In the digital age, organizations must address data leakage if they want to maintain customer trust and protect sensitive information. Data leakage can be described as the unauthorized transmission of data from within an organization to an external destination. Data leakage can occur intentionally or unintentionally, and if left unchecked, it may lead to financial losses, reputational damage, and/or regulatory sanctions. Organizations that fail to address the risk of information exposure may be subject to lawsuits, investigations, and enforcement sanctions, and/or loss of organizational trust by customers.
At Tivazo, we make the safety of sensitive data a priority to ensure data leakage is continuously addressed through technology, policy, and employee education. We accomplish this through controls, encryption, monitoring of employee and other system accesses, and employee training. By emphasizing preventing data leakage, Tivazo helps organizations to limit their risk, maintain compliance, and build a fundamental base of trust internally with employees and externally with clients, stakeholders, and partners. Any organization that takes the prevention of data leakage seriously can, in the end, protect its information assets and ensure its organizational survival.
Key Highlights:
- What Is Data Leakage?
- Common Causes Of Data Leakage
- Methods of Data Leakage
- What Does Leak Mean in Software Platforms?
- Data Leakage Prevention vs Data Loss Prevention
- Human Error and Data Leaks
- 6 Strategies to Prevent Data Leaks
- Tivazo’s Approach to Preventing Data Leakage
What Is Data Leakage?
Data leakage can broadly be defined as the exposure of sensitive data to unauthorized users, networks, or systems.
Data leakage can happen through:
- Email: Accidental reply all, forwarding, and sending attachments to the wrong recipient.
- Cloud Storage: Misconfiguring permissions/access, public links, etc.
- Removable Media: USBs, external hard drives left on the table, or passed on to the wrong person.
- Network Transmissions: Unsecured or tampered connections, exposed APIs, etc.
Even minor data leaks can lead to harm – for example:
- Loss of company intellectual property
- Loss of client trust and negative impacts on the company brand
- Financial penalties for non-compliance: GDPR, HIPAA
- Possible costly competitive disadvantage from exposing trade secrets
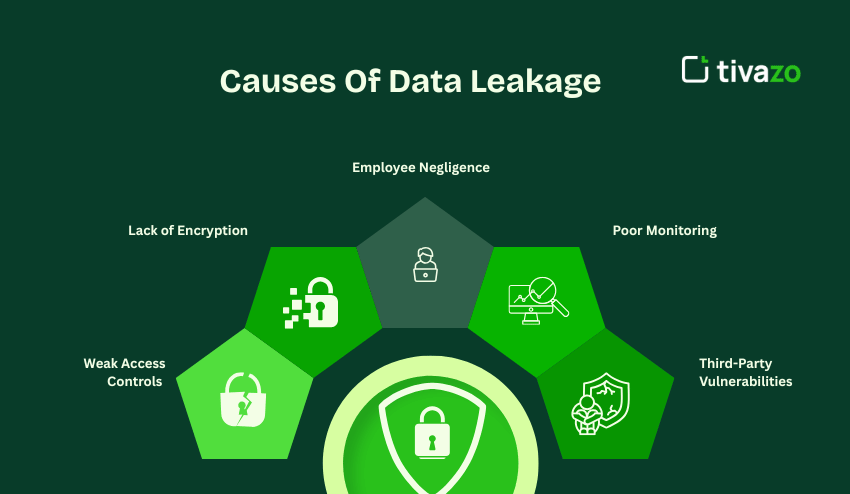
Common Causes Of Data Leakage
The most common causes of preventing data leakage include:
| Cause | Description |
| Weak Access Controls | Overly permissive settings or a lack of user authentication |
| Lack of Encryption | Unsecured data that is potentially vulnerable in transit |
| Employee Negligence | Accidental sharing, loss of devices, and following the targets of phishing |
| Poor Monitoring | Not noticing anomalous access or suspicious behavior |
| Third-Party Vulnerabilities | Vendors or partners with poor security hygiene |
Knowing about these causes can allow you to better formulate a strategy to prevent data leakage.
Methods of Data Leakage
In an increasingly data-focused world, preventing data leakage is a threat that warrants greater consideration by organizations. If organizations can understand how data leakage occurs, they can more effectively direct their remediation efforts to close security gaps and protect sensitive assets.
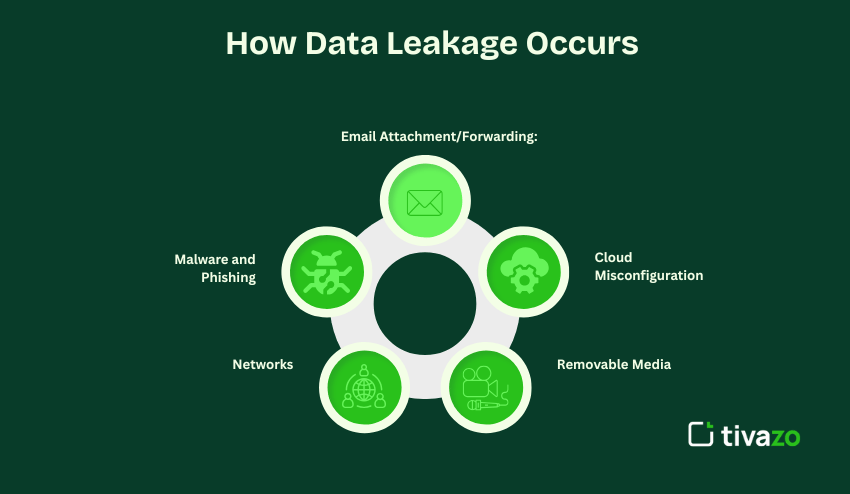
How Data Leakage Occurs
There are many ways an organization can experience data leakage, such as:
- Email Attachment/Forwarding: sensitive data sent unintentionally or sent to other unauthorized recipients
- Cloud Misconfiguration: shared folders are incorrectly configured, with weak permissions access
- Removable Media: USB drive/external hard drives/printed documents
- Networks: unsecured transmissions/exposed APIs
- Malware and Phishing: used as methods by malicious attacks to trick employees into deliberately leaking sensitive data
What Does Leak Mean in Software Platforms?
In the context of software or product platforms, a leak is the unauthorized release of confidential or sensitive information due to inherent weaknesses in the software platform. Weaknesses can occur in several forms, including:
- Vulnerabilities – Security gaps in the code that allow hackers to breach your platform.
- Bugs – Mistakes in programming code that inadvertently release your data.
- Misconfigurations – Improper settings or configurations that expose sensitive information.
- Malicious Attacks – Directed attempts to steal, manipulate, or delete your data
When a leak occurs, the ramifications can be far-reaching, including unauthorized access to user accounts, the theft or misuse of your organization’s proprietary business data, and significant damage to users’ trust on preventing data leakage.

For businesses trying to mitigate or preventing data leakage in software platforms, it is important to:
- Frequently audit the code base for vulnerabilities and incorporate vulnerability testing in the software development process.
- Apply security patches promptly.
- Encrypt data at rest and in transit.
- Implement uncompromising access control.
By taking the leaks in preventing data leakage seriously, organizations can foster overall system integrity, enhance user privacy and security, and ensure the software platform meets standards or regulations.
Data Leakage Prevention vs Data Loss Prevention
Although the objectives are both to protect data, the methods and objectives of data leakage prevention are different from and more critical than data loss prevention. If you are concerned about preventing data leakage, you need to understand the difference to prevent data leakage effectively.
| Aspect | Data Leakage Prevention (DLP) | Data Loss Prevention |
| Main Purpose | Prevent data from being inappropriately, illegally, or non purposefully exposed or shared/ distributed outside of the organization | Prevent data from being purposely or non purposedly lost, deleted, or stolen- regardless of inside or outside |
| Scope | Preventing data leakage from leaving the organization’s perimeter | Protecting data from being lost or destroyed |
| Typical Measures | Access controls, encryption, network monitoring, and user activity monitoring | Backups, recovery systems, anti-theft tools, redundancy |
| Example Use Case | Prevent data from being purposely or non purposedly lost, deleted, or stolen- regardless of inside or outside | Recovering a deleted file (or files) from a server |
To put it simply, preventing data leakage is all about controlling and monitoring the flow of outbound data and making sure it does not end up in the hands of unauthorized people. On the other hand, data loss prevention is all about making sure that data is intact or at least recoverable, even if accidental loss or a breach occurs. While both types of protection are critical components of a solid cybersecurity strategy, it is important to note that preventing data leakage involves constant monitoring, restrictive access to sensitive data, and risk-based management before a breach occurs.
Human Error and Data Leaks
The data backs up what we suspect: human error is responsible for 95% of cybersecurity breaches. Mistakes happen. For example, mistakenly sending a sensitive email to the wrong recipient or using a weak or reused password. Clicking on a malicious link while browsing trusted websites. Clicking on a malicious attachment while viewing otherwise legitimate emails. Misplacing or leaking sensitive files. One slip leads to a data breach that can quickly create a large number of financial and operational complications, compliance obligations, and reputational risk. Most organizations would also say the biggest vulnerability to data leaks is not the technology, but PEOPLE.
Training and awareness of human error are the first and last lines of defense against data leakage. Users need to know that it is important to always check the email recipients if the subject is sensitive before clicking send, to identify phishing emails, and to plan compliance with protocols. And technology can help organizations reduce human error, such as adding multi-factor authentication for logins and sharing sensitive documents, automated alerts when users are sharing large amounts of data to an external recipient, and limiting access to sensitive documents by other employees.
Ultimately, preventing data leakage is about technology (the smart way) and properly trained people. When organizations are proactive in correcting human error when it occurs, they are making their first line of defense against breaches stronger and protecting their data and reputation as a whole.
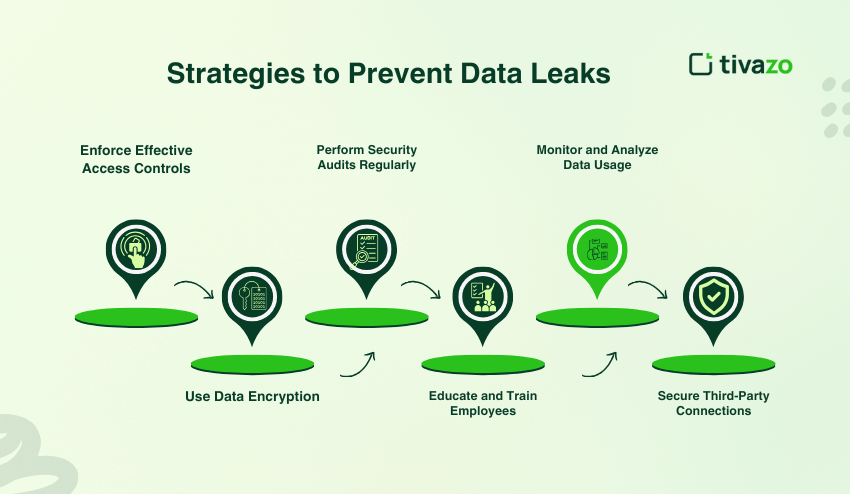
6 Strategies to Prevent Data Leaks
1. Enforce Effective Access Controls
Access to sensitive information should be done through the principle of least privilege. That is, only the people need access to critical data. Furthermore, you should perform regular reviews of access permissions.
Key Actions Include:
- Role-based access management
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA)
- Regular auditing of users’ access
2. Use Data Encryption
Encryption is a mainstay in preventing data leakage. Encryption ensures that what is intercepted in storage or transit is inaccessible information.
Key Actions Include:
- Encryption while at rest and in transit
- Use strong encryption standards like AES-256
- Store decryption keys separately
3. Perform Security Audits Regularly
Security audits should be done continuously. Security audits will allow you to discover any vulnerabilities and also monitor the effectiveness of your security process. Being able to find weaknesses proactively can help prevent data leakage before A data leak occurs.
Key Actions Include:
- Internal audits on systems and processes
- Vulnerability scans and penetration testing
- Review third-party security audits and practices
4. Educate and Train Employees
Employees are your first line of defense against data leakage. Regular training helps ensure employees understand data security, the importance of data security, and what constitutes a data security threat.
Key Actions:
- Phishing awareness programs
- Recommended guidelines for handling sensitive information
- Security guidelines around remote work and cloud usage
5. Monitor and Analyze Data Usage
Monitoring and analyzing how data is accessed and used can identify abnormal activity and can even help to prevent leaks in a real-time manner. In cloud environments, deploying a cloud workload protection platform (CWPP) provides unified visibility, runtime threat detection, and policy enforcement across VMs, containers, and serverless workloads to reduce data leakage risk.
Key Actions:
- Implement real-time monitoring tools
- Set alerts for unusual access patterns
- Keep track of downloads and sharing, and reporting on system activity
6. Secure Third-Party Connections
When you connect with third-party providers and partners, you introduce risk. If they have weak practices, that could allow for data leakage. Be sure to ensure their compliance with your DLP policy is sufficient to mitigate risk through external connections. Partnering with providers that specialize in enterprise managed IT services can also strengthen your security posture, since they bring expertise in monitoring, access control, and compliance that helps reduce vulnerabilities introduced by outside parties.
Key Actions:
- Regularly conduct third-party risk assessments
- Have security requirements in contracts
- Regularly monitor third-party activity and access
Tivazo’s Approach to Preventing Data Leakage
At Tivazo, our end-to-end practice of preventing data leakage encompasses advanced technology and security-oriented behavior:
- Advanced Encryption Methods – Safeguard sensitive data both at rest and in transit.
- Documented Data Loss Prevention (DLP) policies – Lay out your data use, storage, and sharing practices.
- Real-time monitoring tools – Time-sensitive ramp access and large file transfer anomalies.
- Employee training programs – Arm staff with equipment to appropriately handle data.
We make sure that preventing data leakage is more than just a technical solution; it’s a culture—the Tivazo culture. From the automated alerts to the strict access controls we put in place, we can help organizations reduce human error, stop unauthorized transfers, and stay compliant across international regulatory standards. With Tivazo, preventing data leakage becomes a function of waking up each day—protecting intellectual property, keeping client trust intact, and preserving business practices.
Conclusion
In today’s digital world, preventing data leakage is a must for every business. Whether it’s through human error, system failure, or malicious activity, data leakage can incur significant costs, legal ramifications, and irreparable damage to a company’s reputation, in addition to the costs involved to remediate a breach. For data leakage prevention to be effective, businesses need to implement strong encryption, strict access controls, real-time monitoring, and ongoing employee training. Tivazo employs advanced technology and robust policies to make preventing data leakage a seamless and proactive process.
By prioritizing the protection of corporate data, organizations are also protecting their intellectual property and their relationships with their customers, along with compliance issues as they arise in their industry. The goal is not to just respond after a data breach as we do too often, but to create a culture of security first-first – that stops leaks before they begin.