy standards. By thoughtfully applying these Business Data Collection methods, organizations can transform raw information into actionable insights that drive growth, innovation, and long-term success.




