It’s important to know how to calculate net income if you’re managing personal finances, owning a business, or examining business performance. Net income allows individuals or businesses to make more intelligent decisions about how their money should be allocated, whether you are an employee looking at your take-home pay or a business owner reviewing profit.
This entire guide covers everything you need to know about net income: what net income is, how to calculate net income, general formulas, examples, tables, FAQs, and the best ways to track your net income as accurately as possible.
This blog was built around informational search intent; it is meant for users to learn everything about calculating net income.
What is Net Income?
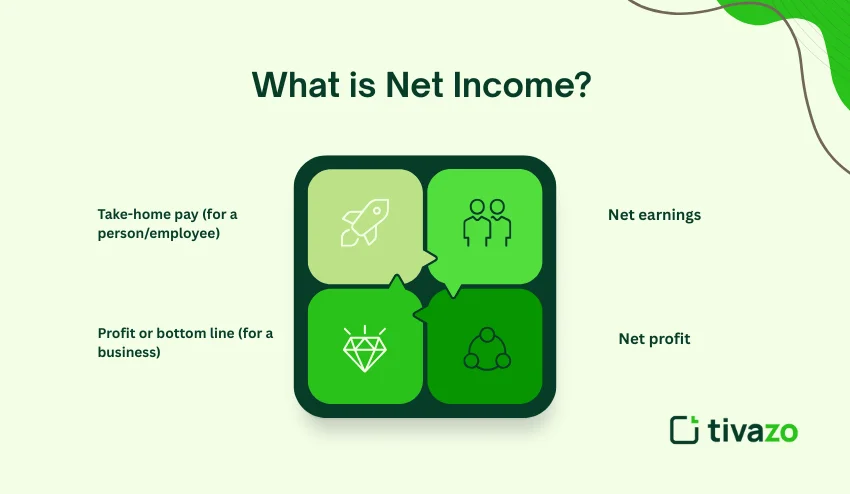
Net income is the total amount of money that a person or business keeps after the total income has had all expenses, taxes, and deductions taken out. Net income is the amount the person or business has actually ‘earned’, also known as:
- Take-home pay (for a person/employee)
- Profit or bottom line (for a business)
- Net earnings
- Net profit
With net income, it is important to understand how the net income calculation works for personal income vs. business income in slightly different ways.
The Importance of Net Income
Knowing how to calculate net income is important because it allows you to:
- Create more accurate budgets
- Monitor spending and saving
- Assess job offers
- Make better investment and tax decisions
- Review business profitability
- Increase financial planning
Knowing how to calculate Net income helps you clearly see an accurate picture of your overall financial well-being.
How to Calculate Your Net Income (For Individuals)
To determine your personal net income, simply start with your gross income on how to calculate net income and then subtract any deductions, both required and optional.
Net Income Formula (Personal)
Net Income = Gross Income – Total of Deductions
Your total deductions can include:
- Federal taxes
- State taxes
- Social Security
- Medicare
- Retirement contributions
- Health insurance
- Your other optional deductions
Example: Calculate your net income from your salary
Suppose your gross annual salary is $60,000.
| Deduction Type | Amount |
| Federal Taxes | $8,000 |
| State Taxes | $2,500 |
| Social Security | $3,720 |
| Medicare | $870 |
| Health Insurance | $1,200 |
| 401(k) | $3,000 |
| Total Deductions | $19,290 |
$60,000 – $19,290 = $40,710
Your net income (or take-home pay) can be estimated at $40,710 per year.
Calculating Net Income (Business)
Businesses on how to calculate net income shows the amount of profit that is left after operating costs, taxes, interest, and other expenses. Calculating net income gives business owners an understanding of how profitable their business is: the owners can make business decisions based on that understanding, as well as plan for future expansion, revenue, and expenses. It is also an indication of how well the company is managing costs and operating efficiency. This can lead the company to identify areas to save money, improving overall profitability.
Total Revenue minus Total Expenses will yield net income.
Net Income = Total Revenue – Total Expenses
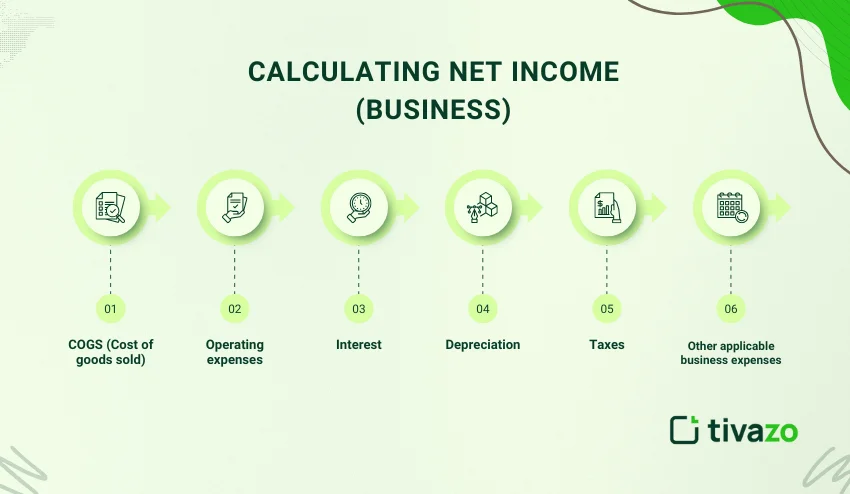
A simplified view of total expenses includes:
- COGS (Cost of goods sold)
- Operating expenses
- Interest
- Depreciation
- Taxes
- Other applicable business expenses
Example Table for a Business’ Net Income
| Category | Amount |
| Total Revenue | $500,000 |
| COGS (cost of goods sold | $200,000 |
| Operating expenses | $120,000 |
| Taxes | $50,000 |
| Interest & Other expenses | $10,000 |
| Total Expenses | $380,000 |
Net income is $500,000 – $380,000, for a total of $120,000
Business owners who track net income regularly can compare business conditions and performance across different periods, evaluate the success of new offerings, new disbursements related to investments and strategic decisions, as well as other business initiatives. Net income helps to make decisions regarding profit maximization and provides valuable metrics for stakeholders, investors, and management teams looking to serve the best interests of business sustainability, profit, financial health, and growth opportunity.
What is the Formula for Net Income?
There are two standard formulas, which may depend on the circumstances.
A formula for individuals:
Net Income = Gross Income – Tax – Deductions
This formula will give an employed taxpayer their take-home income, excluding Federal tax, state tax, social security, Medicare taxes, retirement contributions, etc. The purpose of using a net income calculation is that an employed taxpayer can use their net income to visualize their expenses or savings, rather than attempting to figure out a list of how much money would need to be deducted from gross income to arrive at their real income.
A formula for the Company:
Net Income = Gross Revenue – Total Expenses
This is the simple way of calculating profitability when you still have a way to separate all operating costs, interest, taxes, and any other expenses from the total revenue how to calculate net income.
Although both formulas get the right answer on how to calculate net income, the variables are different for an individual vs. a business. An employed taxpayer or business owner must determine their net income correctly, so they make a correct amount for their financial analysis portion of the budgeting, investment, and planning for future growth.
Where Can I Find Net Income?
There are many ways to obtain net income:
For Individuals
- Your payslip (labeled as Net Pay)
- Your employment contract
- Your annual W-2 form
- Tax returns
- For Businesses
- Income statement (bottom line)
- Monthly/annual financial reports
- Accounting software (QuickBooks, Sage, Xero)
How to Calculate Net Income in a Balance Sheet
A balance does not indicate net income in a similar way to an income statement. Net income is indicated in the income statement and then is transferred to the balance sheet, located in the equity section under retained earnings net income.
Essentially, the process is:
1. Calculate the net income using the income statement
2. Add the net income to retained earnings in the equity section
3. Update the total shareholders’ equity
This is why understanding how to calculate net income is important when learning about financial reporting.
What is My Take-Home Pay if I earn $60,000?
Referring back to our earlier example of gross salary:
If you’re getting paid a gross salary of $60,000, under most circumstances, deductions will bring your take-home salary to around $40,000 – $45,000, depending on:
- State Taxes
- Retirement Contributions
- Medical Benefits
Any other voluntary deductions, such as insurance premiums or flexible spending accounts.
To figure it out exactly, use the net income formula on how to calculate net income.
Net Income = $60,000 – Total Deductions.It’s important to understand your net salary for budgeting, planning expenses, and saving for financial goals. It’s always good to accurately calculate your net salary so you will understand exactly how much money you have for living on a daily basis and for long-term financial planning.
Step-By-Step: How to Compute Net Income with Ease
- Identify Gross Income:
For individuals – total salary before deductions
For businesses – total receipts
- Gather All Deductions or Expenses: Include taxes, reductions, costs of business, and/or fees.
- Calculate Net Income Using the Correct Formula: Depending on whether you are calculating personal income or business income.
- Account for Other Factors: Bonuses, Commissions, Interest, Depreciation, etc.
- Verify Your Net Income: Check the total and confirm that each number is correct and included.
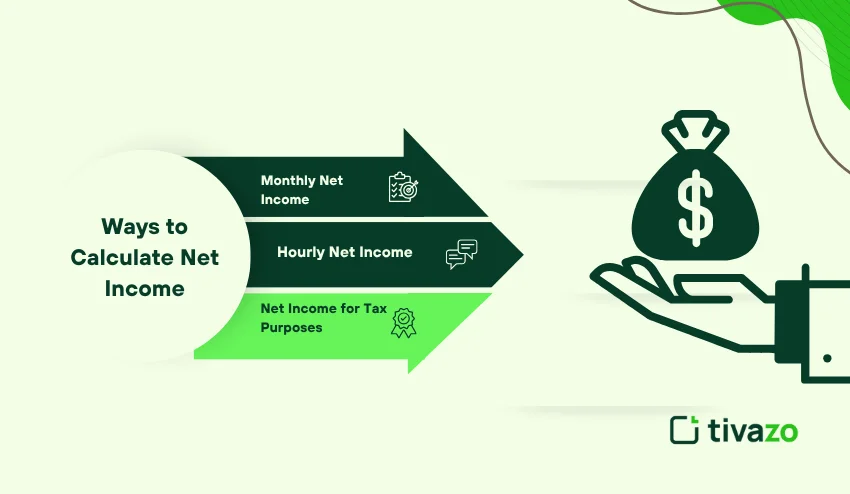
Other Ways to Calculate Net Income
1. Monthly Net Income
Monthly Net Income = (Annual Net Income/12)
2. Hourly Net Income
Hourly Net Income = Net Income/Hours worked
3. Net Income for Tax Purposes
Taxable Net Income = (Gross Income- IRS-approved deductions)
Net Income Limitations
Though it’s a valuable calculation, on how to calculate net income also has limitations:
- It may not include non-cash costs
- It may change indirectly based on the accounting standards followed
- It does not specifically show cash outflow or inflow
- Net income may appear inflated or understated
The accuracy of the computations can be impacted by outside forces (changes in taxes or rules governing deductions)
Being aware of the limitations of the calculation will better prepare you to analyze how to calculate net income.
Real World Illustration: Net Income Calculation From Your Payslip
Your payslip may read:
- Gross Pay: $5,000
- Federal Tax: $500
- State Tax: $150
- Medicare: $72.50
- Social Security: $310
- Insurance: $120
Total Deductions = $1,152.50
Net Income = $5,000 – $1,152.50 = $3,847.50
This is your true take-home pay.
- Master Your Finances Through Accurate Net Income Tracking
- Learning how to determine net income allows you to:
- Set better financial goals
- Make better budget decisions
- Genuinely understand cash flow
- Invest wisely
- Avoid unnecessary debt
If net income is tracked accurately, you can become the master of your financial destiny with confidence on how to calculate net income.
Conclusion
Understanding how to calculate net income is an essential life skill for people and businesses. Once you know how to determine net income, you can accurately see what your earnings are, such as your take-home pay or how profitable your business was. You can successfully calculate an accurate net income figure by using the right formulas, substantiating deductions/expenses, and factoring in different considerations. In addition, it’s great practice to calculate net income periodically for your budgeting process, to help with overall financial planning, and so that you can make decisions that put you in the best position for next time. Take charge of your finances today by becoming proficient on how to calculate net income.