Flexible work is a modern, flexible form of work that doesn’t conform to the structure of a traditional 9-to-5 position at a specific location. “Flexible” means employees are allowed to customize their work hours, location, and sometimes workload based on personal and professional commitments, all within the parameters set by the employer.
Key Highlights:
- What Does Flexible Work Mean?
- Why Flexible Work is Important
- Types of Flexible Work Arrangements
- What is Flexible Work Pay?
- What Does Job Flexibility Mean?
- What is Flexible Work?
- How Long Is a Flexible Schedule?
- How to Earn $2,000 a Week From Home
What Does Flexible Work Mean?
Flexible work can come in many forms, including but not limited to:
- Remote work (working from home or outside of the office)
- Hybrid work (a combination of in-office and remote work)
- Flextime (the employee determines start and end times within a flexible range to complete work hours)
- Compressed workweeks (the employee is required to work longer hours within the compressed model of less than a full workweek, such as four 10-hour days)
- Job sharing (an arrangement where the employee shares duties and responsibilities for one full-time role with another employee)
- Results-only work environment (ROWE) (an hourly rate employer assesses performance based on work produced and not hours worked)
These arrangements fall within the broader category of job flexibility, which enables employees and employers to develop more efficient, productive, and satisfying work environments.
In formal or government specifications—like with the US Office of Personnel Management (OPM), Flexible Work Schedules (FWS) are structured by rules and regulations. The FWS includes:
- Core hours (time when employee must be physically present or available for attending telework)
- Flexible time hours (when the employee determines their work time)
- Variations such as gliding schedules, maxiflex, variable day schedules, and variable week schedules
Of time systems allow federal employees to fulfill the basics of the 40-hour work week (80-hour bi-weekly work requirement), but allow an employee to day-to-day alter their daily hours of work to plan time with their personal life.
At the end of the day, flexible work is about creating autonomy, work-life balance, and developing a results-oriented culture, regardless of being an employee of a private tech company or a formal government agency.
Why Flexible Work is Important (Benefits of Flexible Work)
Does Flexible Work Have Mental Advantages?
Yes, flexible work has benefits:
- Greater employee satisfaction and engagement
- Better work-life balance for caregivers or commuting constraints
- Higher productivity – research indicates people may work more productively during their best hours, U.S. Office of Personnel Management
- Talent attraction & retention: having flexible work offers flexibility to employers seeking to attract talent
- Operational resilience: supports conditions in the event of a disruptive circumstance (e.g., remote ready)
The benefits position flexible work as a dimension that employers and employees can adopt
Types of Flexible Work Arrangements
Several types of arrangements are becoming common in almost every industry as companies position themselves to meet the realities of today’s work and workforce expectations. Flexible work arrangements deliver freedom, autonomy, and efficiency and can be advantageous for both the employee and employer.
6 Types of Flexible Work (in an ActivTrak-style taxonomy)
| Flexible Work Type | Definition |
| Remote work | Employee works entirely online from home or another remote location using digital tools. |
| Hybrid work | Combines some in-office and some remote work days, giving the employee the best of both worlds. |
| Flextime Employees | Choose their start and end time within a range defined by the schedule they. |
| Compressed workweek | Employee works longer to have shorter or fewer workdays each week (working a 10-hour day instead of two days). |
| Job share | Two part-time employees share the responsibilities of a single full-time position for hours and complete the work. |
| Results-based work | Work that is focused on outcomes or deliverables, regardless of when or where work gets done |
These work types go far beyond a traditional 9-to-5 job. They are designed to allow for working in a wide range of styles, for different lifestyles, for caregiving, for geography, and for productivity, consisting of a wide range. With flexible work arrangements, the employer gets not just reduced absenteeism and improved employee morale and commitment, it can access to a far wider talent pool. flexible work.
What is flexible work pay?
Flexible work pay is made up of premiums and credit hours in a flexible work schedule (FWS):
In U.S. federal flexible work schedules, pay policies encompass:
- Basic Work Requirement: 40 hours/week, 80 hours/biweekly, for full-time employees
- Credit Hours: voluntary hours of work above the basic requirement and scheduled in the flexible work bands; not compensated right away, but may be utilized at a later time for time off purposes
- Overtime Pay: only occurs when excess hours of work (to the basic work requirement) are ordered and approved by management
- Night Pay: if you have to finish basic work requirement hours between the hours of 6 pm and 6 am, and there are no available daytime hours to complete the basic work requirement, then you can claim night differential pay
- Sunday/Holiday Premium Pay: if your flexible work bands include Sunday or holiday work toward fulfilling your basic work requirement, then you are eligible for premium pay ( 25% for Sunday, 100% for holiday hours, up to 8 hours)
So flexible work pay in FWS consists of structured policies for premium and credit hours, giving both transparency and fairness.
What Does Job Flexibility Mean?
Job flexibility is the extent to which a job permits an individual to control how, when, and where work is completed. Job flexibility encompasses the various types of flexible work arrangements that provide employees with the ability to define how they work and how they blend their work responsibilities with personal obligations.
Job flexibility can take many forms:
- Schedule flexibility: Employees are allowed to start sooner than traditional hours or start later; they may also work compressed weeks (e.g., four 10-hour days rather than five 8-hour days).
- Location flexibility: A role could provide flexibility in allowing remote work, or a hybrid work structure where employees alternate working from home and working from the office.
- Time for task execution: Some roles allow employees to execute tasks and deliver work products based on deadlines or deliverables rather than specific hours of productivity; this is often called results-based work.
- Flexibility in hours: This could include part-time roles, gig-based work, or roles
In other words, a flexible work job shifts away from “how many hours do you sit at your desk” towards “how well do you get your work done.” This flexibility allows for working from anywhere, at any time, and with greater productivity, satisfaction, and retention for the worker. Whether through asynchronous communication, remote collaboration tools, or output-based assessment or rating, job flexibility allows workers to excel both in their work and personal lives.
When employers offer job flexibility, they are exhibiting trust and support for employee well-being, which is important in today’s emerging and rapidly changing workforce.
What Does It Mean to “Be Flexible at Work”?
When you want to express your adaptability and willingness to adapt to the nuances of flexible work in a professional setting – interview, performance review, resume – it is important to do so with clarity and confidence.
Examples of how to say:
- “I can be flexible in my work schedule, and I’m happy to adapt to when business needs to requires flexibility.”
- “I can provide flexible work hours, and I can condense my work week when needed.”
- “I excel in flexible work arrangements, including remote work, hybrid arrangements, or output-based schedules.”
- “I can adapt quickly to changing priorities and can shift between tasks in the office and tasks at home.”
- “I am used to collaborating across time zones and managing my workload without supervision.”
Each of these statements communicates your ability to be flexible and adapt to change, be productive in a variety of conditions, and be a part of team successes. Flexibility is one thing that employers are looking for in today’s world of flexible work.
Being flexible at work is not only working in different times – it is also a demonstration of emotional intelligence, time management, and a responsiveness to external influences. When applying for a flexible job or pursuing a promotion, communicating as a thinking employee will guide other employees.
Make not only your words show that you are adaptable, but prove it through your outcomes in a flexible work environment.
What is Flexible Work?
When we refer to a flexible job, we mean a job that allows a level of discretion in how, when, and where someone does their work. Flexible jobs are based on flexible work arrangements, such as remote working, hybrid working, flextime, compressed work weeks, and job sharing. Instead of requiring you to be in an office at a specific time, on specific days, and to work set hours, flexible jobs place more importance on productivity, results, or outcomes, rather than the number of hours spent working in an office.
Some common characteristics of flexible jobs will include:
- No requirement to be in an office every day.
- Flexible start and end times.
- You will be measured against performance, not attendance.
- You can choose to do your work at times that align with your most productive times.
Flexible jobs are becoming increasingly popular in technology, marketing, design, customer service, writing, and consulting, among others. A few examples of flexible work jobs are reported, digital project manager, content strategist, virtual assistant, freelance writer, freelance public relations consultant, software developer, etc.
Flexible work is becoming more widespread because many people want a flexible job. Many people want flexibility so they can balance work and personal life better. Others are unable to work due to caregiving commitments or personal circumstances but prefer to work in a non-traditional manner. Additionally, some people want some control over their work lives. As the use of digital tools and asynchronous collaboration grows in the workplace, flexible jobs continue to grow. Flexible jobs show no signs of slowing- making them one of the most desired employment models in the newer employment environment.
How Long Is a Flexible Schedule?
Flexible Work Schedules (FWS) means, as defined by the U.S. Office of Personnel Management (OPM), that a full-time employee is generally expected to complete 80 hours during their pay period (2 weeks). Part-time employees must complete the prorated number of hours as per their employment agreement.
While the FWS is unique because it allows employees to decide when to start and stop their workday during the prescribed flexible bands, as long as they meet the total hours, they are expected to complete their total hours. So an employee can work ten hours on Monday and only six on Tuesday, if it supports their productive way of working or personal time commitments.
Each employee’s flexible schedule can differ significantly during the week and/or month or during each pay period, as the schedule can allow longer days for a shorter workday or even a day off later in the week, also referred to as a compressed work week, not just a clocked-in hour schedule.
CBAs/FWAs with compressed schedules do support each employee’s unique hours in terms of expectations of completing the number of hours required and support fairness and accountability on how the time is managed while promoting independence to support job performance alongside family, educational, or wellness time. Flexible work schedules represent a strategic advantage for employees and organizations to enhance a healthier and more productive workplace in the public and private sectors.
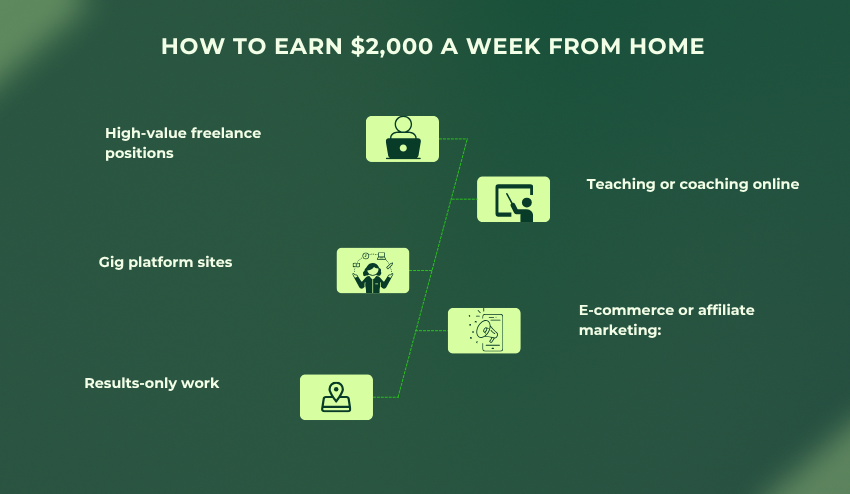
How to Earn $2,000 a Week From Home
Just because you’re working flexibly—in a lot of cases, you will make less money than you would with a full-time employee role. That said, working flexibly does provide you control over how you structure your income. It is very possible to make $2,000 a week working from home with the right combination of skills, platforms, and mindset.
This is how to approach it:
- High-value freelance positions: Work as a consultant, software developer, UX designer, copywriter, and digital marketer to achieve premium hourly rates (~$50/hour or more).
- Gig platform sites: Join gig platform sites (e.g., Upwork, Freelancer, Fiverr). The key to maximizing your income through these platforms is to offer multiple offerings/hours for clients. The site will give you super flexibility here.
- Results-only work: Work on outcome-based projects. Clients pay a weekly fee/milestone. Some really can use flexibility to their advantage. If you’re more qualified or have more experience than they then you will be able to position yourself in a way that they pay for the results you provide to them and not the time that it takes.
- Teaching or coaching online: Be a language teacher. You can even create and market digital courses through sites like Teachable or Udemy.
- E-commerce or affiliate marketing: Create passive income like a dropshipping business, Amazon FBA, or even a monetized blog with affiliate marketing links.
The overall idea is to take flexible work to your advantage by optimizing your time, developing skills that are in demand, and consistently providing results. In the beginning, you might need to combine income streams, but if you are serious and work hard, flexibly can easily be a pathway to working towards $2,000+ a week.
Conclusion
Flexible work is not a passing trend—it represents a paradigm shift in productivity, wellbeing, and satisfaction in the workplace. Remote work, flex-time, and output-based roles allow people to take charge of their time while still producing superior work. For organizations, flexible work can only improve retention, innovation, and productivity. As we continue to adapt to new technologies blended with an increasingly diverse workforce, we must embrace flexible work approaches as more than just an option but a requirement. By understanding the flexible work options available and the opportunities and benefits of flexible work, organizations and professionals can perform and thrive in the future of work with intention and balance.