Process optimization helps businesses work smarter, not harder. In other words, it’s all about finding better ways to do things.
When you remove waste in your processes, you can work smarter, which leads to happier employees and better business outcomes.
In this guide, you’ll learn seven key steps to optimize your processes. You’ll also learn about tools and best practices to support you in your journey.
What Is Process Optimization?
Process optimization is the practice of improving how work gets done to make operations faster, more cost-effective, and more productive. It involves analysis of all the processes involved in a workflow, as well as the elimination of any bottlenecks in these processes.
The main aim of the optimization of processes is to improve efficiency in the operations carried out within an organization. Process optimization ensures that resources, time, and effort are optimally utilized within an organization.
By optimizing processes, an organization can ensure its employees are engaged in productive activities and improve operational efficiency.
Why Process Optimization Matters
Improved processes result in improved results. Organizations that improve their processes experience improvements in their results.
Key benefits include:
- Improved cycle time in completing a process or a task
- Reduced cost of operation
- Improved satisfaction among employees
- Improved customer satisfaction
- Improved revenues and growth
Key Metrics to Track
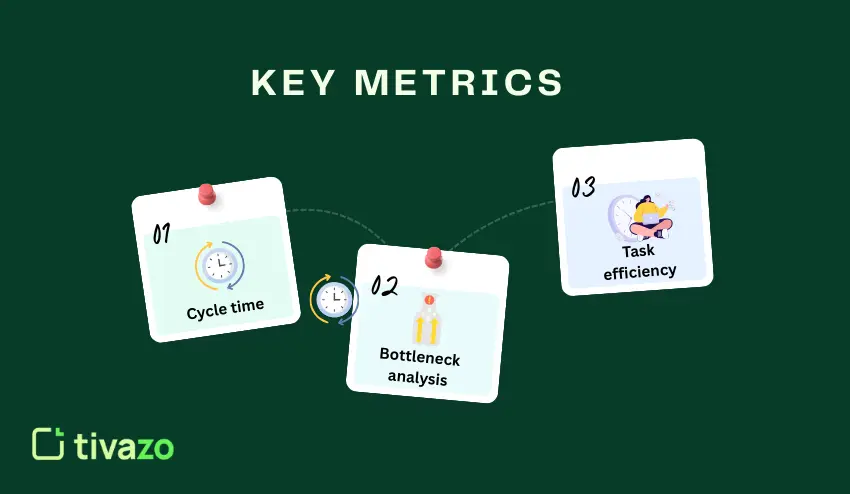
Tracking the right metrics is important in understanding where improvements are needed. These metrics measure the efficiency of your business processes.
Cycle time is a measure of the time it takes to complete a process or a task. It is a measure of time from the start of a process to the completion of the process.
Bottleneck analysis is a measure of a process’s efficiency. A bottleneck is a process or point in a process where a task is delayed.
Task efficiency is a measure of the output of a process compared to the input. Task efficiency is an indicator of how well a business is utilizing its resources.
Digital Tools That Enable Optimization
The good news is that, with today’s technology, optimizing processes has never been easier. The right tools provide you with the visibility you need to understand the flow of work within your business.
Workflow management tools help teams organize and monitor their work. These tools provide visibility into who is working on what and when the work is due.
Productivity-tracking tools help you monitor how you spend your time on a day-to-day basis. This helps you identify opportunities for optimization.
Process automation tools allow you to automate processes without the need for humans. This enables your team to focus on higher-value work.
7 Steps to Process Optimization
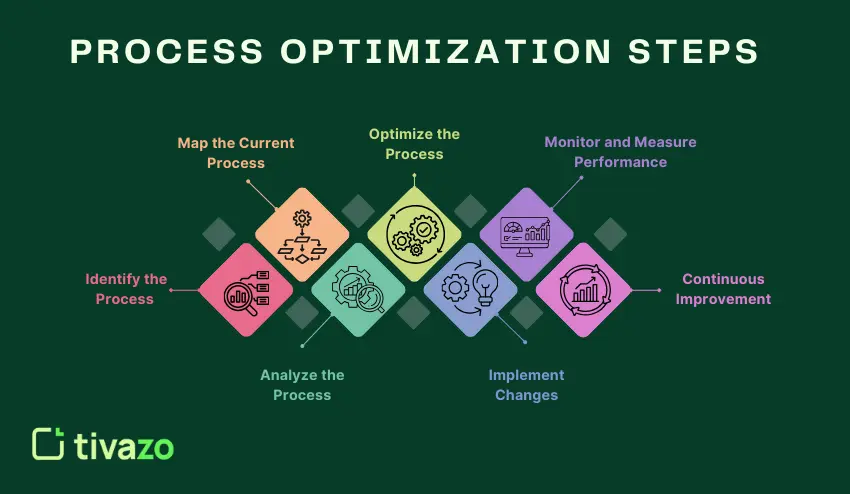
To change the way your team works, follow these seven steps. These steps will build on each other to bring about positive change.
Step 1 – Identify the Process
The first thing to do is to select a process to improve. The best processes to select for improvement are those that have a direct impact on your team’s productivity and performance.
Processes to select include those that:
- Take a long time to finish
- Have a lot of complaints and frustrations associated with them
- Involve many handoffs between people
- Have many errors and quality problems
- Use a lot of resources
You can use process management systems to identify the current processes. This will serve as a basis to measure the improvements made.
Ask the members of your team what processes slow them down the most. This will help you identify the processes to improve.
Step 2 – Map the Current Process
Create a visual representation of how work flows through the process. Include every step, every decision point, and every handoff.
Document who does what and when. Include how long it takes to complete each step.
Include metrics like cycle time and how the process performs.
Write down any problems or delays that people experience.
This map will give you a clear picture of how the process works today. It will become your reference point for creating something better.
Include the people who really do the work. They may know more about the process than the manager does.
Step 3 – Analyze the Process
Now it’s time to take a closer look at what we’ve created. Identify areas of the process that do not add any value or are causing unnecessary delays.
Do a bottleneck analysis. A bottleneck is an area where work is piling up. This is an area where you have problems. This is where you are slowing down the entire process.
Use KPI tracking or efficiency for your tasks. Compare the results with industry standards.
Ask critical questions:
- Which steps could be eliminated?
- Where do errors happen most often?
- What causes delays or rework?
- Are resources allocated properly?
- How does this affect productivity improvement?
The answers reveal opportunities for meaningful change.
Step 4 – Redesign & Optimize the Process
With what you have learned, you can now design a new and improved workflow. You can simplify the process by eliminating steps.
To do this, you should apply the workflow optimization techniques, such as:
- Combine related tasks to reduce handoffs
- Automate repetitive tasks
- Standardize the way work is done
- Clarify roles and responsibilities
- Set quality standards
The focus of workflow efficiency is the optimization of the team. You should design a workflow that makes it easy for people to do their best.
You should try out the new workflow on a small group of people. After this, you should make the necessary changes.
Step 5 – Implement Changes
You should now implement the new workflow on the entire team. Communication is important for the successful implementation of the new workflow.
You should also consider the implementation of workflow automation tools or process automation software. This is important for the successful implementation of the new workflow.
You should also provide training for the entire team. You should let the team know the reason for the changes and the new workflow.
You should also provide support during the transition period. You should know that not all people in the team are able to cope with the changes.
Step 6 – Monitor and Measure Performance
Monitor the performance of your optimized process. Use performance management systems to collect this data.
Measure the improvements you’ve made in:
- Cycle time reduction
- Task efficiency gains
- KPI achievement
- Error rates
- Cost savings
Compare this data to your original numbers from Step 2. This will give you the true impact of your changes. Verify that your changes are indeed making your operations more efficient and productive.
Sometimes you need to make adjustments to your process to achieve the desired results. Schedule regular meetings with your team. Ask them what is working well and what still needs to be improved.
Step 7 – Continuous Improvement
Process optimization is an ongoing process. The markets are constantly changing, as are the technologies.
New challenges are constantly emerging. Regularly review your process to identify new opportunities. What worked last year may not be the best way to go today.
Take advantage of the latest digital process optimization tools. New tools may help you unlock additional efficiency gains. Encourage your employees to think of ways to improve your process.
Implement process optimization strategies for teams that promote learning. Small improvements add up to big results.
Tools That Support Process Optimization
The right software can significantly improve the effectiveness of optimization activities. Here are some tools you can use.
Workflow Management Software
These software tools can help teams better organize their tasks and monitor progress. They can help teams see what they still need to accomplish.
Some common tools in this category include Asana, Monday.com, Trello, among others.
Productivity Tracking Software
Productivity tracking software tracks how an individual is spending their time during the course of their workday. This data shows patterns and areas for improvement.
Productivity tracking software also helps identify areas where an individual may be wasting their time. Managers can also identify training needs for their employees.
Some of the available options include RescueTime, Toggl, and Clockify.
Time Tracking Tools
Time tracking software tracks how much time is spent on tasks and projects. This data is useful for project management.
Having accurate data on how much time tasks take also allows for better project estimates. This data also shows where most value is being generated.
Some options for time tracking tools include Tivazo, Timely, and Hubstaff
Process Automation Tools
Automation software helps to complete repetitive tasks without the involvement of humans. This helps to reduce errors and allows humans to focus on more creative tasks..
These tools can be used for:
- Sending automatic email notifications
- Moving files from one system to another
- Updating spreadsheets and databases
- Creating reports
- Scheduling appointments
Zapier, Make, and Microsoft Power Automate are some popular tools.
Best Practices for Sustainable Process Optimization
To be successful in the long term, it takes more than just going through the seven steps. The best practices outlined here will help you sustain and improve your progress.
Follow Workflow and Process Optimization Best Practices
Begin with small projects and demonstrate the value of the process. This will encourage and generate interest in the changes.
Involve the people who will use the new process in the solution’s design. They will provide valuable insights to improve the outcome.
Document all processes to ensure that the information does not leave with the people who know it. This will also ensure that training new members of the team is simpler.
Maintain Long-Term Team Productivity Growth
Involve your team in the benefits of the optimization process. People will be willing to work with you if they can benefit from the changes.
Offer training to the members of the team as the processes change. Training is essential in the long term to ensure that the team’s skills improve.
Celebrate the changes and acknowledge the members of the team who have contributed to the process. People will be encouraged to continue finding better ways to work.
Continuously Adapt to Evolving Operational Needs
Stay updated on the latest industry trends and emerging technology. What is now possible was not available a year ago.
Regularly review your processes every quarter or whenever significant changes occur. This helps prevent problems from becoming too large.
Be willing to change your processes whenever they are no longer working. Flexibility is a necessity in a constantly changing business world.
Conclusion
Productivity gains are the ultimate goal of process optimization. Begin by identifying your existing processes, evaluating what is working and what is not, and making improvements to get better results.
Implement your improvements using the right tools to assist you in being more productive. Remember, process optimization is a journey, and it is critical to review your processes regularly to ensure they are effective and up-to-date.
The benefits are obvious: efficiency, cost savings, quality, and a more productive and competitive workforce. Begin with one process, go through the seven-step process, and watch your productivity soar.