Time zones have become a very crucial aspect of our lives, and they have touched all aspects of our lives, including our personal schedules as well as international business activities. But have you ever thought why there are so many time zones in the world? And what is the contribution of these zones to world cooperation and communication? This paper will reveal the most important facts about time zones, the fundamentals of the differences between the regions, how they occurred, and why we must know them to conduct business and personal activities.
Key Highlights:
- What Are the Different Time Zones
- Why Do We Have Different Time Zones
- Understanding UTC, GMT, BST, and Local Time
- What Are the 4 Time Zones in the U.S.
- Tips to Master Time Zone Management for Global Success
- How Many Different Time Zones Exist Today
- What Are the Different Time Zones of the World
- Global Map Overview of Different Time Zones
- Different Time Zones in the United States
- Daylight Saving Time and Its Impact on Different Time Zones
- Common Challenges When Working Across Different Time Zones
- Best Practices for Working Across Different Time Zones
- Tools That Help Manage Different Time Zones
What Are the Different Time Zones?
A time zone is a geographical area in which the local time is identical. The aim of introducing this system was to standardize time over large distances so that locations in the same zone would have the same time. It is premised on the rotation of the earth, where the day is 24 hours, and the length of the longitude is 360 which implies that every time zone would be about 15 degrees.
Funny enough, there exist over 24 time zones in the world. Offsets of half-hour or quarter-hour have been adopted in many countries, extending the system beyond the usual whole-hour separations. Such variance will make it easier to accommodate countries that have special geographical or political boundaries.
Why Do We Have Different Time Zones?
This was due to the necessity to have time that is standardized time, particularly in transport. Before the concept of time zones, the United States alone had more than 144 local time settings. This proved to be confusing, particularly due to the emergence of railroads, since the trains that moved all over the nation could not coordinate their timetables. This usually led to missed connections and accidents.
Four major time zones in the U.S. were implemented in 1883, and this move assisted in the coordination of the train schedules. This was subsequently extended and synchronized with Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) to give the world a time scale.
Understanding UTC, GMT, BST, and Local Time
Timekeeping systems in the entire world run under a standardized framework to enable people to coordinate diverse regions. Such time standards facilitate synchronization, which is particularly optimal in international communication, travel, and business.
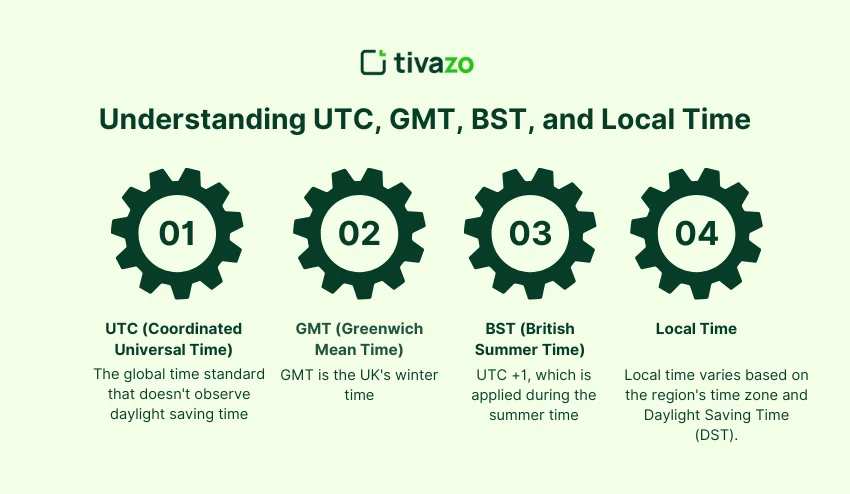
- UTC (Coordinated Universal Time) is the global time standard that doesn’t observe daylight saving time.
- GMT (Greenwich Mean Time) is commonly used as equivalent to UTC, although during the winter season, it is attached to the United Kingdom.
- BST (British Summer Time) is UTC +1, which is applied during the summer time.
- The local time may change according to the time zone of a region and whether the area is under the Daylight Saving Time (DST).
These terms are key to the communication of activities in various time zones, and mostly in the workplace.
What Are the 4 Time Zones in the U.S.?
In 1883, the railroad system in the United States instituted four time zones in order to standardize the timetables of trains. These were:
- Eastern Time (ET) – UTC−5
- Central Time (CT) – UTC−6
- Mountain Time (MT) – UTC−7
- Pacific Time (PT) – UTC−8
It is these time zones that formed the basis of the present U.S. time system, comprising nine time zones, not only on the mainland but also in the U.S. territories.
5 Tips to Master Time Zone Management for Global Success
Time management is a very important aspect that requires proper management in remote teamwork, international companies, and any other individual who operates in various locations. It guarantees the efficiency of effective communication, avoids delays in schedules, and monitors the working flows. These are five tips that can assist you in overcoming the problem of time zones to enhance productivity.

1. Use Universal Time:
The use of UTC as a standard assists in the harmonization of all teams and saves confusion in time zones. It facilitates international coordination easily and effectively.
- Streamlines time between regions.
- Aids in arranging overseas conferences.
- Eliminates mistakes caused by the local time difference.
2. Plan Overlapping Work Hours:
The overlapping working hours will provide real-time complementary working and decision-making in different time zones. This is a critical strategy towards successful teamwork.
- Allows real-time communication.
- Minimizes time delays in decision-making.
- Promotes collaboration even in the presence of time zone disparities.
3. Leverage Time Zone Tools:
Sources such as World Time Buddy simplify the process of scheduling and help to locate the best meeting time. Such tools reduce time zone errors.
- Fastly locate the best meeting times.
- Monitor the local time of every member of the team.
- Saves time in the hand calculation of time zones.
4. Set Clear Expectations for Async Communication:
Promote asynchronous workflow to ensure projects remain on track even when teams are disconnected. Estimating the expectations of responses is a way of making sure that no one is held up.
- Determine guidelines on response time.
- Focus on the tasks that do not have to be responded to urgently.
- Continue business processes across time zones.
5. Avoid Mixed Time Formats:
Using one obvious time format, such as UTC, will eliminate the confusion in scheduling across jurisdictions. This will simplify the process of scheduling meetings.
- Clock or UTC should be 24-hour.
- Avoid AM/PM confusion
- Streamlines the process of making appointments for every member of the team.
How Many Different Time Zones Exist Today?
There are 38 local time variations that are known in the world today. Out of them, 25 of these time zones use whole-hour UTC offsets, and 8 include half-hour ones (including India’s UTC+5:30). Also, 3 time zones run on a 45-minute difference (such as Nepal, which is UTC +5:45).
The greatest offset is UTC+14 (also used in the Phoenix Islands in Kiribati) and the smallest is UTC-12 (also used in the Baker Islands in the U.S.). These various variations can be used to suit the different regions of the world and also to make sure that the local time is as accurate as possible.
What Are the Different Time Zones of the World?
The world functions on 38 different time zones, which are not limited to the normal 24-hour model, and this is to suit the requirements of the world. These differences are founded on the geographical circumstances, such as the movement of the earth, as well as political choices made by various nations. Time zones are beneficial in that they unify time over a huge area, yet they also indicate the difficulty in regulating time among multiple cultures and economies.
- Whole-hour UTC offsets (UTC−12 to UTC+14)
- Half-hour UTC offsets, like UTC+5:30 (India) and UTC+3:30 (Iran)
- Quarter-hour UTC offsets, such as UTC+12:45 (New Zealand’s Chatham Islands)
The nations having the most time zones are:
- France: 12 time zones (because of its territories)
- Russia: 11 time zones
- USA: 9 time zones (including territories)
These differences can be attributed to the geographical as well as political factors, and they serve the purpose of leveling local time arrangements with the requirements of an internationalized world.
Global Map Overview of Different Time Zones
The geographical boundaries do not always coincide with the time zones. Other countries, such as China, have only one time zone in spite of having five natural time zones. There are others, like France, which have a complicated time zone system because they have many territories that are located abroad.
Time zones do not necessarily take a straight line along the longitude and can vary based on political choices. France has been cited as an example of a country with a time zone that cuts across the continent and remote territory worldwide.
Different Time Zones in the United States
There are 9 official time zones within the United States, which include the continental U.S and its territories. They are used to coordinate actions in the whole country, and there are several states that do not observe Daylight Saving Time (DST), such as Arizona and Hawaii. The reason is that it is important to understand these time zones and their UTC offsets to coordinate them effectively.
- Atlantic Time Zone
- Eastern Time Zone
- Central Time Zone
- Mountain Time Zone
- Pacific Time Zone
- Alaska Time Zone
- Hawaii-Aleutian Time Zone
- Samoa Time Zone
- Chamorro Time Zone
A graph to show these time zones and their respective UTC offsets can be used to illustrate the difference between the two. Daylight Saving Time (DST) is not celebrated in some states of the U.S., such as Arizona and Hawaii, making the management of time zones even more complicated.
Daylight Saving Time and Its Impact on Different Time Zones
Over 70 countries worldwide observe Daylight Saving Time (DST), which was standardized in the United States of America by the Uniform Time Act of 1966. But not every part prevails by DST. States such as Hawaii and Arizona, as well as other territories in the U.S., are not part of DST. This implies that the time gap between some parts of the world can be an hour at some point in the year.
Common Challenges When Working Across Different Time Zones
Working in time zones can cause several issues within the team, which may impede the workflow and efficiency. These problems are caused by the different working hours, delay in communication, and confusion of schedules. The following are the most prevalent challenges of time zones:
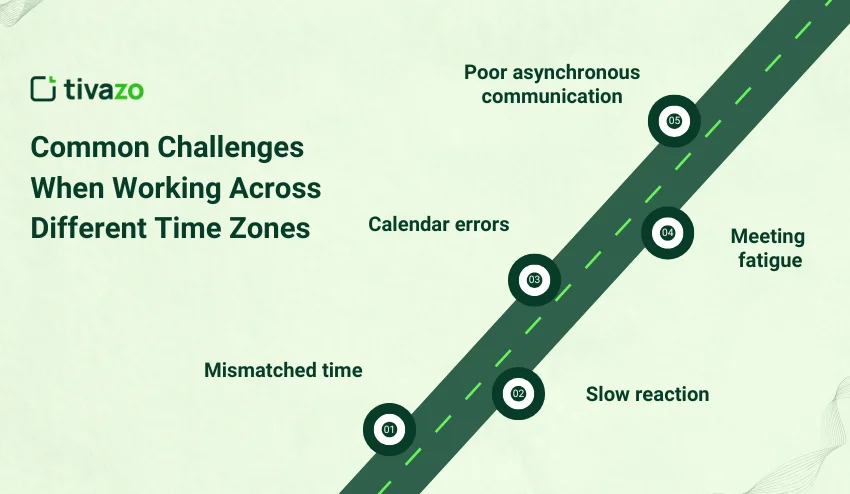
- Mismatched time: Team members can work when other people are not online.
- Slow reaction: The communication will slow down decision-making.
- Calendar errors: There may be confusion over time differences, which may create a scheduling problem.
- Meeting fatigue: The ability to change the time of meetings all the time may be exhausting.
- Poor asynchronous communication: This occurs because of the absence of synchronous cooperation.
Best Practices for Working Across Different Time Zones
Time zones do not have to be managed without careful planning that enhances proper communication and effective workflow. With the use of best practices, teams are able to reduce delays, keep up with team communication, and reduce confusion. The following are some tips that can be put into action to maintain smooth operation across time zones:

- Use universal timestamps: This will make everyone on the team be on the same page and will not confuse them due to the different local times.
- Maintain a 4-hour overlap: It is advised to have a point in time when the members of the team in the different zones can work together in real time, even though it might be only a few hours.
- Build async-first workflows: Cultivate a culture of having an asynchronous team that does not require real-time meetings and enables projects to proceed in a steady flow.
- Avoid mixed time formats: Stick to a single, consistent time format (like UTC) to prevent mistakes and misunderstandings.
- Set clear expectations: The parties involved are supposed to know when and where to communicate to prevent wastage of time and misunderstanding.
Tools That Help Manage Different Time Zones
Having to control time zones manually can be difficult; however, with the help of the appropriate tools, the process can be made much easier. The tools assist the business and remote workers to prevent misunderstandings, enhance the precision of the schedule, and facilitate the flow of coordination among the areas. The tools that best manage the differences in time zones are the following:
- Time.is
- World Time Buddy
- Scheduling apps like Google Calendar
- Global clocks for real-time tracking
These tools will assist in the minimization of mistakes and uninterrupted integration between various regions
Conclusion:
Being aware of the various time zones is not only significant to personal scheduling, but it is also vital to a business that has international operations or remote staff. Through proper time zone management, you will be able to have a higher quality of communication, better productivity, as well as better coordination of activities, which will result in more successful global operations.