Full Time Equivalent (FTE) is a concept that a business, HR manager or anyone dealing with workforce planning or budgeting should understand. FTE gives you a clear view of the amount of work being done in relation to full-time workers whether you are determining staffing requirements, cost allocation, or productivity.
The fact that FTE is not headcount or relevant to HR is a common misunderstanding among many people. As a matter of fact, FTE is a highly flexible measure that is applied in payroll, project management, finance as well as team planning. Knowing how to calculate FTE, organizations and freelancers can make proper decisions regarding staffing, workload, and resource allocation.
In this guide, the Full Time Equivalent concept will be broken down, the reasons why it is important, how to calculate it and how to effectively apply it in various industries and situations. The most frequent mistakes, tools, templates, and tips to be applied in order to manage FTEs correctly will also be discussed.
What is Full Time Equivalent (FTE)?

Full Time Equivalent is a common metric that is utilized to denote the workload of an employee in a manner that can be compared with part-time and full-time employees. Basically, it translates hours that are being worked by several employees into the number of full-time employees.
To illustrate, two employees working 20 hours per week each would amount to a single full-time employee assuming that the normal full-time schedule is 40 hours per week. This method will give a better insight into the capacity of the workforce regardless of the real number of people.
FTE is widely applied in HR to calculate staffing requirements, in finance to distribute costs, and in project management to schedule resources of a team efficiently. FTE is a measure of the real work being done as opposed to headcount which merely enumerates the number of people doing the work.
Example Calculation:
- Normal full time working hours per week: 40.
- Employee A has a workload of 30 hours/week = 30/40= 0.75 FTE.
- Employee B has 20 hours/week, which translates to 20/40 = 0.5 FTE.
- Combined FTE = 0.75 + 0.5 = 1.25 FTE
Why Full Time Equivalent is Important
FTE is a standardized method of measuring and managing the workforce resources. It assists organizations to know the extent to which work is actually being done irrespective of whether employees are full-time, part-time or working on a flexible schedule.
In the case of businesses, FTE is essential in workforce planning and budgeting. Managers can use the number of hours worked to translate it into full-time equivalent and thus allocate resources more precisely, detect staffing needs, and plan future hiring. It also allows a better control of costs as it relates salaries, benefits, and overheads in relation to the quantity of work being done.
To the employees, Full Time Equivalent provides fairness and transparency. It demystifies workloads, performance expectations and benefits eligibility based on full-time status. FTE calculations can also be used by freelancers and contractors to know how their hours are related to full-time workloads, so that they can plan schedules and pricing.
Example: An organization intending to undertake a new project can discover that the work would require the equivalent of 5 full time workers. With the help of FTE, they will be able to decide whether to employ full-time employees, part-time employees or a combination of contractors to satisfy the demand effectively.
How to Calculate Full Time Equivalent
To compute Full Time Equivalent, one must multiply the number of hours that the employees spent at work by the number of full-time workers. It is a process that assists organizations and freelancers to know the total capacity of the workforce and resource allocation.
Basic Full Time Equivalent Calculation Formula
The simplest formula is:
FTE = Total hours worked ÷ Standard full-time hours
Example:
- Standard full-time schedule: 40 hours/week
- Employee A works 32 hours/week → 32 ÷ 40 = 0.8 FTE
- Employee B works 24 hours/week → 24 ÷ 40 = 0.6 FTE
- Total FTE = 0.8 + 0.6 = 1.4 FTE
Full Time Equivalent for Part-Time Employees
Part-time workers are factored by dividing the hours worked by the full-time norm. This is to make sure that part time employment is well captured in the planning of the workforce.
Example:
- Full-time standard: 40 hours/week
- Employee C works 15 hours/week → 15 ÷ 40 = 0.375 FTE
FTE in Project Management or Team Planning
FTE is applicable in project resource allocation. Assuming that a project will take 200 hours of work and a full-time employee has a workweek of 40 hours/week, then the project will take 5 FTE weeks to finish. This aids managers to budget schedules and allocate duties effectively.
Full Time Equivalent in Different Contexts
FTE is a flexible measure applicable in various spheres of business and project management. Knowing how it is used in other situations would guarantee proper planning and reporting.
1. HR & Payroll
Full Time Equivalent is used in HR to calculate payroll expenses, benefits eligibility, and staffing levels. It makes sure that part-time and full-time employees are recorded on a regular basis. Indicatively, the eligibility of benefits or calculation of overtime is usually based on FTE as opposed to headcount.
2. Project Management
FTE is used by project managers to estimate capacity in a team and allocate resources. Managers can allocate workloads better and create realistic deadlines by putting hours into full-time equivalent. As an example, the availability of a team of 3 FTE allows knowing that a project can be completed on time.
3. Finance & Budgeting
Finance departments use Full Time Equivalent to help them allocate labor costs to departments or projects correctly. FTE offers a standard measure of budgeting, forecasting and cost control. This avoids over or underestimating the cost of labor and that the financial reports are based on the real use of resources.
Example: A department of 10 employees who work different hours may seem to be overstaffed in terms of numbers. The calculation of FTE demonstrates the real full-time working load, which allows to make changes to budgets.
Advantages of Using Full Time Equivalent
There are a number of advantages of using FTE both to organizations, teams and even individual contractors. It standardizes the measurement of workload and enhances the management of workforce.
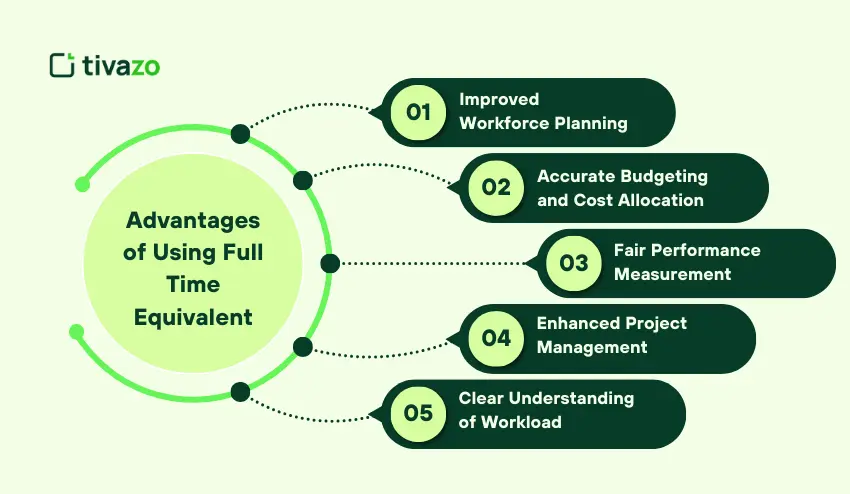
1. Improved Workforce Planning
FTE enables managers to observe the real potential of their team. It assists in finding the gaps in staffing, preventing overstaffing, and making sure that the projects are sufficiently staffed.
2. Accurate Budgeting and Cost Allocation
Translating hours into full-time equivalent enables the finance teams to estimate the allocation of salaries, benefits, and overheads more accurately. This will avoid any surprise labor expenses and help in making financial predictions.
3. Fair Performance Measurement
FTE guarantees that work loads are compared on a constant basis. The proportion of full-time work could be used to assess the fairness of part-time and full-time employees.
4. Enhanced Project Management
With Full Time Equivalent, project managers are able to allocate tasks based on the real capacity, create achievable deadlines, and allocate the resources effectively. This reduces the time wastage and enhances project results.
5. Clear Understanding of Workload
In the case of employees and freelancers, FTE helps to set expectations and balance of workload. It can be used to avoid burnout and it is also able to evenly distribute work among the team.
Common Mistakes in Full Time Equivalent Calculation
Despite having a definite formula, errors in calculating FTE may result in incorrect workforce planning, budgetary errors, and poorly managed projects. Knowing pitfalls to avoid is a way of being accurate.
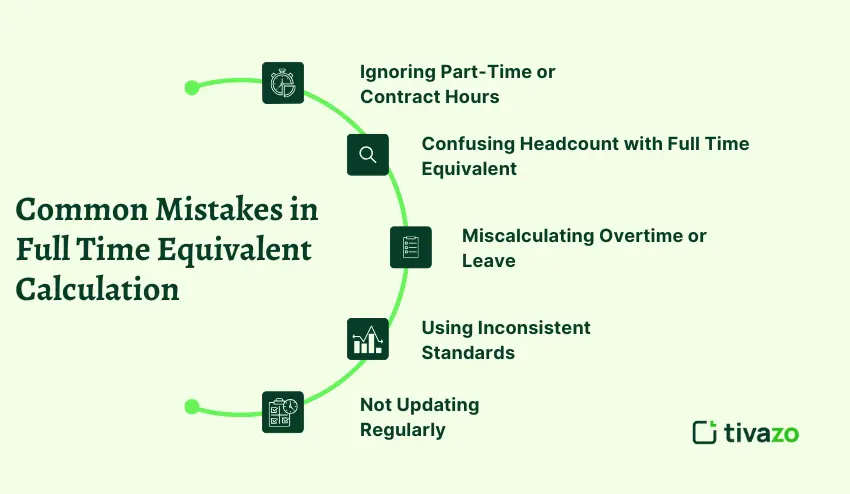
1. Ignoring Part-Time or Contract Hours
Failure to consider part-time or contractor hours may undervalue overall workforce capacity. The number of hours worked by each worker must be transformed into full time equivalent to have a full picture.
2. Confusing Headcount with Full Time Equivalent
The number of employees alone is not an indicator of real work done. Two part-time employees could be equivalent to one FTE, yet headcount would imply two full-time employees.
3. Miscalculating Overtime or Leave
Calculation of FTE can be distorted by not considering overtime, vacation or sick leave. When calculating equivalents, make sure that hours are actual productive work.
4. Using Inconsistent Standards
The number of full-time hours can be determined differently by different organizations (e.g., 35 vs. 40 hours/week). The inability to use similar standards may lead to inaccurate comparisons between teams or departments.
5. Not Updating Regularly
Project requirements, work schedules and staffing change frequently. Obsolete FTEs can be inaccurate in terms of capacity or resource requirements.
Tips to Avoid Errors:
- All working hours, part-time and full-time.
- Equalize full-time hours within the organization.
- Periodically re-calculate FTEs.
- Assumptions and transparency methods in documentation.
Tools & Templates for Full Time Equivalent Calculation
The tools and templates make the FTE calculation easier, minimize mistakes, and enhance the efficiency of the workforce planning. Structured resources can be useful to both businesses and freelancers.
1. Spreadsheet Templates
Excel or Google sheets templates enable you to put in hours worked and calculate FTE automatically. Ready-made formulas can work with a number of employees, part-time work, and overtime. This suits well with small enterprises or freelancers working on their own projects.
2. Payroll and HR Software
The FTE can be calculated automatically by use of software such as ADP, BambooHR or Gusto that can keep track of employee hours and benefits eligibility. These platforms also connect with payrolls and reporting systems hence save time and are accurate.
3. Workforce Planning Tools
Keka, Workday, or Microsoft Power BI dashboards are tools that enable managers to visualize FTE by department and project. They assist in budgeting, forecasting and strategic planning because they indicate real-time staffing capacity.
4. Custom Templates for Projects
Project managers are able to develop FTE templates that can be used to assign hours to team members on certain initiatives. These templates are used to find out if the existing staffing is sufficient to meet the project needs and to detect the gaps at the initial stage.
FTE Benchmarks and Industry Standards
Knowing the common FTE standards assists organizations in contrasting their workforce effectiveness with the industry standards. Benchmarks are different according to sector, role and model of operation.
Industry Examples
- Technology: The average number of FTE per team member is between 0.9 and 1.0, which is a typical full-time schedule with few part-time positions.
- Healthcare: Nurses and support staff have a tendency to have different shifts, and therefore the FTE ratios can be 0.6 to 0.9 based on the schedule and overtime.
- Manufacturing: Shift based jobs may lead to FTE of 0.7 to 1.0 depending on production cycles and seasonal staffing.
- Education: The FTE of teachers can be between 0.5 and 1.0 based on part-time work, adjuncts, or administrative work.
How to Use Benchmarks
Comparing your organization’s FTE ratios with industry standards helps:
- Determine understaffed or overstaffed departments.
- Plan hiring strategies in a better way.
- Match project expectations with workforce capacity.
Conclusion
It is important to understand full time equivalent for businesses, managers, HR professionals, and freelancers who are aspiring to oversee workforce capacity, plan projects, and control budgets. Organizations are able to visualize workforce staffing needs and assignment of resources when they convert hours worked into a standardized equivalent.
When FTE calculations are completed accurately, organizations are able to avoid overstaffing, underestimating workloads and budgeting errors. Calculating FTE provides sufficient information about work effort to formal conversations around fairness both when comparing part-time to full-time employees. Additionally, FTE enables equitable assignment of work across teams. After FTE is reported for staff to HR, finance, or project management, it can continue to be tracked for comprehensive conversations about decision making and overall operational efficiency.