Employee turnover is not an HR measure, but it is the pulse of your work environment. The departure of personnel affects productivity, morale, and your bottom line.
Not every turnover is equal. Knowing the different types of employee turnover, you discover some very useful information about why employees leave and what you can do to keep the good ones. There are healthy exits, and there are exits that point to more underlying issues that need urgent handling.
In this competitive employment market, companies cannot afford not to pay attention to turnover patterns. Voluntary and involuntary turnover, functional, dysfunctional, avoidable, and unavoidable turnover are all different stories. Such differences can be explored to assist leaders in improving employee retention policies, lowering recruitment expenses, and creating healthier work environments. What then are the different types of employee turnover, and how can these be used to determine your organization’s future? Let’s dive in.
Different Types Of Employee Turnover To Know
The first step to better retention and workplace culture is understanding the different types of employee turnover. All types display different causes, outcomes, and approaches to managing workforce issues.
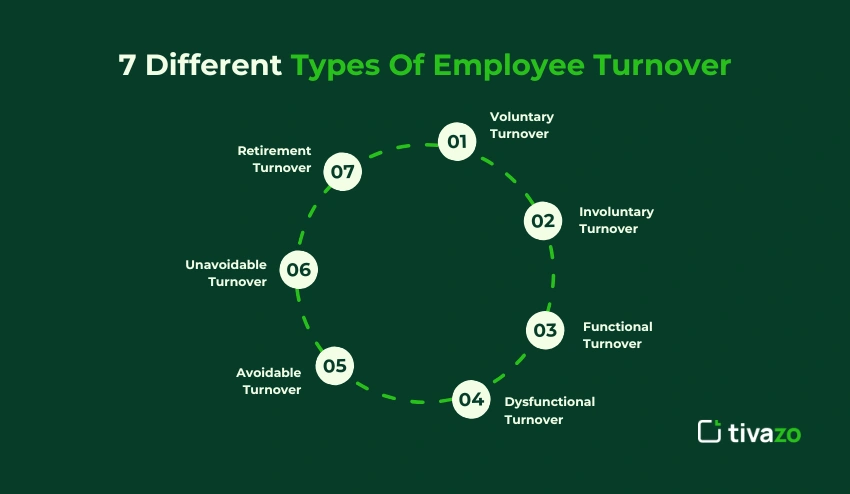
1. Voluntary Turnover
Voluntary turnover is when an employee willingly decides to quit a company. This types of employee turnover is usually a result of improved opportunities, dissatisfaction with management, or lack of career advancement. It is the most widespread and most often talked about type of turnover.
The problem with voluntary turnover is that, in most cases, high performers are the ones who are involved, making it expensive. Gallup says that with the right retention strategies, a big percentage of voluntary turnover can be avoided. Organizations can minimize this type of employee turnover through the improvement of job satisfaction and recognition.
For HR, tracking voluntary turnover trends can highlight gaps in leadership, compensation, or culture. Companies that focus on employee engagement and development programs are more likely to lower this type of employee turnover.
👉Related: 10 Proven Ways to Boost Job Satisfaction at Work
2. Involuntary Turnover
Involuntary turnover occurs when the employer takes the initiative to separate, and in most cases, the separation is based on performance or organizational restructuring. These types of employee turnover are necessary at times, but may affect morale.
Although involuntary turnover can eliminate non-performers, it is a cause of instability when it occurs at a high rate. Companies that reorganize too frequently can ruin their image as an employer. This types of employee turnover is critical to handle with caution to ensure trust.
The negative impact of involuntary turnover can be mitigated with the assistance of clear performance management systems and open communication. Organizations can safeguard their brand and workplace culture by managing this kind of employee turnover in a fair manner.
3. Functional Turnover
The functional turnover will occur when the poor performers leave the company and create healthier team dynamics. These types of employee turnover may be advantageous in that they enable organizations to attract more talent.
According to many HR experts, functional turnover is not necessarily a bad thing. Properly handled, this type of employee turnover may increase productivity and performance in general.
The trick is to make sure that functional turnover does not create skill gaps that are critical. This kind of employee turnover can be used as a competitive advantage through strategic hiring and training programs.
4. Dysfunctional Turnover
The opposite of functional turnover is dysfunctional turnover, which occurs when the best performers quit. This type of employee turnover is harmful to organizations in that it affects productivity, knowledge, and client relationships.
High levels of dysfunctional turnover often reveal deeper issues like poor leadership, lack of recognition, or limited growth opportunities. This types of employee turnover need specific retention strategies to prevent.
Dysfunctional turnover can be reduced by companies that invest in competitive pay, career growth, and a healthy workplace culture. Retention of key talent is among the best methods of managing this type of employee turnover.
5. Avoidable Turnover
Avoidable turnover is a type of employee turnover that happens due to reasons that the employer could have avoided. This type of employee turnover highlights internal issues like weak leadership or unfair pay.
To combat preventable turnover, exit interviews and feedback must be analyzed. Companies can minimize these types of employee turnover by recognizing trends.
Employees will feel appreciated when HR and the leadership take action on the feedback, and they will not want to go. This kind of employee turnover can be reduced through proactive changes.
6. Unavoidable Turnover
Inevitable turnover occurs when the employee quits because of factors that are outside the company, like transfer, sickness, or retirement. This kind of turnover cannot be completely eliminated.
Although inevitable, succession planning and workforce forecasting will help companies plan for it. Organizations minimize the impact of such employee turnover by planning.
This is not aimed at stopping unavoidable turnover but rather predicting it. An effective plan will make sure that these types of employee turnover do not bring down operations.
This way, HR leaders and managers can make evidence-based decisions to reduce risk by understanding the nature of employee turnover. We are going to discuss the key categories and their impact on organizations.
7. Retirement Turnover
Retirement turnover is when workers leave the workforce because of age or intentionally retire. This types of employee turnover is foreseeable, but it may cause serious knowledge gaps in key positions.
The development of succession plans and mentoring programs can help organizations maintain institutional knowledge by transferring it through retirement turnover. Industry research indicates that planning retirement turnover early minimizes operational disruption by 30% percent.

Retirement turnover is also a good place to promote internal talent and refresh teams with new skills, so it is a good strategic workforce planning point.
Avoidable and Unavoidable Turnover
In the larger range of categories of employee turnover, functional and dysfunctional turnover demonstrate how the exit of employees may affect organizational health differently. Functional turnover is a good thing- it is a turnover that happens due to poor-performing employees leaving and giving way to more talented and high-performing employees in the team. Even strategic HR policies can take advantage of these types of employee turnover to increase team efficiency and productivity in general.
On the contrary, dysfunctional turnover is harmful. The loss of skilled and effective employees or key professionals may contribute to knowledge gaps, project delays, and decreased team morale. These types of employee turnover can be a warning that there is a leadership problem, that there is a lack of engagement, or that there is a lack of development. Monitoring these exits would allow companies to use retention measures to retain the best talent so that the best employees are not lost to other companies.
Functional vs Dysfunctional Turnover
The other important difference between types of employee turnover is between dysfunctional and functional turnover. Functional turnover happens when poorly performing employees exit the company, and this can be positive as it enhances the overall performance of the team. These types of employee turnover can even be utilized tactically to allow companies to replace underperformers with more skilled talent.
On the contrary, dysfunctional turnover occurs when employees who are performing well or of great importance quit. Such employee turnover is not only expensive and harmful, but also may decrease productivity, knowledge base, and morale. Dysfunctional turnover can be avoided by organizations targeting employee engagement, recognition, and career development programs.
Knowing the distinction between dysfunctional and functional turnover enables companies to focus on retention, save money, and retain the best employees.
👉Related: 9 Powerful Strategies for Employee Development Program
Voluntary vs Involuntary Turnover
The other method of classifying the types of employee turnover is based on whether the turnover is employee turnover or employer turnover. Voluntary turnover occurs when employees resign on their own free will and usually due to factors such as career advancement, workplace culture, or even a more favorable remuneration elsewhere. Trends in voluntary turnover can help understand how satisfied employees are, and where an organization must focus on better engagement and retention strategies.
Involuntary turnover is a situation where the employer terminates the employment relationship because of performance-related problems, misbehavior, or reorganization. Although it is occasionally required, high rates of involuntary turnover can lead to instability, impact morale, and negatively influence the employer brand of an organization. The ability to distinguish between these two categories of employee turnover enables businesses to introduce specific solutions that will either prevent unnecessary turnover or separate unavoidable exits in a more efficient way.
Putting It All Together: Table of Turnover Types
| Turnover Type | Definition & Context | Strategic Insight |
| Voluntary | Employee resigns willingly | Focus on job satisfaction, engagement, compensation |
| Involuntary | Employer initiates separation | Review performance management and restructuring practices |
| Functional | Departure of low performers | Often healthy—ensure replacement hires add value |
| Dysfunctional | Exit of high performers | High risk—prioritize retention efforts, surveying |
| Internal Transfer | Employee moves within company | Can signal both mobility and pain points in originating team |
| External Departure | Employee leaves organization entirely | Kitchen-sink category—analyze root causes |
| Avoidable | Due to fixable internal factors | Low-hanging fruit for HR strategy |
| Unavoidable | Driven by uncontrollable external factors | Plan succession and anticipate these exits |
| Retirement | End of career | Plan succession pipelines |
Data Speaks: How Much Does Turnover Cost?
- Replacement of an employee could be between 30% to 200% of the annual employee salary, including recruiting, training, lost productivity, and damaged morale.
- These costs can only be increased by low morale, where studies have shown that it can be up to 30%-400% percent of salary, and due to disengagement, it can cost the organization a staggering 350 billion in lost productivity each year.
- According to Gallup, 42% percent of voluntary turnover can be avoided, most commonly related to recognition and compensation problems.
- IKEA and other companies have cut turnover rates in the UK by 41% to 27% percent by increasing wages, introducing buddy systems, and offering flexible working hours.
- Summer turnover peaks in fields like hospitality and education, especially among young, low-wage (less than 10K-30K/hour) part-time employees, where almost 7% percent leave the industry in summer.
Reducing Employee Turnover: How Tivazo Empowers Organizations
With Tivazo, organizations can address one of the most pressing HR issues, high employee turnover, through actionable insights and solutions that are specific to each workplace.
By conducting employee engagement surveys, receiving feedback, and tracking employee performance, Tivazo identifies areas in which employees experience a lack of engagement or feel undermined. Companies can then take targeted action to minimise unwarranted turnover and keep the best talent in the company by initiating career development, recognition, and personalized learning tracks.
Furthermore, Tivazo also simplifies workforce planning, succession, and onboarding, which means that key positions will be occupied in an efficient manner and expertise will be preserved. With the help of evidence-based information and business-focused HR solutions, Tivazo will help organizations reduce the rates of employee turnover, promote workplace satisfaction, and improve retention over the long term.
Conclusion
Knowledge of employee turnover will enable organizations to understand the reasons behind employee turnover and implement measures to retain talent. Voluntary and involuntary exits, functional and dysfunctional, avoidable and unavoidable, retirement turnover; all types of employee turnover provide practical lessons to enhance interest and output. Tivazo is one of the tools that allows businesses to monitor trends, solve problems, and introduce specific retention efforts, which will keep the most important positions vacant and keep knowledge safe. With these strategies in mind, businesses can lower operating expenses, increase morale, and develop a more powerful and tougher workforce.




