In business, time, money and opportunities are wasted in every delay. Time is one of the factors that keep on reoccurring regardless of what you are doing; be it inventory, shipping goods or planning projects. That’s why so many professionals search for lead time meaning because understanding it can directly improve efficiency and customer satisfaction.
In simple terms, lead time meaning is about the total time it takes to move from the start of a process to its completion. It may be time between issuing a purchase order and delivery of materials, or time between beginning a task and giving the end product. Regardless of the industry, this concept defines the ease of running operations and the effectiveness of teams to fulfill promises.
This guide will break down lead time meaning step by step. We will define it, discuss why it is important, and see how it is used in business in the real world. You will also see examples, ways to compute it and how to minimize it so that when you walk away you know not only what it means but also how to apply it in your personal work to enhance performance.
What is Lead Time?

At its simplest, lead time meaning refers to the total amount of time taken for a process to be completed from start to finish. It does not have to be applied to a single industry or activity, it can be applied to supply chains, manufacturing, project management, software development, and even to personal tasks in everyday life.
For example, in a supply chain, lead time meaning could be the time between ordering raw materials and receiving them at your facility. In project management it may be the time between giving an assignment and finishing it. Although the context varies, the nature is the same: lead time is about the difference between beginning something and completing it.
Why does this matter? Because understanding lead time meaning gives you better control over planning, forecasting, and efficiency. Companies that monitor and minimize lead time can usually reduce costs, eliminate stockouts and deliver products or services more quickly than their rivals. This renders it to be one of the most viable ideas to any individual interested in the running of processes or provision of outcomes.
The Role of Lead Time Meaning to Business Value
Defining lead time meaning is not simply about knowing a definition. It is about understanding how meaning of time noticeably impacts all areas of an operation. A company that shares an ability to effectively track lead time has a greater opportunity to optimize a firm’s business resources; minimize unnecessary costs; and maintain happy customers.
For example, lead time directly impacts inventory decisions in the supply chain. When materials take longer than expected to arrive, it delays production, and puts you behind on your orders. By knowing lead time meaning it allows a company to plan with a more accurate demand and reduces the chance of running out of stock, or having excess stock.
For project managers, lead time influences deadlines and productivity of teams. If your project team has an understanding of lead time meaning, they can develop more accurately project delivery timelines, and allow for smoother workflow. For instance, in the software development space, lead time meaning is often deployed as a signal to indicate when to expect regular releases, and rise in overall user experience.
Even for the customer service aspect of the business, lead time delivers an expectation of overall satisfaction. For instance, clients expect a prompt response to their questions, and timely delivery. By tracking, and eventually, seeking to minimize lead time, companies can uniquely establish trust with clients by separating themselves from competitors.
But, overall, knowing lead time meaning does not need to be optional. Understanding lead time meaning is critical to making timely decisions, reducing waste, and recognizing areas for performance improvements.
Types of Lead Time
Understanding lead time meaning also means knowing that not all lead times are the same. There are various forms based on the context and each one has a specific purpose in planning and operations.

Customer Lead Time
Customer lead time refers to the time that transpires between a customer making an order and getting the product or service. As an illustration, when a client orders a custom product today and it takes five days to arrive then the customer lead time is five days. Monitoring this assists companies to achieve the delivery expectations and enhance customer satisfaction.
Material Lead Time
Material lead time is defined as the duration of time needed to get raw materials after an order has been placed with the suppliers. This is vital to manufacturers because the production can be stalled by a delay in the supply of materials. Understanding lead time meaning in this context helps with inventory planning and reducing production downtime.
Production Lead Time
The lead time of production is the duration in which materials are transformed into finished products. An example is that after raw materials get to a factory, it can take three days to finish manufacturing. This tracking assists companies to simplify operations and determine the operational bottlenecks.
Cumulative Lead Time
Cumulative lead time: This is the time since the beginning of a process until the end of the process including all the sub-processes of ordering materials, production and delivery. This is usually the most important step towards overall efficiency of operation.
Project or Task Lead Time
Lead time in project management or services may also mean the time between the assignment of a task and the completion of the task. Knowledge of this kind of lead time aids teams to create achievable deadlines and to manage workflow better.
Lead Time vs. Cycle Time
Lead time and cycle time are used interchangeably by many people yet they are not identical. Understanding the difference is a key part of grasping lead time meaning.
The lead time is the sum of time required to complete a process. This encompasses active work as well as waiting. To illustrate, when you order raw materials today and the completed product will be received in 10 days, then the lead time will be 10 days, although it may actually take three days to produce.
Cycle time on the other hand, just counts the time that is taken in actively working on the task or the process. The cycle time is the three days production using the same example.
It is important to know the distinction between lead time and cycle time in order to plan, allocate resources and optimize processes. Whereas lead time is concerned with the overall speed of delivery, cycle time assists in determining efficiency in the real work processes. They combine to give a complete image of performance in operations.
How to Calculate Lead Time
Understanding lead time meaning is only useful if you can measure it accurately. Lead Time Calculation is useful in business planning, demand forecasting and efficiency.
The basic formula is simple:
Lead Time = Delivery Date – Request Date
As an illustration, when a customer orders a product on September 1 and the product is delivered on September 10, then the lead time is 9 days.
On more complicated cases, you might like to divide the lead time into phases:
- Material Lead Time: Time between ordering of raw materials and receiving.
- Production Lead Time: The time taken between the beginning of the production and the product.
- Delivery Lead Time: Time between the completion of the product and delivery to the customer.
The sum of these stages gives you the cumulative lead time, which is the process duration.
Pro Tip: Remember to add both active work time and waiting time to the calculation of lead time. Omitting waiting time would provide an unrealistic perception of your process efficiency.
Ways to Reduce Lead Time
Understanding lead time meaning can be useful, but actually improving lead time is where the real gain is. Here are practical ways to cut down on lead time and improve performance:
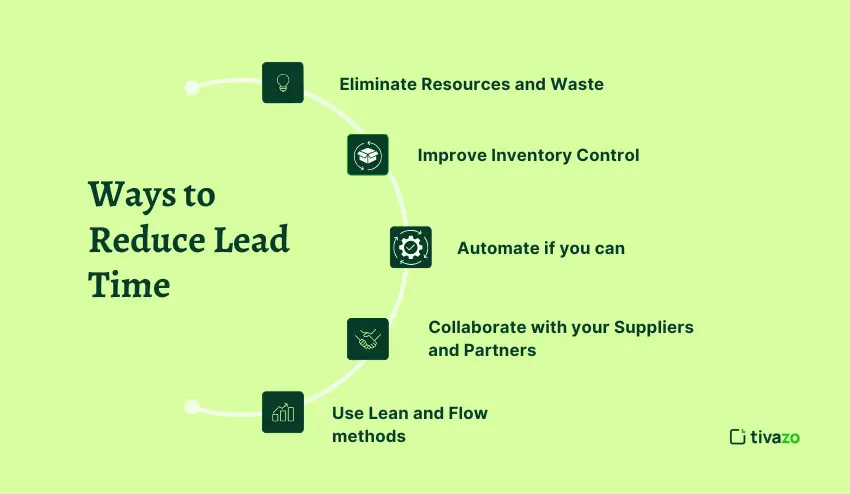
- Eliminate Resources and Waste
Review each step within your processes and eliminate any unnecessary tasks or approvals. This reduction in processes, will allow you to reduce wait times, and decrease overall delivery time.
- Improve Inventory Control
Keep even stock levels of key materials on hand and consider leveraging systems such as just-in-time (JIT) or reorder point systems. Having the appropriate material on hand when you need them will no longer have longer lead time associated with material.
- Automate if you can
Automation can be leveraged to assist in some repetitive task where approvals or data entry is necessary. Lessening the delays, serious delays as well as associated issues of human error. Generally, tools such as the ERP system or workflow software would assist in making these adjustments.
- Collaborate with your Suppliers and Partners
Communicate clearly and have established a good learning relationship with your suppliers or outside partner to ensure that you will have the needed supplies timely. Where possible, share a general forecast and timelines. Many suppliers will have requests for lead times and limited time frames for new orders.
- Use Lean and Flow methods
Identify bottlenecks in your production operation or project workflows, preferably using lean principles or you can follow the Theory of Constraints. When you are able to reduce bottlenecks or constraints internally, this will speed the process up and streamline the workflow.
Once an organization assume or improves people’s perspective of lead time meaning you can reduce lead time, improve operations, and increase customer satisfaction, again bringing the good from lead time meaning to the organization.
Conclusion
Knowing what lead time means is not merely knowing a definition but taking control of the processes, enhancing efficiency and getting better outcomes. Lead time influences planning, resource allocation, and customer satisfaction whether in supply chains, project management, service delivery.
Dividing lead time into types, computing it correctly, and determining which factors influence it, businesses are able to make wise decisions to minimize delays and maximize performance. Practical cases indicate that even minor changes in lead time can affect the operations and customer confidence substantially.
The bottom line is that understanding lead time meaning enables organizations to think smarter, work quicker, and stay ahead of the competitors. You can begin to measure, analyze, and optimize your lead times today to change the way your business works.