Have you ever thought about how much you lose in productivity when you are caught up in unforeseen work gaps? The time during which employees, machines, or resources are idle and yet to be utilized may quietly gnaw productivity and raise the costs of operation. Idleness in the workplace, be it due to waiting to get approvals or machine failures, workflow delays, or absence of work, has a greater effect on performance than most leaders think.
In this blog, we will deconstruct what idle time is, why it occurs, and the usual causes of employee idle time that businesses have to deal with on a daily basis. You will get to know what kind of employee idle time is, the actual effect of idle time on productivity, the practical means of reducing idle time, and how to calculate idle time using the idle time formula. We will also discuss idle time/downtime and provide actual examples of idle time and how you can reduce the idle time efficiently with the help of modern tools, such as Tivazo.
What is an Idle Time?
Idle time refers to the time during which employees, machines, or other resopreventive maintenance urces are present, yet they are not productive. It may occur in any workplace, office, factory, or service setting, whenever the workflow is broken.
What is an Employee Idle Time?
Idle time for employees is the time when employees are free to work yet are not occupied with productive activities. This may occur because of waiting to be given instructions, awaiting approvals, unavailability of materials, unresponsive workflow systems, or unresponsive workflow processes. As much as a break is acceptable, too much idleness will lower the total output of an organization and lead to higher operational expenses.
What are the Causes of Employee Idle Time

Idle time occurs when employees, machines, or resources are available but not actively performing tasks, and it can significantly affect productivity and operational efficiency. Understanding the causes of idle time is the first step toward reducing it. Common causes include:
- Waiting for Materials or Information: Employees may be idle while waiting for raw materials, approvals, or instructions.
- Machine or System Downtime: Technical failures, maintenance, or software glitches can halt workflow, leading to idle time in production.
- Poor Workflow or Task Allocation: Inefficient scheduling or unclear responsibilities often leave staff unoccupied.
- Lack of Training or Skills: Employees unable to complete tasks efficiently may spend time idly.
- External Factors: Delays from suppliers, clients, or dependencies in the supply chain can create unplanned idle time.
By identifying these causes, businesses can implement solutions to reduce idle time, improve efficiency, and increase overall productivity.
Benefits of Tracking Employee Idle Time
Idle time is one of the most important aspects that should be tracked by any organization that intends to maximize productivity and minimize operational costs. By keeping track of the unoccupancy of employees, machines, or resources, businesses will be able to detect workflow inefficiencies, unrecognized bottlenecks, and employ measures to ensure maximum efficiency. Knowledge of employee idle time and idle time in production not only enhances output, but it will helps in decision-making and workforce management.

1. Improves Overall Productivity
Following the idle time enables managers to establish the time when staff or machinery are not fully exploited. By eliminating these time-wasting activities, the teams are able to be more concentrated on the activities that create value, which is a direct increase in the efficiency of the workplace.
Employees can engage in more productive activities when downtimes are reduced, resulting in increased levels of output. This will help to make sure that the idle time of the employees does not have an adverse impact on the overall organizational performance.
2. Reduces Operational Costs
Unmonitored idle time may silently add costs either through unutilized labor hours or machine time. Through the data on idle time, companies are able to identify those areas where resources are not being utilized fully and redistribute them efficiently to eliminate unnecessary expenses.
Attention to time wastage at the workplace will aid in better scheduling and workflow, as well as giving attention to whether the employees and machinery are working effectively. This would lead to high savings in the long run and a high payback.
3. Enhances Workflow Management
Monitoring time wastage can be used to identify where the production or business process has bottlenecks and inefficiencies. Managers are able to make changes in the workflow, reallocate tasks, or automate them to minimize the delays and increase the overall rate of accomplishing the tasks.
The idle time monitoring tools are also useful in the future planning of projects. Organizations can understand the activities that are wasting time when they do not need them, and can more intelligently distribute resources.
4. Supports Employee Performance Evaluation
The idle time of the employees is useful information in the performance review. The managers will be able to differentiate between the inevitable downtime and inefficiencies, thus being able to more fairly judge the staff productivity.
The knowledge about the forms of idle time allows companies to offer specific training or assistance to those employees who fail to cope with workflow issues. This fosters the culture of responsibility and constant growth.
5. Improves Customer Satisfaction
The time wasted is minimized, making sure that tasks are done at the right time, and this aspect has a positive influence on the customer service and delivery schedules. Customers become happier with products or services because it takes less time to complete them, and the operations are more efficient.
The monitoring of idle time among production or service organizations also enables companies to react quickly to lag time, thus maintaining uniform quality and dependability. In the long run, this enhances customer loyalty and trust.
Tracing idle time, businesses are able to detect inefficiencies and introduce effective solutions to increase productivity and cost reduction. Frequent observation will make sure that the resources and employees are used in the best way possible, which will enhance performance in the workplace.
Types of Employee Idle Time
Knowledge of the kind of idle time of employees is critical to enhancing productivity and decreasing inefficiencies in operations. Idle time is not all equal, and the classification of the idle time assists managers in adopting specific strategies aimed at reducing the unproductive time. Generally, idle time by employees is categorized into the following:
1. Planned Idle Time
This is done when the employees are deliberately idle, like during planned vacations, training, or a change of shift. Although idle time is required to rest and enhance skills, there is a need to check it so that it does not become too much.
2. Unplanned Idle Time
This occurs without planning because of the workflow delays, waiting for material, machine, or waiting for approvals. Spontaneous downtime is usually the most expensive since it interferes with production and efficiency.
3. Employee-Caused Idle Time
In other cases, human factors can lead to idle time, such as poor work habits, inability to focus, or skills deficiency. The recognition of this type enables managers to offer training, improved allocation of tasks, or support of the workflow.
4. External Idle Time
The cause of this type is not in the control of the organization, but it occurs due to delays by suppliers, client approvals, or external dependencies. Monitoring of external idle time assists in planning and risk reduction.
When these forms of idle time are identified, companies can take the right measures to minimize idle time among the employees, enhance the efficiency of the workflow, and make sure that human and machine resources are optimally utilized.
Ways to Reduce Employee Idle Time
Minimizing idle time is essential in enhancing productivity, decreasing operational expenses in an organization, and ensuring that the workflow is smooth. With the need to deal with the factors that lead to idle time and the adoption of workable measures, businesses can always keep the employees and machines at the maximum level of productivity. The best methods of eliminating idle time are as follows:
1. Optimize Workflow and Task Allocation
Optimizing workflow is one of the best methods used to minimize idle time. Having well-thought-out schedules, tasks, and workloads will mean that the employees will never have nothing to do. This reduces unplanned downtime and enhances efficiency.
Workflow management tools may be used to allow managers to monitor the idle time of employees and find out the bottlenecks, which enable the smarter distribution of tasks. This also helps in eliminating delays brought about by confusion or overlapping of tasks.
2. Implement Employee Training and Skill Development
Idle time is usually the time when employees are not able to work effectively due to a lack of skills or knowledge to do it. Training programs help in ensuring that the staff know how to deal with several responsibilities and minimize the unproductive waiting time.
Constant skill training also offers employees the capability to operate without depending on their supervisors or co-workers. It is possible to measure increases in productivity by monitoring the idle time of employees after training.
3. Use Technology and Automation
The incorporation of technology and automation in the business processes would help to greatly reduce idle time. Automated systems also deal with routine jobs, minimise manual errors, and enable employees to work on high-value jobs.
Project management software, real-time monitoring systems, and automated alerts are tools that can be used to monitor idle time in production or employee workflows so that managers can take corrective measures instantly.
4. Improve Communication and Collaboration
Idle time is also caused by delays caused by a lack of communication or a lack of clarity in instructions. The use of regular team meetings, instant messaging tools, and well-defined reporting structures promotes being informed amongst employees and also minimizes waiting time.
Through teamwork, the groups will be able to predict the disruption of the workflow and react promptly, reducing the planned and unplanned idle time.
5. Monitor and Analyze Idle Time Regularly
Monitoring idle time using the data-driven tools can enable organizations to notice the repetitive trends and solve the root causes. The breakdown of such metrics as the time spent idle, frequency, and idle time source gives a quantifiable insight into the ways to improve.
Monitoring on a regular basis makes sure that processes are always optimized to minimize wastage and enhance efficiency. The idle time reports can also inform decision-making and strategic planning of the workforce management.
Through these, the businesses are able to minimize the wasted time, increase the productivity of the employees, and streamline their businesses. This is done by regular monitoring and process improvements to make sure that resources, including human and machine, are completely maximized to ensure the best use of resources.
Examples of Idle Time
The knowledge of real-life situations involving idle time can enable the organization to determine where there is inefficiency and use the knowledge to change inefficient activities into productive ones. Idle time may not be conspicuous, but it silently affects production, raises expenses, and slows operations. The following are the typical examples:
1. System or Machine Downtime
Failure of technical reasons, software malfunction, or machine maintenance may stop the process, and this will mean that the employees are idle or the production is at a standstill. As an example, when a printer or packaging machine malfunctions, employees cannot carry on with their work until the problem has been fixed.
Observation of idle time at the workplace as a result of technical failures assists in prioritizing preventive maintenance and has the effect of not letting the machine that is most important be out of commission.
2. Approval or Decision Delays
Delays in work are frequent since staff members are waiting to get approvals from their supervisors or managers. As an example, a design team can complete a project, but will be unable to do anything until a client or senior manager reviews and approves it.
Monitoring such delays enables companies to simplify the approval procedures and to minimize the bottlenecks and transform the unproductive idle time into active working time.
3. Lack of Clear Tasks or Instructions
When tasks are not clear or instructions are not complete, then the employees can get idle. Indicatively, newly recruited staff members may be doing nothing pending a time when they can be instructed on their duties.
By giving clear workflows, task lists, and training, it reduces dead time for the employees, and all employees are involved effectively towards organizational objectives.
4. External Dependencies
In other cases, unproductive time may be brought about by external forces that are not within the organization, like delays by suppliers, customer response, or shipment complications. As an example, employees at the warehouse can be waiting around, awaiting a late delivery from a supplier.
The study of idle time patterns under external dependencies assists businesses in planning contingencies and minimizing the disruption of workflow.
Identifying such instances of waste time, companies can take specific measures to reduce the time of unproductive work. The recognition and resolution of such situations are useful in enhancing productivity, reducing expenses, and ensuring that work processes operate efficiently.
Idle Time Formula
Idle Time (IT) = Available Time (AT) – Productive Time (PT)
Where:
- Available Time (AT): Total time an employee, machine, or resource is available for work
- Productive Time (PT): Time actually spent performing productive tasks
Percentage of Idle Time:
Idle Time (%) = (Idle Time ÷ Available Time) × 100
Example:
- Available Time (AT) = 8 hours (480 minutes)
- Productive Time (PT) = 6 hours (360 minutes)
Calculation:
- Idle Time (IT) = 480 – 360 = 120 minutes
- Idle Time (%) = (120 ÷ 480) × 100 = 25%
Interpretation:
This means the employee spent 25% of their available time idle.
Idle Time vs. Downtime
| Feature | Idle Time | Downtime |
| Definition | Period when employees, machines, or resources are available but not performing productive tasks. | Period when machines or systems are completely unavailable due to breakdowns, maintenance, or external factors. |
| Cause | Workflow delays, waiting for approvals, lack of tasks, or employee inefficiency. | Equipment failure, technical issues, maintenance, or external disruptions. |
| Impact on Productivity | Reduces efficiency but work can resume immediately once tasks are available. | Stops operations entirely; productivity cannot continue until the issue is resolved. |
| Planned vs. Unplanned | Can be both planned (breaks, training) and unplanned. | Mostly unplanned, though some scheduled maintenance is planned downtime. |
| Management Approach | Optimize workflow, allocate tasks efficiently, track employee idle time. | Preventive maintenance, rapid repair, and contingency planning. |
| Example | Employee waiting for materials or instructions. | Machine breakdown halting production for 2 hours. |
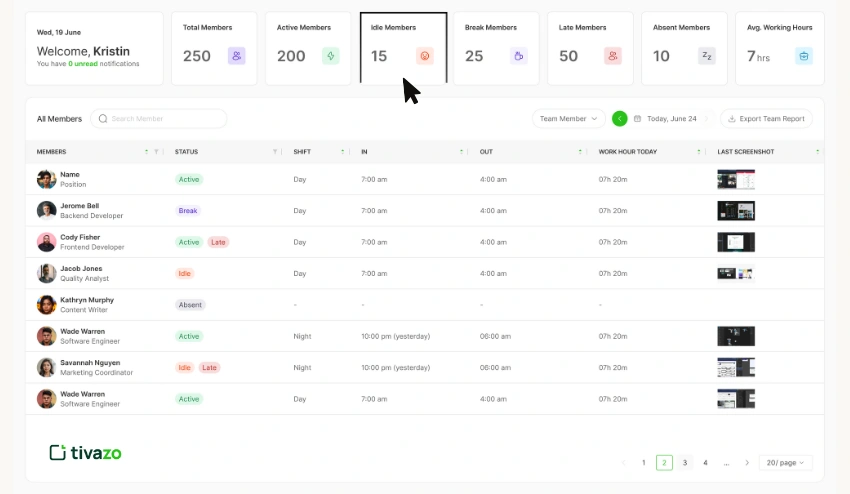
How can Tivazo help you reduce Employee Idle time?
Tivazo assists companies and workers in optimizing their idle time by offering automatic time tracking, real-time tracking, and comprehensive productivity reports. The platform identifies the time of inactivity and captures it, and notifies the managers the employees, and teams can easily identify the unproductive gaps promptly. Tivazo helps managers to streamline the workflow, reallocate tasks, and reduce wastage of time by employees through idle time and the manner in which tasks are accomplished, and by eliminating time wastage due to waiting to receive materials, approvals, or a lack of clear instructions.
Besides that, Tivazo maximizes accountability with team dashboards, role-based insights, and optional screenshots to allow employees to be conscious of their work habits and trust and privacy. Both remote and on-site teams have these features, which guarantee the complete use of human and machine resources. Tivazo, through the analysis of idle times and offering actionable information, will enable organizations to cut wasted time and increase productivity and efficiency.
Conclusion
The management as well as the minimization of idle time is essential in enhancing productivity in the workplace, reducing the cost of operations, and also maximizing employee and machine productivity. Through the knowledge of the various forms of idle time, the causes of idle time, and the various strategies of reducing idle time, i.e., workflow optimization, training, automation, and monitoring tools like Tivazo, businesses can reduce the idle time and increase their overall performance.
Monitoring idle time in the production process regularly and applying the actionable information on idle time reports helps to facilitate the operations, accelerate the completion of tasks, and enhance the productivity of the employees. Finally, the active management of idle time improves efficiency as well as enhances customer satisfaction, lowers downtime, and builds a more responsible and result-oriented work environment.