Insider threats are one of the cybersecurity risks that can hardly be detected and prevented. As opposed to external attacks, insider threats are perpetrated by people who already possess legitimate access to systems and data in an organization. Insider threats may cause a catastrophic effect, whether in the form of a sloppy employee, a disgruntled staff, a hacked user account, data breaches, reputational damage, monetary loss, or regulatory fines.
The 2024 Ponemon Institute report says that the cost of an insider threat incident has skyrocketed to 15.38 million dollars, and sometimes it takes more than 85 days to contain an insider threat. These statistics make it impossible to deny the importance of a well-developed Insider Threat Program (ITP) that cannot be disregarded by organizations.
What then is the objective of an insider threat program? Fundamentally, an ITP is meant to detect, prevent, and counter risks by trusted individuals within the organization. Nevertheless, its mission is not limited to detection; it is also to secure assets, develop a culture of security, and be legally and ethically compliant.
This blog will discuss the 5 most important objectives of an insider threat program, its types, importance, and give practical tips to help you create or improve one that is better than the industry benchmark.
💡Key Highlights:
- Importance of Insider Threat Program In Your Organization
- Types of Insider Threats
- What is the Goal of an Insider Threat Program?
- Common Signs of Insider Threats
- Five Threat Categories
- Difference Between Insider vs. External Threats
- Use Of Tivazo in the Implementation of the Insider Threat Program?
- Tivazo vs. Other Insider Threat Tools
Importance of an Insider Threat Program In Your Organization
An insider threat program is no longer an option; it has become an essential part of the contemporary cybersecurity strategy. Increasingly damaging and more frequently occurring insider incidents require organizations to take a proactive approach to mitigating risks caused by employees, contractors, and trusted third parties. The goal of an insider threat program is useful to understand in order to enable leaders to align security measures to business continuity, data protection, and compliance goals.
Contrary to the cases of external threats, insiders already have access to sensitive systems and data, which makes their actions more difficult to detect and thus more harmful. An effective insider threat program will assist in detecting risky behaviors at the initial phases, so that intervention can be done before the incidents become severe. It also assists in the implementation of policies, constant monitoring, and training of staff, which all go towards minimizing the intentional and unintentional insider risks.
Investing in an insider threat program will be a show of commitment to guarding the assets, reputation, and people of your organization. It could be protecting intellectual property, ensuring regulatory compliance, or avoiding data breaches, but understanding what is the purpose of an insider threat program will enable a proactive, multifaceted approach to the internal threats that are constantly changing.
Types of Insider Threats
It is important to understand the various categories of insider threats in order to develop a multi-dimensional security approach. Understanding what to look out for will enable organizations to design their insider threat program in a way that focuses on every risk.
All forms of insider threats have different issues and implications. It is necessary to consider all of them to reach the general aim of an insider threat program.
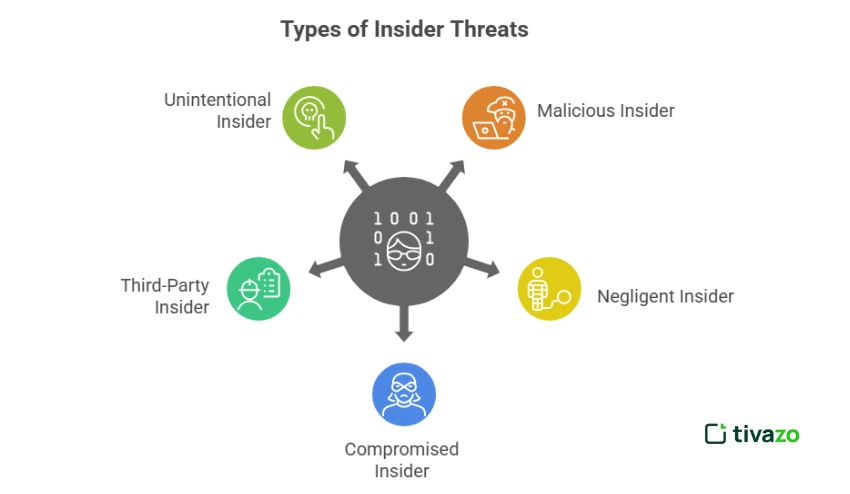
1. Malicious Insider
A malicious insider is an employee or a contractor who is maliciously inclined to do harm to the organization. Such people tend to use their authorized access to misappropriate sensitive information, disrupt systems, or divulge confidential information. The objectives of an insider threat program are identified by first identifying the indicators of malicious intent, including frequent access to unauthorized files or trying to circumvent security procedures.
2. Negligent Insider
Negligent insiders refer to employees who, without any intention, breach security, usually because of carelessness or ignorance. The most common examples include clicking on phishing links, misconfiguring systems, and not adhering to security policies. One of the primary objectives of an insider threat program is to address the problem of negligence, and this is done through training and frequent audits in order to minimize human error.
3. Compromised Insider
A compromised insider is one whose credentials or account have been stolen by an outside attacker. The threat is real and dangerous, even though the insider might not be aware of the breach. One of the things that are goals of an insider threat program is to have strong authentication and monitoring tools that help in discovering and reacting to compromised accounts within a short time.
4. Third-Party Insider
Insider threats also exist in the form of vendors, contractors, or partners with access to your systems. Such third-party insiders are not directly controlled by the organization, making it even more difficult to manage the risks. Third-party oversight should be part of the objectives of an insider threat program to ensure that all the internal access points are covered.
5. Unintentional Insider
The given kind of insider threat is caused by innocent mistakes, including sending sensitive information to the wrong person or losing a device. Although this is not done in bad faith, the harm may be serious. Training employees and implementing strict data handling procedures is one of the objectives of any insider threat program that seeks to minimize such risks.
What is the Goal of an Insider Threat Program? (5 Key Goals)
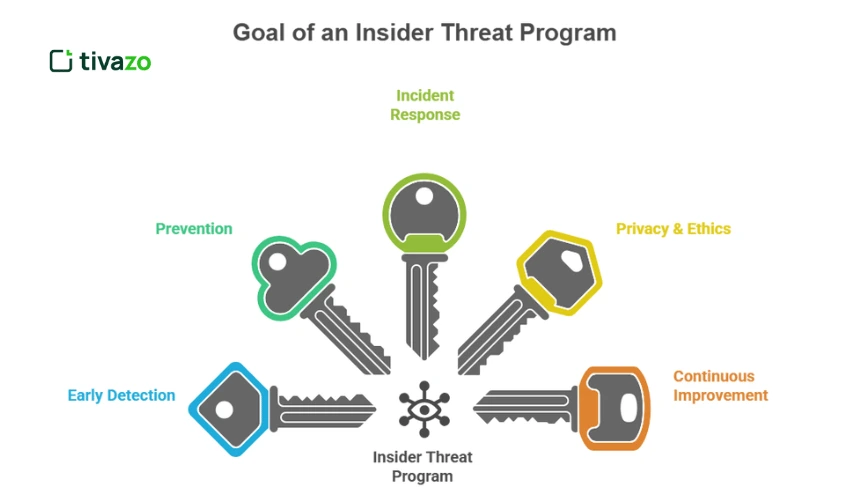
1. Early Detection of Risky Behavior
Early detection of suspicious or abnormal behavior is one of the major objectives of an insider threat program. This early detection of possible threats provides the security teams with a chance to act before actual damage is caused.
One important attribute of any successful insider threat program is the employment of User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA). This is a high-level technology that uses machine learning to set up a baseline of normal behavior of the users and entities on the network. In case there are deviations in this norm, like logging in at irregular hours or transferring large data, the system marks it as a possible risk.
Real-time monitoring tools also augment the detection of an insider threat program. Such tools constantly monitor user activity, and it is simpler to detect attempts at unauthorized access, unauthorized alterations of data, or violations of policies. Constant monitoring of user activities forms a strong defense mechanism against insider threats that keep changing.
Risk scoring gives each user a dynamic score based on many different factors, including access privileges, behavioral history, and sensitivity of data accessed. This scoring system assists in prioritizing investigations and responses. With the use of such layered detection methods, the success rate of the insider threat will be dramatically decreased by organizations.
2. Prevention Through Policy, Training, and Technology
The second important objective of an insider threat program is to stop threats in advance. This is a combination of proactive policy enforcement, extensive employee education, and leading-edge technology.
The first step to avoiding insider threats is the development and implementation of clear internal security policies in the organization. These must contain acceptable use policies, data classification policies, and confidentiality agreements that stipulate the responsibilities of the employees. These policies, coupled with technical tools of enforcement, can curb risky behavior.
A successful insider threat program has training as a primary component. Routine awareness programs give employees the knowledge to be aware of the early indicators of malicious or careless activity. A culture that values education concerning insider risks will greatly diminish the chances of accidental breaches and allow employees to report any suspicious activity.
Technological safeguards such as Data Loss Prevention (DLP) systems, role- or privilege-based access controls, and multi-factor authentication are important in the prevention of threats. These technologies can be used to automatically halt unauthorized access or data transfers when they are part of a broader insider threat program. A combination of policy, training, and technology can be used to form a preventive barrier against internal threats.
3. Rapid and Coordinated Incident Response
Even the most robust defenses are vulnerable, and a rapid and organized reaction is an essential objective of an insider threat program. The swift action can considerably restrict the harm that an internal attack can cause.
Insider threats can only be controlled with a detailed incident response plan (IRP). This paper will give a clear procedure to be followed in case a threat is suspected. It makes the response systematic, timely, and in accordance with internal policies and external regulations.
The insider threat response should be coordinated by collaboration across departments, including IT, HR, legal, and security. Every one of them has its specialized fields like technical investigation, employee relations, and legal ramifications. This interdisciplinary method will make sure that incidents are addressed from all possible angles, making the risk of neglect low.
Recent insider threat systems also use forensics to gather digital evidence, including session records and system screen captures. Such tools are essential in establishing intent and making any actions that are implemented reasonable and legally permissible. The ability to respond effectively to any risk not only reduces risk, but it also enhances the overall security of the organization.
4. Maintaining Privacy and Ethical Oversight
A good insider threat program needs to find the balance between good security and the privacy of employees. The obvious purpose of ensuring ethical oversight is to create trust and compliance.
Privacy-by-design is a good practice that integrates data protection principles into all the phases of the development of a system. In terms of an insider threat program, it implies the design of monitoring tools that would gather only the information needed to identify a potential threat. Surveillance without any reason will hurt employee confidence and possibly be against the law.
The openness is also paramount. The staff must know which monitoring occurs, why, and how their data will be utilized. Fear and suspicion can be minimized through open communication, and, as a result, a security-conscious culture can be enhanced that facilitates the objectives of the insider threat program.
Lastly, ethical control should be just in terms of monitoring practices. It is also necessary to use bias-tested algorithms and avoid profiling because all workers should be treated equally. Insider threat programs can work efficiently without interfering with the organizational values when the legal and ethical considerations are put at the forefront.
5. Continuous Program Improvement and Maturity
Continuous improvement is the last and continuous objective of an insider threat program. The program that is aimed at detecting and preventing the threat should also change along with it.
The insider threat program ought to have a maturity model based on the existing capabilities of the organization and provide guidelines for future levels. Each stage, from reactive to adaptive, is a more in-depth integration of technology, process, and governance. This strategic development guarantees the effectiveness of the program throughout the years.
Continuous evaluation and frequent audits are important in determining shortcomings and streamlining the process. Such KPIs as time-to-detect, incident numbers, and user risk scores are to be monitored and measured on a regular basis. Such insights inform data-informed gains and allocation of resources.
Mature insider threat programs have an established framework by which professionals can organize and scale their program, such as the NIST Insider Threat Framework or the IRPEM model. Such tools can assist in aligning the strategy of your organization with industry best practices, which will allow a proactive and future-proof approach to insider risk management.
Common Signs of Insider Threats
It is essential to detect insider threats as early as possible in order to reduce possible damage. Although these threats may be discrete, there are various behavioral and technical warning signs that show that a user is likely to be a risk to the organization.
- Unusual access to sensitive information that is not part of job requirements or at odd hours.
- Repeated policy breaches, like going around security controls or turning off monitoring programs.
- Abrupt behavior changes; more secrecy, aggression, or unhappiness with the company.
- Too much downloading/sending files, particularly to external storage or cloud storage.
- Efforts to open closed systems or access information without permission.
- Several unsuccessful logins, or attempted logins made with a new or unauthorized device.
- Inappropriate use of unauthorized software or tools, e.g., personal email or file-sharing applications.
- Not collaborating with the team or losing interest in the culture of the workplace.
- Personal or financial complaints, which might make one prone to malicious activity.
- Resignation or notice period conduct that builds up unusual access to data or use of systems.
These are the signs that must be noted to have a successful insider threat program. Organizations can also defend their data, systems, and people by taking proactive steps when it is discovered early.
What Are the Five Threat Categories?
The five core threat categories are important to understand when designing an insider threat program that is effective and concentrated. These categories can assist organizations in predicting, detecting, and handling internal risks in a more accurate and comprehensive way.
All categories emphasize particular risk profiles that the organization should be ready to face. Being informed about the goal of an insider threat program will help ensure that these categories are actively involved in prevention and response measures.
1. Sabotage
Sabotage is an action of intentional malice by an insider that is aimed at destroying systems, data, or operations. It may include the destruction of important files, the insertion of malware, or the shutdown of infrastructure. When it comes to defining what is the goal of an insider threat program, the identification of sabotage should be of utmost priority because the sooner it is identified, the earlier it can be stopped before it affects the operations in a very expensive manner.
2. Fraud
Insider fraud is the use of deceptive acts to make a financial or personal gain, e.g., reporting false data, altering data, or embezzlement. Knowing the purpose of an insider threat program will help organizations to employ behavioral surveillance and access controls as means of fraud detection and prevention.
3. Theft of Intellectual Property
This threat involves the theft of proprietary data such as source code, patents, customer lists, or strategic plans. An effective insider threat program is aimed at avoiding intellectual property theft, imposing data loss prevention tools and tight access controls, which is a logical continuation of the main objective to protect sensitive assets.
4. Espionage
When insiders sell confidential information to competitors, foreign governments, or other unauthorized parties, it is called espionage. In identifying what is the object of an insider threat program, it is important to note that it is by establishing barriers to such high-stakes risks that are conducted by incorporating advanced monitoring, auditing, and security clearances.
5. Unintentional Disclosure
This includes accidental release of sensitive information due to human error, like misdirected emails or any form of sharing files publicly. Reduction of unintentional leakage is a critical component of what is the purpose of an insider threat program, frequently fulfilled by continuous training, automated warnings, and transparent data handling policies.
Difference Between Insider vs. External Threats
It is important to know the distinction between an insider and an external threat to develop a comprehensive approach to cybersecurity. Even though they are both dangerous, they have different sources and should be detected and prevented differently.
| Aspect | Insider Threat | External Threat |
| Source | Comes from within the organization (e.g., employees, contractors). | Originates outside the organization (e.g., hackers, cybercriminals). |
| Access Level | Has legitimate access to systems and data. | Has no authorized access and tries to breach systems. |
| Motivation | Can be malicious, negligent, or accidental. | Typically motivated by financial gain, espionage, or disruption. |
| Detection Difficulty | Harder to detect due to trusted access. | Easier to flag due to unauthorized activity. |
| Examples | Phishing, malware attacks, DDoS attacks, and hacking attempts. | Phishing, malware attacks, DDoS attacks, hacking attempts. |
| Response Approach | Requires behavior analytics, training, and internal policy enforcement. | Needs perimeter defenses, firewalls, and intrusion detection systems. |
These two types of threats can be very damaging; however, insider threats are not addressed as much as they should be and are more difficult to spot. An effective cybersecurity strategy should focus on both internal and external attacks so as to secure the entire organization.
Use Of Tivazo in the Implementation of the Insider Threat Program?
The key to any effective insider threat program is the balance between effective monitoring and good privacy and compliance practices. Tivazo is a strong basis of this, providing real-time tracking of activity, encrypting data, and open policies that match the intentions of what is the goal of an insider threat program. It provides transparency in user activity without compromising moral supervision, which is essential in the balancing of security and employee trust.
The features of Tivazo facilitate the operational objectives of what is the goal of an insider threat program because it allows taking live screenshots, tracking the usage of applications, idle-time detection, and behavioral analytics. Tivazo has adjustable alert thresholds and role-based access controls that allow security professionals to identify anomalies early, prioritize users based on risk scores, and react promptly, streamlining incident response and making it more proactive. Moreover, Tivazo is designed with compliance first (GDPR, HIPAA alignment) and thus, privacy-by-design, which will help organizations to fulfill their regulatory requirements without difficulties.
Tivazo vs. Other Insider Threat Tools
| Feature/Capability | Tivazo | ObserveIT (Proofpoint) | Forcepoint Insider Threat | Veriato |
| Real-Time User Activity Monitoring | ✅ Live screenshots, activity logs | ✅ Screen recordings | ✅ Behavior monitoring | ✅ Session recording |
| Behavioral Analytics | ✅ Built-in risk scoring + trends | ✅ Contextual behavior analysis | ✅ Machine learning insights | ✅ Pattern-based anomaly detection |
| Privacy-Focused Design | ✅ GDPR & HIPAA aligned, role-based access | ⚠️ Basic privacy policies | ⚠️ Limited customization | ⚠️ May require manual configuration |
| Idle Time & App Usage Tracking | ✅ Granular tracking by app | ❌ Limited app-level tracking | ✅ With configuration | ✅ Basic activity tracking |
| Ease of Setup & Use | ✅ Intuitive dashboard, quick deploy | ❌ Complex deployment | ❌ Requires advanced setup | ⚠️ Moderate learning curve |
| Third-Party Access Monitoring | ✅ Yes | ⚠️ Limited | ✅ Yes | ⚠️ May need custom rules |
| Alerts & Incident Workflow | ✅ Custom thresholds + alerts | ✅ Pre-built alerting rules | ✅ Integrated incident management | ✅ Custom rule setup |
| Cost-Effectiveness | ✅ Affordable for SMBs & Enterprises | ❌ Expensive for small teams | ❌ Premium pricing | ⚠️ Mid-range pricing |
| Cloud & Hybrid Support | ✅ Full support | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Training & Support | ✅ Live support + documentation | ✅ Enterprise support | ✅ Premium support | ✅ Knowledge base & tickets |
Conclusion
In order to safeguard your organization against insider threats, it is important to know what is the objective of an insider threat program. Through a combination of early detection, prevention, rapid-response, ethical oversight, and continuous improvement, in combination with tools such as Tivazo, you can develop a proactive defense against attacks that protect your data, staff, and reputation both internally and externally.



