What are Financial Incentives?
Financial incentives use money-based rewards to encourage people to work harder, stay engaged, or make better decisions.
In other words, Financial incentives refer to monetary compensations provided to people or employees in order to encourage them to follow certain behaviors, enhance performance, or attain desired results. They operate with direct financial reward in exchange for accomplishing tasks, meeting targets, or showing the desired behaviors.
What are the Different Types of Incentives?
There are various types of financial incentives that are aimed at motivating employees to enhance productivity and help the organization achieve its objectives. All these types of incentives are beneficial to businesses in that they enable businesses to customize their compensation strategies and improve overall performance.
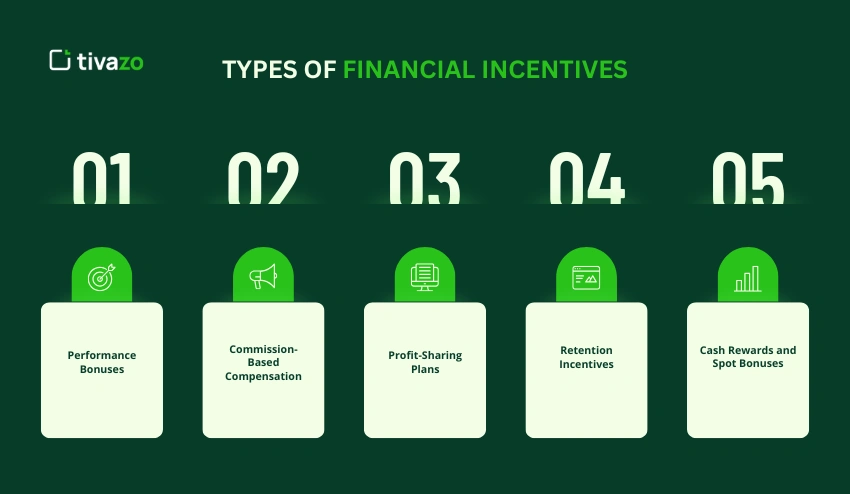
1. Performance Bonuses
One of the most commonly used financial incentives is performance bonuses, which are given to employees who either match or exceed certain performance goals. These goals can be either productivity, quality of work, customer satisfaction, or individual accomplishments. Since the rewards are tied to quantifiable outcomes, employees will be motivated to achieve greater performance.
Performance bonuses help companies to reinstate the desirable behaviors and emphasize the worth of quality work. This kind of incentive pay establishes a direct relationship between effort and reward, and the employees know how their efforts contribute to the overall performance.
2. Commission-Based Compensation
The commission-based compensation is a payment system that rewards employees (those working in sales) according to the amount of revenue or transactions they generate. This system is an effective financial incentives mechanism since the greater the number of employees who make sales, the greater the income they receive. It promotes perseverance, planning, and building rapport with customers.
Commission-based pay is good as it enhances the level of engagement and aligns the employees with the goals of the company in relation to revenue. Commissions, being one of the most effective variable pay structures, bring forth clarity in the earning potential and assist the companies in retaining the top-performing sales talent.
3. Profit-Sharing Plans
The profit-sharing plans involve the employees of an organization sharing a part of the profit generated by the organization, and this makes them have a personal interest in the success of the organization. Such a monetary reward motivates the staff to act as a team, make cost-efficient decisions, and contribute to long-term development. Workers are more attached to the performance of the business since the level of individual payout depends on the overall performance of the business.
Profit-sharing is a frequent method of increasing loyalty, enhancing team spirit, and retaining employees by employers. Employees will be more encouraged to remain committed and ensure that their productivity is high when they realize the rewards of their combined efforts.
4. Retention Incentives
Retention incentives refer to monetary compensations that are used to retain good employees in the organization. They can be stay bonuses, milestone rewards, or long service payouts. The incentives can be used to minimize the turnover expenses and safeguard the knowledge within the institution.
To the employees, retention incentives are a source of financial stability, and they reward long-term commitment. Such economic incentives are particularly applicable during the time of organizational change, mergers, or when an organization intends to retain some of its top performers.
5. Cash Rewards and Spot Bonuses
Spot bonuses and cash rewards are immediate and short-term monetary compensation awarded due to a particular performance, like outstanding performance, innovation, or problem-solving. They are able to offer immediate rewards and strengthen positive behavior in real-time.
These incentives are frequently employed to sustain motivation on a year-round basis, as opposed to having a year-end bonus period. Spot bonuses, as an adaptable type of reward system in the workplace, can serve to promote the ethos of appreciation and make the employees feel appreciated due to their continued efforts.
Importance of Financial Incentives
Monetary rewards are important in motivating employees, enhancing productivity, and making organizations successful. Providing financial incentives based on performance will help companies to focus the effort of the employees on the objectives of the business, as well as to create engagement and loyalty.

1. Boosts Employee Motivation
Financial incentives are a good financial motivating tool that can make employees do their best. Employees will tend to remain engaged, become proactive, and aim at excellence in their work when they recognize an apparent relationship between effort and reward.
2. Enhances Productivity
The provision of performance bonuses, commissions, or profit-sharing plans directly has an effect on productivity. These incentive compensation plans make employees strive towards the attainment of quantifiable objectives, leading to increased efficiency and overall organizational performance.
3. Improves Employee Retention
Stay bonuses or long-term rewards are retention incentives that are used to reduce turnover by retaining the best talent in the organization. These economic incentives show that organizations value loyalty, and they develop a feeling of security, which motivates employees to be loyal.
4. Aligns Employee and Organizational Goals
Monetary rewards such as profit sharing or commission-based plans streamline the efforts of the employees in line with the goals of the company. This reward system in the workplace makes sure that workers are not only motivated to work so that they can make a profit, but also helps the organization to succeed, and that the people work together and make strategic decisions.
5. Encourages Skill Development and Innovation
The motivational tools, such as spot bonuses or cash rewards for outstanding contributions, motivate employees to acquire new skills, become proactive and creative. Such financial incentives will support a culture of constant improvement and innovation at the workplace.
Why do Countries Provide Financial Incentives?
The financial incentives offered by countries are aimed at boosting economic growth, promoting investments, and encouraging certain behavior of enterprises and individuals. These economic incentives may be in the form of tax breaks, grants, or subsidies that spur innovation, job creation, and sustainable development. Through these monetary rewards, the governments encourage businesses to increase operations, to embrace new technologies, and to contribute to the national productivity, as well as to fund industries that are essential for long-term economic stability.
What are Non-Financial Incentives?
Non-financial incentives are the rewards or motivators that are not directly related to monetary compensation but are aimed at inspiring employees to become engaged, enhance their performance, and become more satisfied. Such incentives are based on recognition, personal development, and a favorable work environment instead of monetary gains.
Non-financial rewards supplement financial incentives in the sense that they serve the psychological and emotional needs of employees, give them more job satisfaction, and retain them in the long term without raising the direct payroll expenses.
Difference between Financial and Non-financial Incentives
| Aspect | Financial Incentives | Non-Financial Incentives |
| Definition | Non-monetary rewards are designed to encourage engagement, satisfaction, and loyalty. | Bonuses, commissions, profit-sharing, retention bonuses, and cash rewards. |
| Examples | Recognition, career growth opportunities, flexible working hours, skill development, and awards. | Recognition, career growth opportunities, flexible working hours, skill development, awards. |
| Purpose | Directly motivates employees by providing tangible financial benefits. | Indirectly motivates employees through recognition, personal growth, and job satisfaction. |
| Impact on Performance | Drives measurable improvements in productivity, sales, and goal achievement. | Enhances morale, loyalty, engagement, and long-term retention. |
| Cost to Organization | Often involves direct payroll or budgetary expenditure. | Usually low-cost or resource-based, not requiring direct financial outlay. |
| Timeframe of Effect | Immediate or short-term motivation with direct results. | Long-term impact on employee satisfaction and organizational culture. |
| Employee Perception | Viewed as a reward for achieving specific targets. | Seen as appreciation, support, or recognition of effort and contribution. |
What are the Nonfinancial Incentives to Motivate Employees?
Common nonfinancial incentives include:
- Recognition and Appreciation: Public acknowledgment, awards, or verbal praise for achievements fosters a sense of accomplishment and boosts morale.
- Career Development Opportunities: Training programs, mentorship, and promotions encourage skill growth and long-term engagement.
- Flexible Work Arrangements: Options like remote work, flexible hours, or compressed workweeks support work-life balance and improve satisfaction.
- Job Enrichment and Responsibility: Providing employees with challenging tasks, autonomy, or leadership opportunities increases motivation and commitment.
- Workplace Culture and Environment: A supportive, collaborative, and positive work culture enhances loyalty and productivity.
- Non-Monetary Benefits: Perks like extra leave, wellness programs, or access to learning resources act as additional motivators.
By combining nonfinancial incentives with financial motivation, organizations can create a holistic approach that drives productivity, retains top talent, and fosters a motivated workforce.
What are the ethics of financial incentives?
The moral of the monetary reward is to make sure that the financial incentives are employed in an equitable, open, and sustainable manner to inspire the workers or influence their behavior without causing any harm or encouraging unethical behavior. Although monetary rewards may stimulate productivity and performance, they should be well considered so as not to encourage unhealthy competition, manipulation, and short-term thinking that can destroy organizational integrity.
Key ethical considerations include:
- Fairness: Rewards should be distributed equitably, based on clear, measurable criteria, to prevent favoritism or discrimination.
- Transparency: Employees should clearly understand how incentives are earned, ensuring trust in the system.
- Avoiding Harmful Behavior: Incentive schemes should not encourage cutting corners, misreporting results, or unethical decision-making.
- Sustainability: Incentives should balance short-term performance with long-term organizational goals and employee well-being.
Financial incentives, when used ethically, are a form of responsible tool in monetary motivation that increases productivity, engagement, and retention rates without compromising integrity and trust in the workplace.
Tivazo’s Role in Rewarding and Motivating Employees Effectively
Tivazo is more of a time-tracking/productivity monitoring software, which accommodates remote and hybrid teams, including real-time monitoring capabilities, task monitoring, and analysis dashboards. Although it cannot be considered a complete employee incentive platform, its transparency and productivity data could help organizations to tie measurable performance to rewards and recognition.
Tivazo can be used to identify high performers and trace productivity trends by helping managers see activity by employees, project progress, and goal alignment, which can be used to apply financial incentives (such as bonuses) and non-financial incentives (such as recognition or skill development opportunities) more data-driven and effectively.
Conclusion
Financial and non-financial rewards are very instrumental in motivating employees, increasing their productivity, and organizational success. With a well-planned amalgamation of monetary and non-monetary rewards, such as bonuses, commissions, and profit sharing, with non-monetary ones such as recognition, career advancement, and work-life arrangements, companies can develop a well-balanced and efficient system of rewards. It is also complemented by such tools as Tivazo, which give managers an insight into data that will assist in identifying high performers and aligning incentives with performance. These incentive strategies, when applied ethically and strategically positively influence engagement and retention, as well as a good workplace environment that contributes to long-term development and organizational excellence.




