Remember tracking HR rules in a rainbow spreadsheet? One tab held training sign-offs, another poster deadlines, while sticky notes shouted “Update handbook.” That system worked—until remote teams and a flood of new laws turned your checklist into a 2 a.m. scramble. In a recent survey, 50% of HR professionals said using technology to automate workflows is among their top challenges. Pay-transparency mandates, AI-in-hiring rules, and shifting wage laws now move faster than any manual tool can refresh. This article traces HR compliance’s shift from binders to real-time automation—and shows how you can modernize without extra headcount or jargon.
The paper & spreadsheet phase
Ten years ago, your compliance files sat in two places: a steel cabinet and a swelling Excel workbook. Each new law meant another row, another column, another neon Post-it on the monitor.
This lack of oversight called for more robust computerized monitoring systems, in which continuous observation and automated alerts help maintain compliance. Tivazo defines computer monitoring precisely this way: the continuous observation, recordkeeping, and analysis of activities to support regulatory adherence. When one reminder email disappeared, the whole chain broke.
The workload piled up. According to Vanta’s 2023 State of Trust Report, respondents spend an average of nine working weeks per year on security compliance. Signatures, policy printouts, and midnight wage-table checks stole time from retention and culture projects.
Regulations also multiplied. In a 2021 IT Compliance Benchmark survey from Hyperproof, 65% of all survey respondents reported managing IT risks with an ad-hoc, reactive approach, using siloed processes and disconnected tools. Spreadsheets captured history; they couldn’t prevent errors. By 2020, most teams saw the truth: manual tracking cannot scale. Something smarter had to replace the clipboard, which is why automated compliance has emerged as the modern standard for keeping organizations continuously audit-ready
The first wave of digital tools
Cloud HR suites delivered real relief. Forms moved online, managers received pings when training expired, and payroll taxes calculated themselves. For the first time, compliance lived somewhere other than a filing cabinet.
Yet these early platforms were stitched from acquired modules. Integration gaps forced teams like yours to juggle three or more systems for one task. A Lumesse survey of 1,293 HR leaders found that 52 percent strongly agreed that the complexity of their jobs has grown significantly, and 61 percent reported feeling overwhelmed by it.
The symptoms were obvious. The handbook sat in a document portal, wage data in payroll, and training records in a learning-management system. Come audit time, someone still had to cross-reference every file.
Workflow engines helped; email reminders replaced sticky notes. Without true integration, though, they stayed digital to-do lists. As one buyer guide notes, templates “may suffice, but automated workflows boost efficiency only when systems connect end to end.”
The first digital wave saved paper and clicks, but it never solved the root issue: fragmented data breeds fragmented compliance. HR needed software that could not only store information but also watch it, link it, and act in real time.
Modern compliance software: automation arrives
Today’s best platforms do more than store files; they watch every rule in real time, cross-check records, and alert you the moment something drifts offside. Continuous monitoring has become the benchmark, with platforms like Vanta running numerous automated tests to surface compliance issues before they turn into audit findings.
- Live rule libraries. Federal, state, and city labor laws update overnight, so your checklists stay current.
- Audit-ready reporting. Continuous evidence capture cuts prep time by up to 82 percent per framework.
- Secure record vaults. Documents, signatures, and retention clocks sit in one encrypted hub.
- Automated document flows. The system pre-fills state forms during onboarding and attaches them to the employee profile.
- Built-in risk scoring. Dashboards surface the highest-impact gaps first.
When Colorado raises its overtime threshold, payroll rules recalculate before your next run. When a new hire signs the handbook, the signature logs automatically without HR lifting a finger. Human effort shifts from data entry to decision-making.
This kind of compliance monitoring makes real-time oversight possible, with automated platforms like Vanta running more than 1,200 hourly tests that flag issues long before an auditor can. The goal: stay audit-ready every day, not just once a year.
Modern tools also connect to your human resource information system (HRIS), payroll, and learning-management system, so data moves quietly in the background. Instead of juggling three dashboards and a spreadsheet, you open one window and see real-time compliance health.
Automation turns compliance from guesswork into a daily confidence check, so HR can focus on people, not paperwork.
2024–2025: why automation is now non-negotiable
Regulatory whiplash
- Pay-transparency surge. A growing number of states and cities now require salary ranges in job ads or upon request, and this trend is expected to continue.
- Overtime upheaval. The U.S. Department of Labor’s 2024 final rule raised the white-collar salary threshold to $844 per week on July 1, 2024, and $1,128 per week on January 1, 2025; litigation soon paused parts of the rule, so HR must track both the regulation and the court docket.
- AI rules go global. Europe’s landmark AI Act is expected to come into force in stages, with some provisions applying as early as late 2024 and the majority of the regulation taking effect in 2026.
The common thread is speed. Statutes appear, shift, and collide across jurisdictions faster than any quarterly checklist can update. Manual tracking loses before the whistle sounds.
Automation flips the script. Live rule libraries refresh the moment a measure becomes law, dashboards flag which roles need new disclosures, and alerts land in managers’ queues before penalties hit. Instead of Friday-night blog dives, you wake up Monday to a to-do list already sorted by risk.
In short, the 2024–2025 period proved that compliance is no longer episodic; it is real time. Only software that works in real time can keep up.
Five benefits of embracing automated compliance
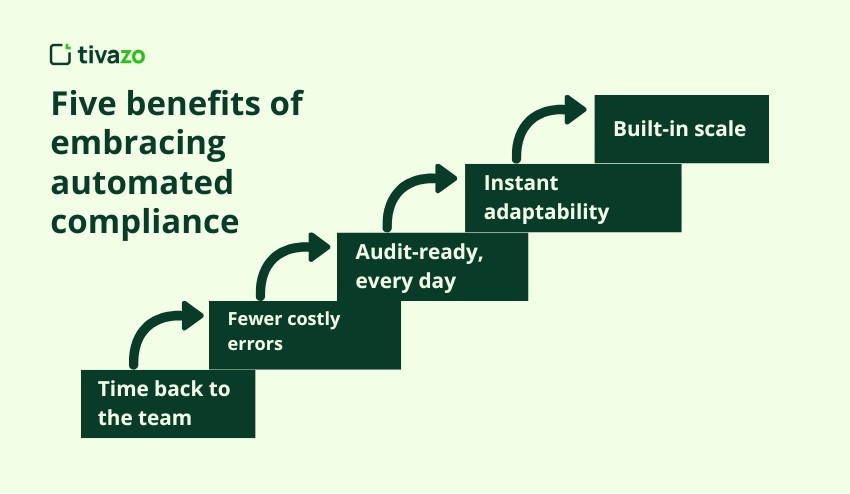
- Time back to the team. According to Vanta, organizations using continuous monitoring can significantly reduce the time spent gathering evidence for audits. Hours once lost to screenshots and spreadsheets now go into hiring, engagement, and strategy.
- Fewer costly errors. Gartner research suggests that embedded controls are significantly more effective at reducing missed obligations than training-only programs.
- Audit-ready, every day. Gartner has reported that automation of internal controls can lead to significant savings in external audit fees. Instead of an annual fire drill, evidence sits one click away.
- Instant adaptability. When Colorado updates its pay-range disclosure rule, the rule library refreshes overnight and tasks reach the right managers by morning; no legal memo and no frantic spreadsheet edits.
- Built-in scale. PwC’s research indicates that a significant number of firms are realizing benefits from compliance technology, including productivity gains and faster issue identification.
Your six-step roadmap to automated compliance
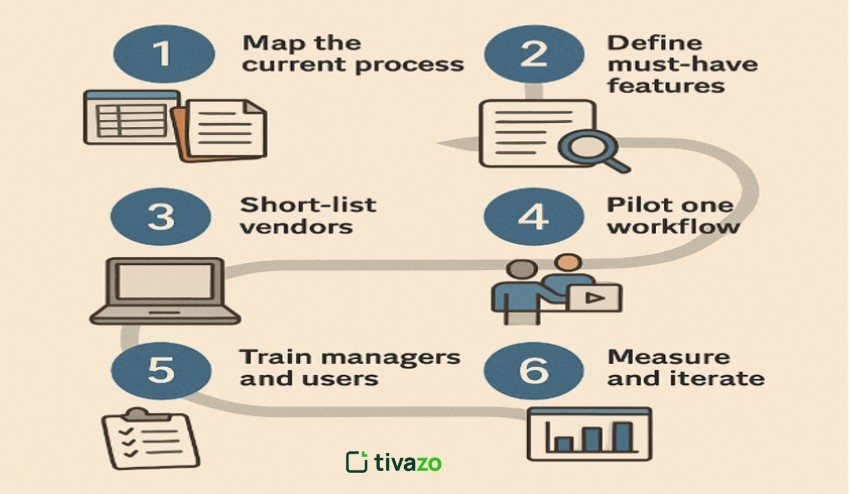
Step 1 – Map the current process. Open every spreadsheet, checklist, and shared drive. Note where data lives, who owns it, and which deadlines slip. According to Gartner, failing to map current processes is a significant factor in software purchase regret.
Step 2 – Define must-have features. Rank needs by risk and pain, such as multi-state labor-law tracking, e-signatures, or SOC-2 level security, so demos stay focused. A structured approach like using an HR data security risk register can also help clarify which controls and tools should sit at the top of your priority list when evaluating vendors.
Step 3 – Short-list two or three vendors. Schedule live demos, test real scenarios with reps, and loop in payroll or IT. Gartner notes that misaligned stakeholders create the highest buyer regret among midsize firms.
Step 4 – Pilot one workflow. Run a 30-day test on something contained, like onboarding forms. Easy wins build momentum and executive goodwill.
Step 5 – Train managers and users. A McKinsey study found two-thirds of large tech programs fail on schedule, scope, or budget; training sets the successful third apart. Record short screencasts and place “how-to” links in the wiki.
Step 6 – Measure and iterate. After 60 days, compare time saved, on-time task completion, and audit-readiness scores. Use the results to secure a budget for the next module, perhaps training compliance or policy management.
Building a Future-Ready HR Compliance Strategy
Automation is not just a convenience, but a value statement and organizational shift in how HR approaches risk, regulations, and operations. Instead of static spreadsheets and fragmented systems, moving to real-time compliance platforms provides organizations with visibility over each process, each employee record, and every regulatory requirement, all in real-time. This means instant alerts when impending deadlines loom, policy changes automatically propagate, and managers spend less resources tracking down signatures or cross-verifying forms.
This future-ready strategy also allows for scalability: as your employee base grows, so does your compliance ecosystem, without adding employees or more manual effort from your time. This enables HR to focus on those high-value activities engagement, training, and retention while simultaneously minimizing legal risks. Following the six-step roadmap doesn’t just digitize old processes; it positions HR compliance as a significant component of proactive, ever-changing oversight that Initial optimal HR compliance strategy aligns with adaptive legislation, makes informed decisions, and always keeps the organization audit-ready.
Conclusion
Follow these six steps and the move to automation feels less like an overhaul and more like a series of smart, low-risk changes that deliver value each week.



